Table 1
Baseline characteristics of the study population (n = 22).
| CHARACTERISTICS | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Age | 71.8 ± 9.6 |
| Sex Male Female | 20 (90.9%) 2 (9.1%) |
| Malignancy Bladder cancer Prostate cancer | 19 (86.4%) 3 (13.6%) |
| Number of TAE 1 2 | 17 (77.3) 5 (22.7) |
| Follow‑up (months) | 7.6 ± 4.8 |
[i] TAE, transcatheter arterial embolization.
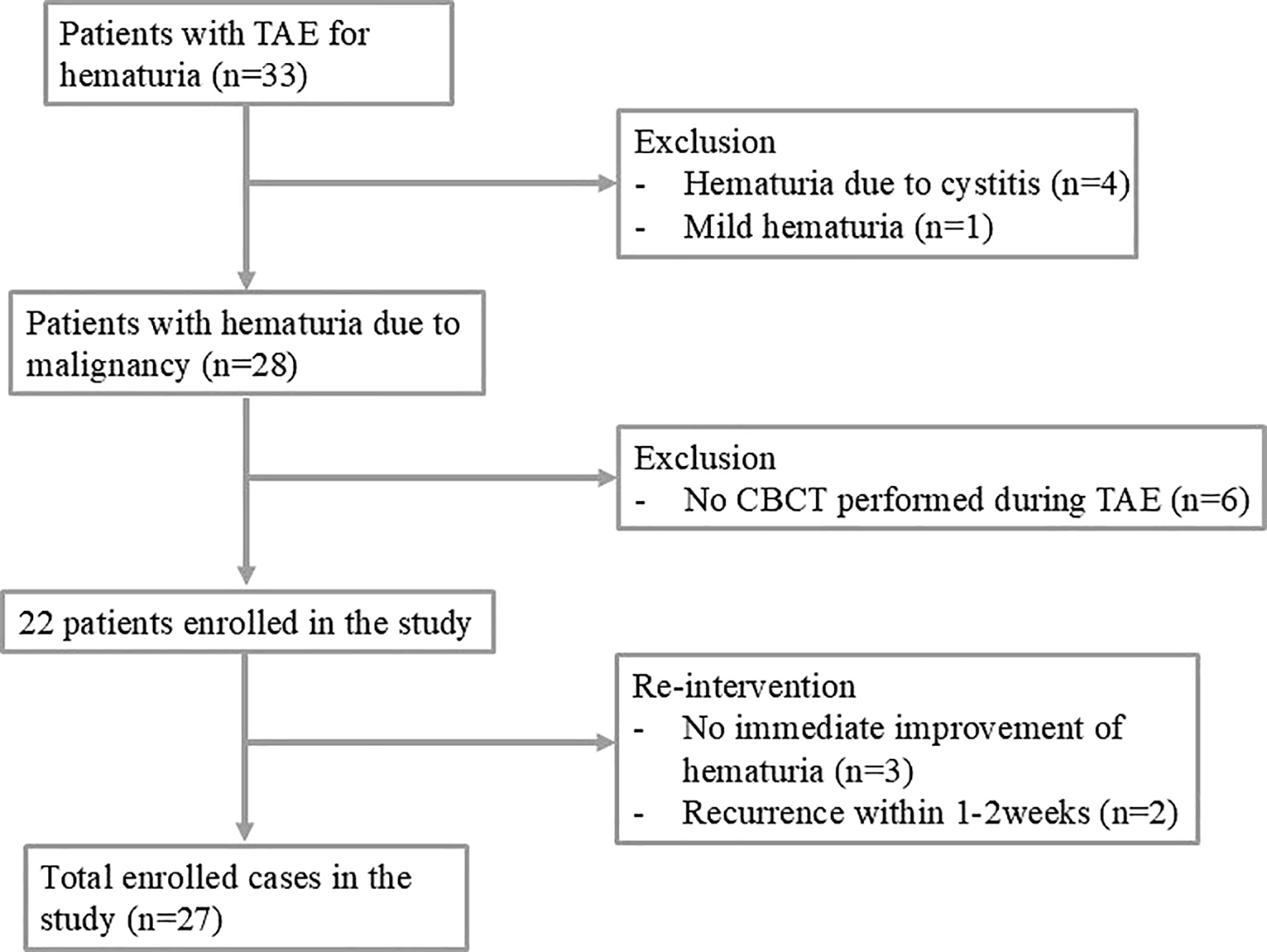
Figure 1
Flowchart of transcatheter arterial embolization in patients with malignant intractable hematuria.
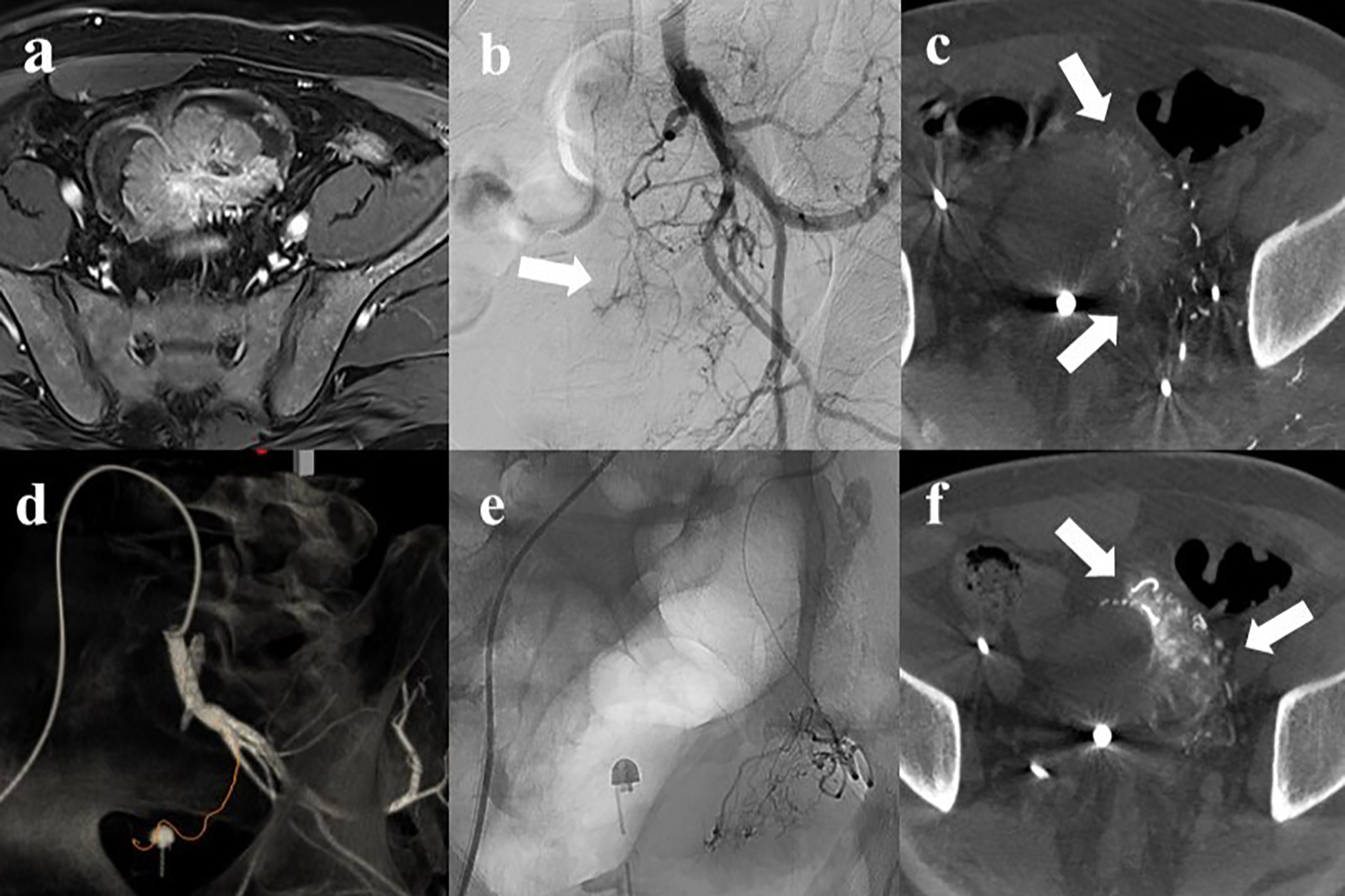
Figure 2
A 53‑year‑old male with intractable hematuria due to bladder cancer. (a) Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 7 cm enhancing bladder dome mass. (b) Left internal iliac angiography showed hypervascular tumor staining (arrow) with complex vascular anatomy. (c) Axial cone‑beam CT (CBCT) showed perfusion to the left side of the tumor (arrow). (d) Automated feeder detection identified the vessel pathway (red line) leading to the tumor. (e) Superselective embolization was performed using tris‑acryl gelatin microspheres. (f) Post‑embolization CBCT revealed contrast retention (arrow) within the tumor, followed by contralateral embolization using the same protocol.
Table 2
Interpretive categories and criteria for CBCT for embolization in patients with intractable hematuria.
[i] CBCT, cone‑beam computed tomography; DSA, digital subtraction angiography.
Table 3
Summary of characteristic details of total 27 procedure cases.
| CHARACTERISTICS | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Time to selection of target vessel | 9.6 ± 7.1 min |
| Fluoroscopic time | 23.5 ± 8.2 (11.0 ~ 45.0) min |
| Number of CBCT scans | 2.82 ± 1.05 |
| Bilaterality Unilateral Bilateral | 6 (22.2%) 21 (77.8%) |
| Embolic materials TAGM GSP NBCA with iodized oil Microcoils Multiple agents | 26 (96.3%) 12 (44.4%) 2 (7.4%) 2 (7.4%) 11 (40.7%) |
| Embolized arteries Superior vesical artery Inferior vesical artery Prostatic artery Other internal iliac branches | 49 36 9 2 |
| Category 1 2 3 | 4 (8.3%) 19 (39.6%) 25 (52.1%) |
[i] CBCT, cone‑beam computed tomography; TAGM, tris‑acryl gelatin microspheres; GSP, gelatin sponge particles; NBCA, n‑butyl cyanoacrylate.
Table 4
Comparison of laboratory data and tumor size before and after the procedure.
| CHARACTERISTICS | PRE‑PROCEDURE | POST‑PROCEDURE | P‑VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.48 ± 1.73 | 8.86 ± 1.69 | <0.001 |
| Blood pressure (mm Hg) | 126.6 ± 11.6 | 132.9 ± 12.6 | 0.080 |
| Heart rate (per min) | 83.5 ± 16.7 | 76.7 ± 10.1 | 0.009 |
| Platelet count | 214.5 ± 97.3 | 206.6 ± 99.7 | 0.571 |
| INR | 1.10 ± 0.09 | 1.08 ± 0.84 | 0.105 |
| Transfusion (pRBC) | 2.41 ± 1.68 | 0.64 ± 0.58 | <0.001 |
| Tumor size (cm)* | 5.47 ± 1.53 | 3.61 ± 1.35 | <0.001 |
[i] INR, International nomalized ratio; pRBC, packed red blood.
[ii] *Patients who did not receive radical cystectomy after the procedure.
