Anysmay, polysplenia syndrome is an unusual disposition of intra-abdominal organs and unlike situs inversus it’s a spectrum of abnormalities and not a single set.
Report
An asymptomatic 62-year-old woman underwent abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) for inaugural diabetes.
CT showed dorsal pancreatic (P) agenesis (A) (Figure 1a).
Incidental abnormalities were found, including:
– Four spleens (S), one adjacent to the stomach (Figure 1b).
– Right renal hypotrophy (Figure 1c).
– Midline falciform ligament (Figure 1d).
– Duplicated inferior vena cava system (IVC) with dilated azygos (A) and hemiazygos (H) continuation and no communication with hepatic veins (N) (Figure 2).
– Intestinal nonrotation: the small bowel was right-sided (S), the colon was left-sided (C), the superior mesenteric artery (A) was to the right of the vena (V), and there was no midline crossing by the duodenum (D) under the aorto-mesenteric junction (P) (Figure 3).
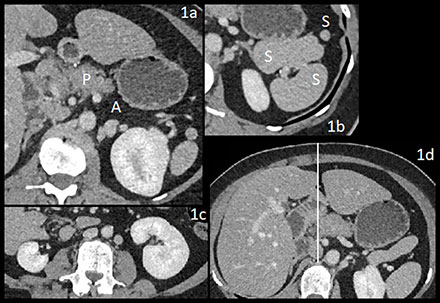
Figure 1
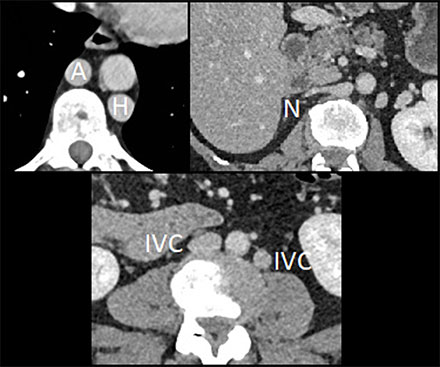
Figure 2
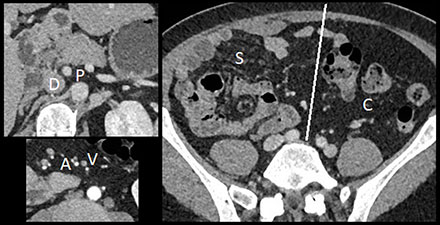
Figure 3
The diagnosis of type II diabetes was retained and after four months of metformin and insulin therapy, the rate of HbA1c was almost normalized. The remaining of the follow-up was unremarkable.
Comment
Heterotaxy syndrome (HS) (or situs ambiguus) is the result of an early embryological developmental failure in which there is an abnormal arrangement of thoraco-abdominal organs. In contrast to situs inversus, HS is not characterized by a single set of abnormalities but rather a spectrum.
Polysplenia syndrome (PS) (or left isomerism) is the subtype of HS with features of bilateral left-sidedness. No single anomaly is pathognomonic but the association of a sufficient number allows the diagnosis. The commonest is the presence of multiple spleens, right- or left-sided, with a consistent relationship to the stomach.
As in the present case, the other intra-abdominal abnormalities include:
– midline liver with or without biliary abnormality,
– truncated pancreas with presence of the head and a variable portion of the body,
– azygos continuation of the IVC,
– midline or right-sided aorta,
– right-sided stomach and/or abnormalities of the mesentery rotation.
Compared to the other HS (i.e., right isomerism [or asplenia]) PS is often detected incidentally in adults. Indeed, it is associated with less severe or no congenital heart disease and no immune system deficiency [1].
Competing Interests
The author has no competing interests to declare.
