Table 1
Characteristics of SANT based on a review of literature.
| Age |
|
| Gender |
|
| Clinical findings |
|
| Morphology |
|
| Computed Tomography |
|
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
|
| Ultrasound |
|
| FDG-PET |
|
[i] Abbreviations: M = Male; F = Female; n = number; CEUS = Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound; FDG-PET = Fluoro-deoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography; SUVmax = Maximal Standardized Uptake Value.
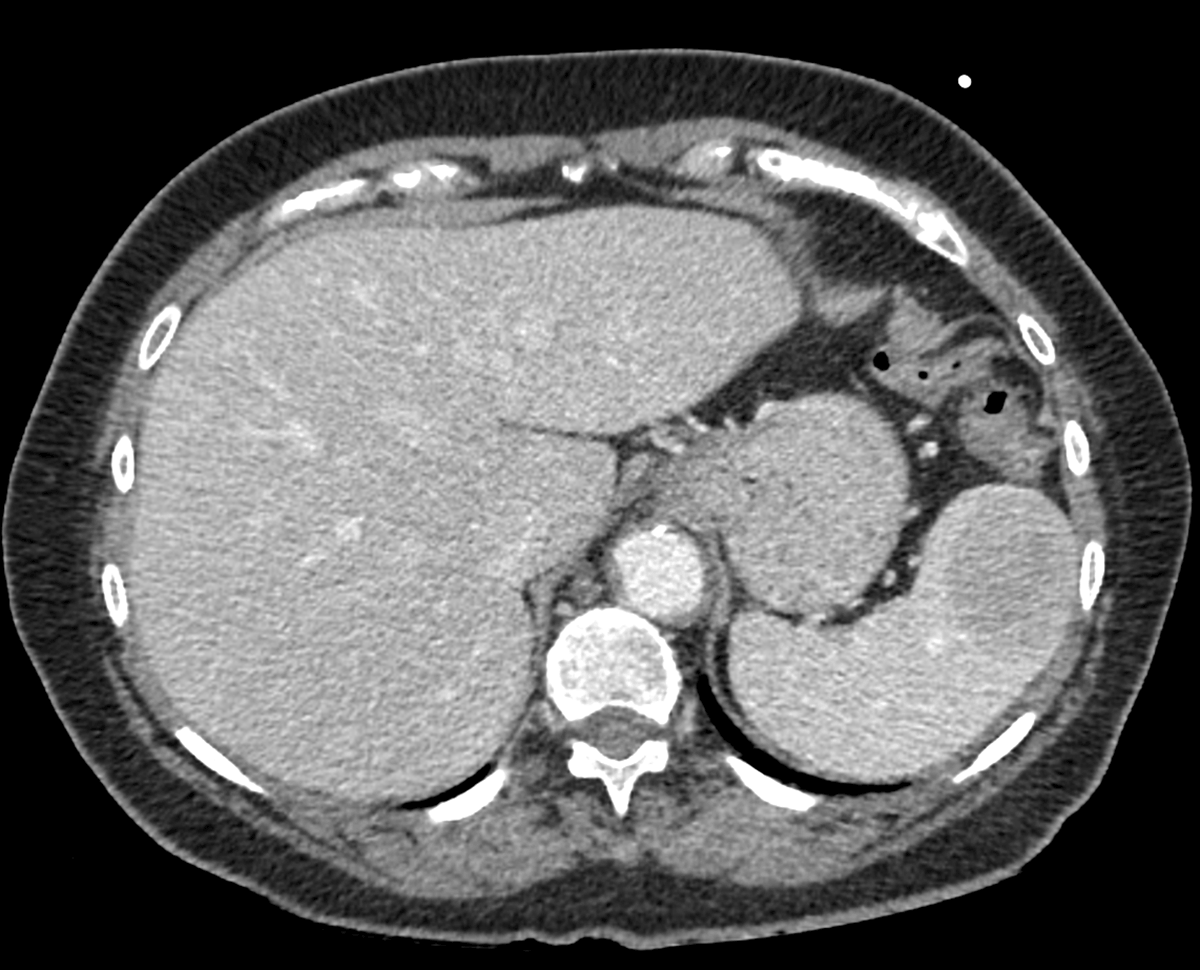
Figure 1
Axial Computed Tomography in the porto-venous phase depicts a sharply delineated lesion anteriorly in the spleen with relative hypo-enhancement compared to the surrounding splenic parenchyma.
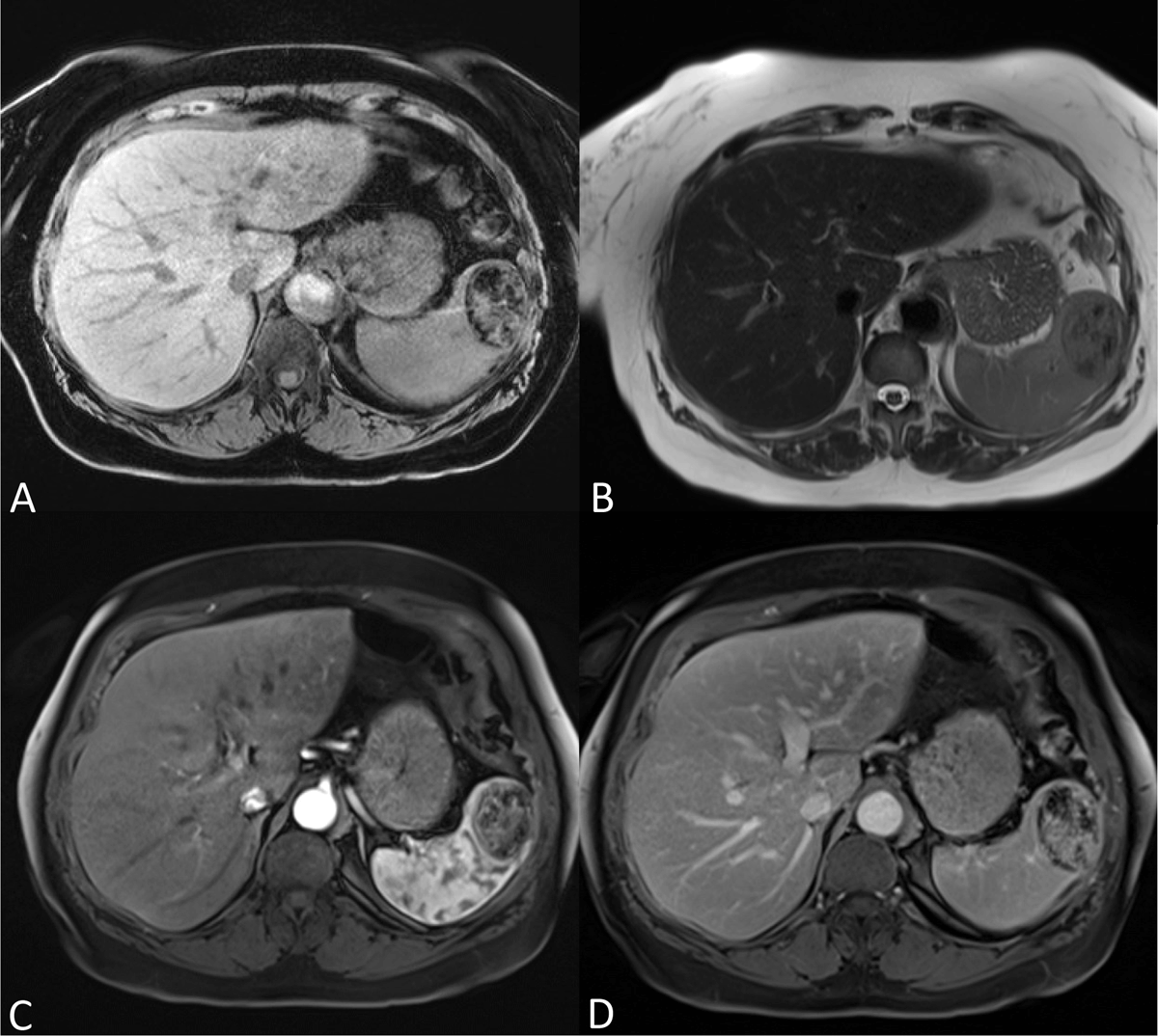
Figure 2
(A) Unenhanced axial fat suppressed T1-weighted imaging shows the lesion is sharply delineated with abundant hypointense foci. (B) Axial T2-weighted imaging shows a sharply delineated heterogeneous mass with both iso- and hypointense components. (C–D) Axial fat suppressed T1-weighted imaging after injection of gadolinium contrast shows a relative heterogeneous and weak enhancement in the arterial phase progressively filling in at the delayed phase, although remaining heterogeneous. No central scar or spoke-wheel enhancement pattern was present.
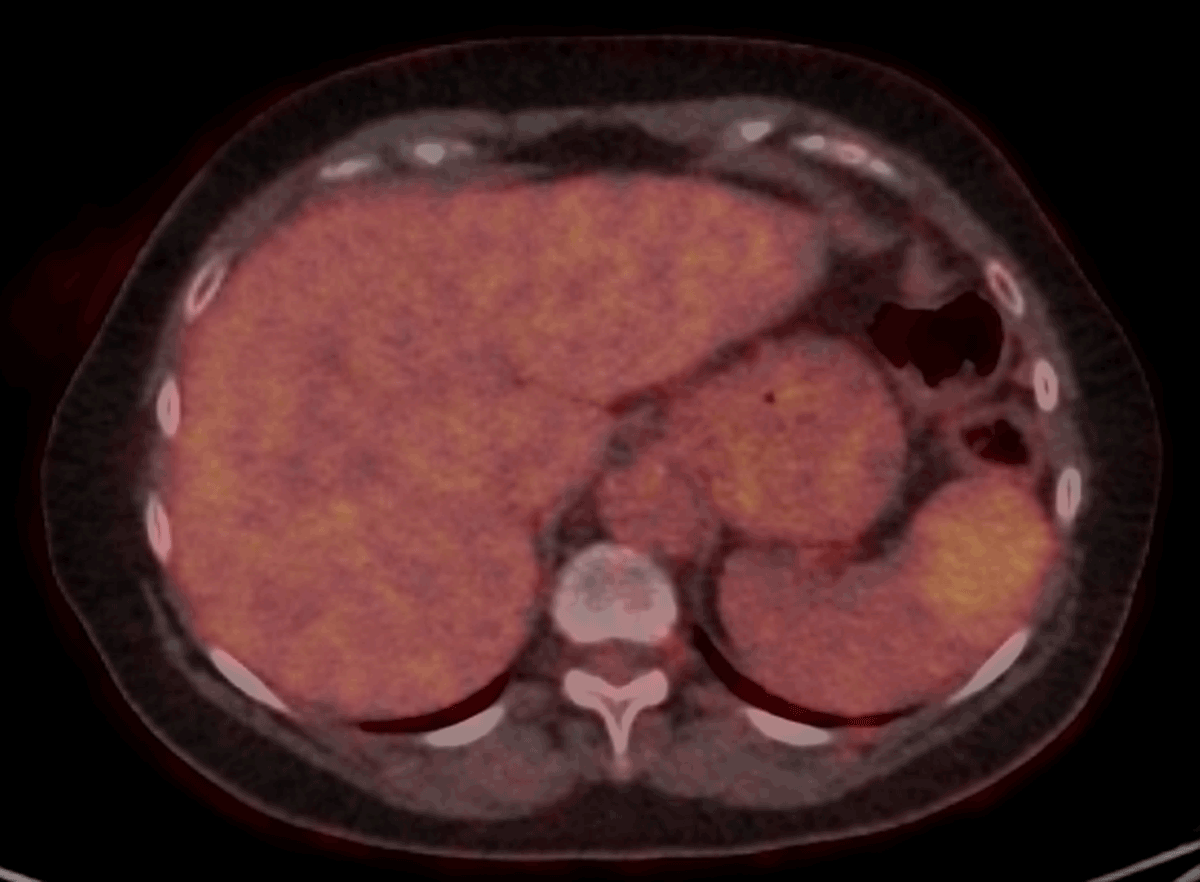
Figure 3
Axial Fluoro-deoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography shows a moderate uptake in the splenic lesion. Extra-splenic lesions were absent.
