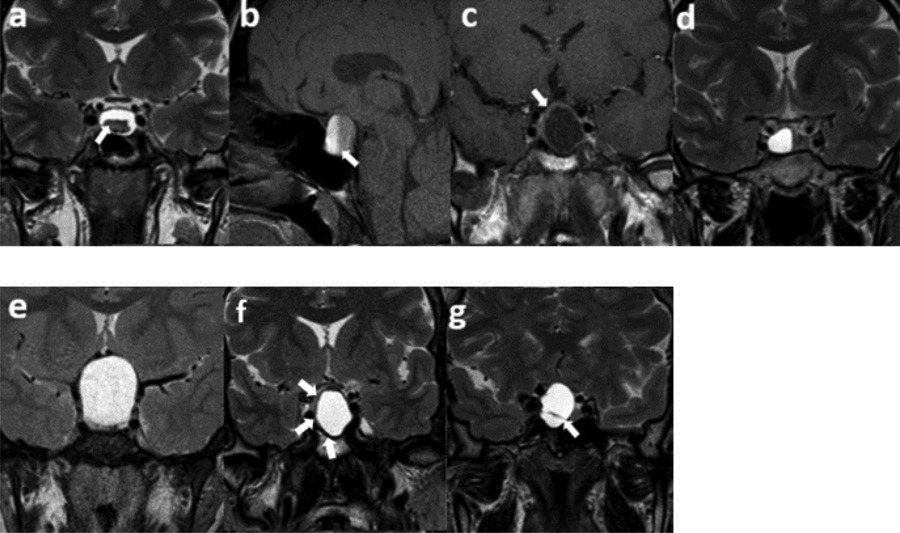
Figure 1
Semantic features. (a) An intracystic nodule on T2WI, (b) intralesional fluid–fluid level on SPIR T1WI, (c) ≥2 mm thickness of contrast-enhancing wall, (d) off-midline location, (e) suprasellar extension, (f) hypointense rim on T2WI, (g) intralesional septation on T2WI.
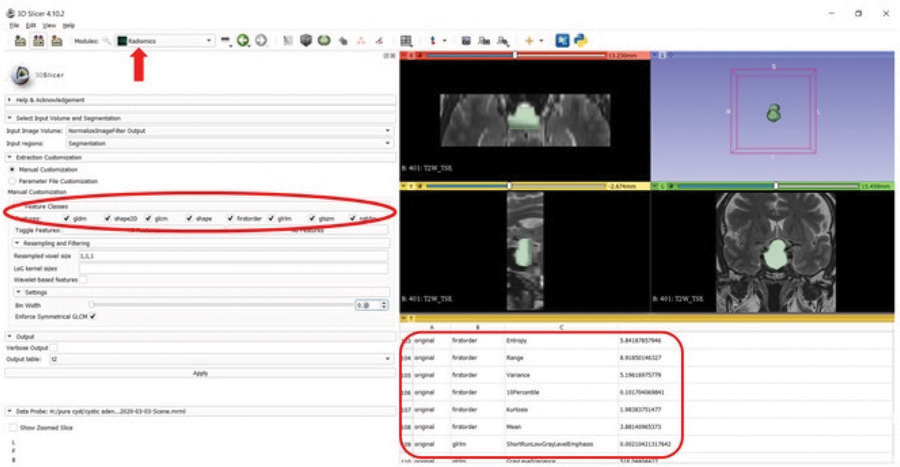
Figure 2
Segmentation and feature extraction (red rectangle, red ellipse) from the segmented volume using the Radiomics extension (arrow) of the 3D Slicer software on T2W image.

Figure 3
Schematic representation of the feature extraction process and the subsequent steps taken in developing machine learning models.
Table 1
Interobserver agreement analysis for semantic features
| SEMANTIC FEATURE | 1ST OBSERVER | 2ND OBSERVER | KAPPA AGREEMENT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NONE | PRESENT | |||
| Fluid–Fluid level | None | 52 | 7 | 0.578 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 0 | 6 | ||
| Septa | None | 37 | 5 | 0.428 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 11 | 12 | ||
| Intracystic nodule | None | 44 | 10 | 0.491 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 2 | 9 | ||
| Hypointense rim | None | 32 | 7 | 0.654 High agreement |
| Present | 4 | 22 | ||
| Suprasellar placement | None | 14 | 3 | 0.490 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 12 | 36 | ||
| Wall enhancement >2 mm | None | 40 | 9 | 0.512 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 4 | 12 | ||
| Off-midline location | None | 16 | 16 | 0.442 Moderate agreement |
| Present | 2 | 31 | ||
Table 2
Semantic features of CPA and RCCs
| SEMANTIC FEATURE | CYSTIC PITUITARY ADENOMA N = 37 | RATHKE CLEFT CYST N = 28 | P VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid–Fluid level | 6 (16.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.003 |
| Septa | 19 (51.4%) | 4 (14.3%) | < 0.001 |
| Intracystic nodule | 1 (2.7%) | 18 (64.3) | < 0.001 |
| Hypointense rim | 20 (54.1%) | 6 (21.4%) | 0.008 |
| Suprasellar placement | 24 (64.9%) | 24 (85.7%) | 0.058 |
| Wall enhancement >2 mm | 16 (43.2%) | 0 (0%) | < 0.001 |
| Off midline location | 24 (64.9%) | 8 (28.6%) | 0.008 |
Table 3
Various metrics of different models on both the testing and training datasets, utilizing SVM, LR, and LGB algorithms
| DATASET | ALGORITHM | SEMANTIC MODEL | T2W MODEL | T1W MODEL | T1C MODEL | COMBINED MODEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test accuracy | SVM LR LGB | 0.846 0.892 0.877 | 0.923 0.938 0.908 | 0.892 0.877 0.892 | 0.892 0.892 0.892 | 0.892 0.923 0.892 |
| Train accuracy | SVM LR LGB | 0.923 0.942 0.954 | 0.954 0.977 1.000 | 0.931 0.946 0.996 | 0.931 0.942 0.977 | 0.935 0.950 0.992 |
| Test AUC | SVM LR LGB | 0.956 0.956 0.951 | 0.960 0.980 0.945 | 0.956 0.970 0.980 | 0.980 0.981 0.954 | 0.990 0.985 0.961 |
| Test precision | SVM LR LGB | 0.905 0.898 0.975 | 0.925 0.928 0.933 | 0.902 0.880 0.921 | 0.888 0.909 0.913 | 0.884 0.927 0.928 |
| Test recall | SVM LR LGB | 0.836 0.943 0.807 | 0.950 0.975 0.918 | 0.918 0.918 0.889 | 0.943 0.914 0.914 | 0.943 0.943 0.889 |
| Test F1 score | SVM LR LGB | 0.853 0.913 0.876 | 0.937 0.950 0.922 | 0.906 0.894 0.900 | 0.911 0.904 0.904 | 0.909 0.933 0.901 |
| Test specificity | SVM LR LGB | 0.853 0.807 0.960 | 0.887 0.887 0.880 | 0.860 0.820 0.893 | 0.813 0.847 0.847 | 0.813 0.887 0.887 |
