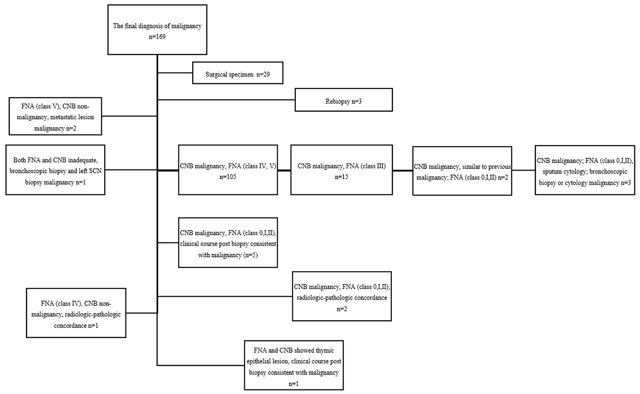
Figure 1
The final diagnosis of malignancy.
Note. FNA-fine needle aspiration biopsy. CNB-core needle biopsy. SCN-supraclavicular lymph node.
Table 1
Results of 166 malignant lesions.
| Diagnosis | No. of cases | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | 90 | (54.2) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 39 | (23.5) |
| Small cell carcinoma | 14 | (8.4) |
| Metastatic adenocarcinoma | 4 | (2.4) |
| Pleomorphic carcinoma | 3 | (1.8) |
| Large cell carcinoma | 2 | (1.2) |
| Thymoma | 2 | (1.2) |
| Metastatic melanoma | 2 | (1.2) |
| Others | 10 | (6.0) |
[i] Others are the diagnoses with fewer than 2 cases.
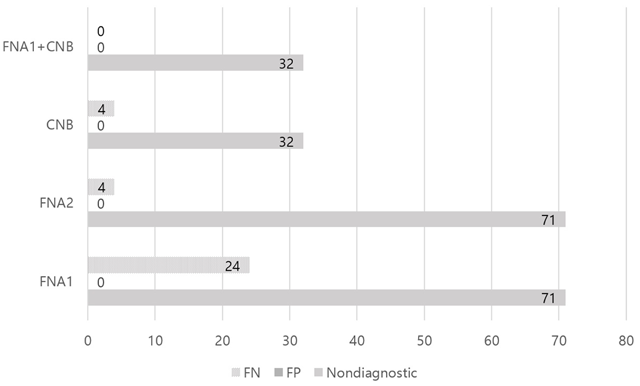
Figure 2
Comparison of FNA or CNB.
Note. FNA = fine needle aspiration. In FNA1, atypical cells classified as benign. In FNA2, atypical cells classified as malignant. CNB = core needle biopsy. Nondiagnostic means inadequate sample or indeterminate of final diagnosis. FN = false negative. FP = false positive.
Table 2
Result of FNA or CNB.
| FNA (atypical cells classified as benign) | FNA (atypical cells classified as malignant) | CNB | FNA (atypical cells classified as benign) + CNB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| True-positive | 133 (44.3%) | 153 (51.0%) | 162 (54.0%) | 166 (55.3%) |
| True-negative | 72 (24.0%) | 72 (24.0%) | 102 (34.0%) | 102 (34.0%) |
| False-positive | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| False-negative | 24 (8.0%) | 4 (1.3%) | 4 (1.3%) | 0 (0) |
| Nondiagnostic | 71 (23.7%) | 71 (23.7%) | 32 (10.7%) | 32 (10.7%) |
[i] Note. FNA = fine needle aspiration, CNB = core needle biopsy. Nondiagnostic means inadequate sample or indeterminate of final diagnosis. N = 300.
Table 3
Result of both FNA and CNB adequate sample.
| FNA (atypical cells classified as benign) | FNA (atypical cells classified as malignant) | CNB | FNA (atypical cells classified as benign) + CNB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| True-positive | 133 | 153 | 153 | 153 |
| True-negative | 72 | 72 | 72 | 72 |
| False-positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| False-negative | 24 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
[i] Note. FNA = fine needle aspiration, CNB = core needle biopsy, N = 229.
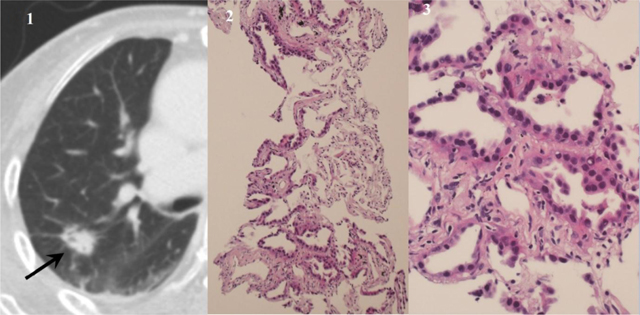
Figure 3
An adenocarcinoma with lepidic pattern diagnosed using samples from core needle biopsy. Diagnosis of fine needle aspiration was highly suspicious for adenocarcinoma. (1) CT image shows a nodule with inner bubble-like lucency in the right upper lobe (arrow). (2) Photomicrograph of a core biopsy (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification × 100) shows lepidic growth along the alveolar interstitium with preserved alveolar architecture. (3) Magnified photomicrograph (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification × 400) shows characteristic nonmucinous lepidic adenocarcinoma.
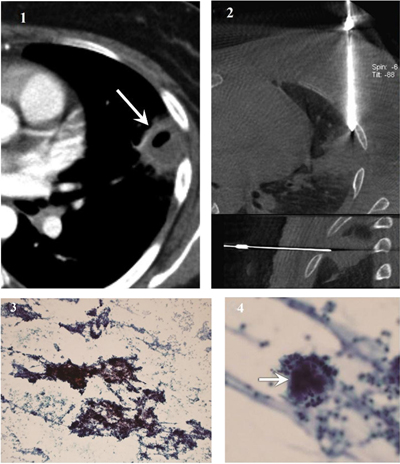
Figure 4
Actinomycosis diagnosed using samples from fine needle aspiration. (1) CT image shows a subpleural cavitary consolidation in the left upper lobe (arrow). (2) Cone-beam CT-guided CT images (upper, axial; lower, sagittal) show coaxial guide-needle placement to the target lesion. (3) Photomicrograph of cytological smear (Papanicolaou stain, original magnification × 100) shows clumps of basophilic bacterial colonies admixed with neutrophilic suppurative inflammatory infiltrates (4) Magnified photomicrograph of cytological smear (Papanicolaou stain, original magnification × 400) shows sulfur granules with dense center (arrow) surrounded by delicate filaments. The left upper lobe lesion disappeared after appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Table 4
Results of FNA and CNB in the diagnosis of benign-specific lesions.
| Final diagnosis | No. (%) of final diagnosis by FNA | No. (%) of final diagnosis by CNB |
|---|---|---|
| Tuberculosis (n = 24) | Tuberculosis, 10 (41.7%) | Tuberculosis, 24 (100%) |
| Benign-nonspecific lesion, 14 (58.3%) | ||
| Fungal infection (n = 11) | Fungal infection, 7 (63.6%) (Aspergillosis 4, Cryptococcus 1, Pneumocystis jirovecii 1, nonspecific fungal infection 1) | Fungal infection, 11 (100%) (Aspergillosis 4, Cryptococcus 4, Histoplasmosis 1, Pneumocystis jirovecii 1, nonspecific fungal infection 1) |
| Benign-nonspecific lesion, 4 | ||
| Actinomycosis (n = 4) | Actinomycosis, 4 (100%) | Actinomycosis, 2 (50%) |
| Benign-nonspecific lesion, 2 (50%) | ||
| Hamartoma (n = 4) | Hamartoma, 1 (25%) | Hamartoma, 4 (100%) |
| Benign-nonspecific lesion, 3 (75%) |
[i] Note. FNA = fine needle aspiration, CNB = core needle biopsy.
Lesions in which both FNA and CNB showed adequate samples are shown. Final diagnoses with fewer than 3 cases are not shown.
