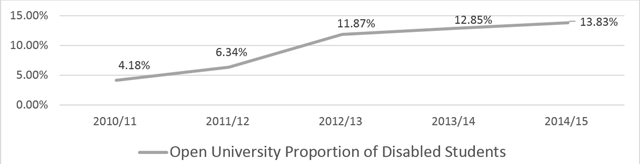
Figure 1
Adapted from Widening Access and Success. Monitoring Report: Disability (CICP, 2016).
Table 1
Sample of MOOC platform providers, MOOC course providers, platform developers/designers and researchers in the MOOC community for the study.
| Profile and number | Five accessibility content managers of MOOC platforms, three platform software developers and four researchers in the MOOC community |
| Contexts | Europe, North America and Latin America |
| Countries | UK, Spain, Portugal, The United States, Ecuador and Guatemala |
| Platforms | ECO eLearning project, FutureLearn, UNED COMA, UAb iMOOC, edX and Telescopio |
| Expertise | Accessibility experience in eLearning projects and research in MOOCs |
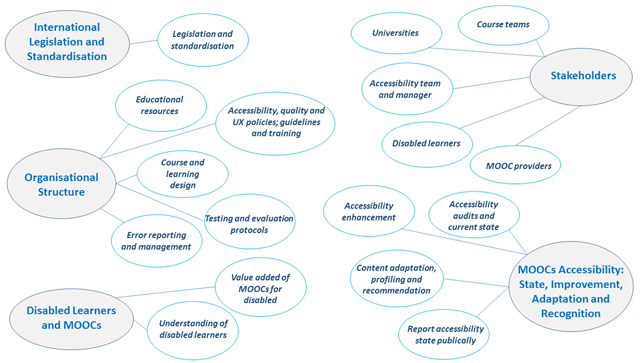
Figure 2
A thematic map representing the themes and codes.
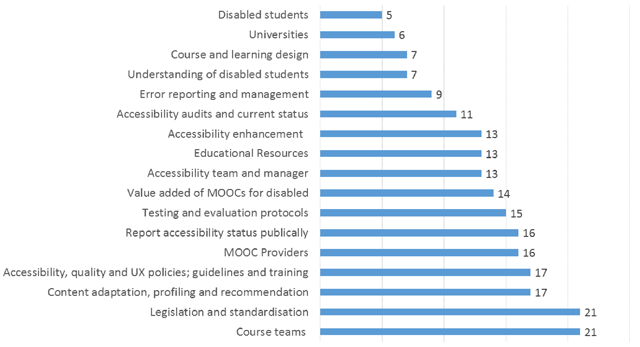
Figure 3
Most frequent codes appearing in the interviews.
Table 2
Positions and comments from the analysis of the interviews.
| Theme | Position | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Stakeholders | There is a general view that responsibility of creating accessible content falls on course teams. | Providers should increase the effort in developing the skills of the course teams to create accessible content. |
| Organisational Structure | Accessibility is not always embedded in the routine design and development activities of the educational context of organisations. | Producing accessible educational resources requires clarity from the organisation in accessibility policies, guidelines and managing reported accessibility incidences. |
| International Legislation and Standardisation | Legislation and standards play a predominant role in the development of accessible MOOCs. | Further focus on learners, their preferences and learning design, has to be offered rather than aiming only to follow the minimum legal requirements. |
| Disabled Learners and MOOCs | General perceptions are that MOOCs can be valuable for disabled learners if they are accessible. | Explore the potential of developing MOOCs based on social models of disability. |
| MOOCs Accessibility: State, Improvement, Adaptation and Recognition | There is a common understanding that MOOC platforms do not profile the learner’s preferences. It would also be useful to indicate the accessibility state of the course. | Not profiling the preferences of learners makes it difficult to deliver, or even recommend, the content in an accessible way to the learner. A first step would be to clearly inform learners about the different formats available and the accessibility of course content. |
