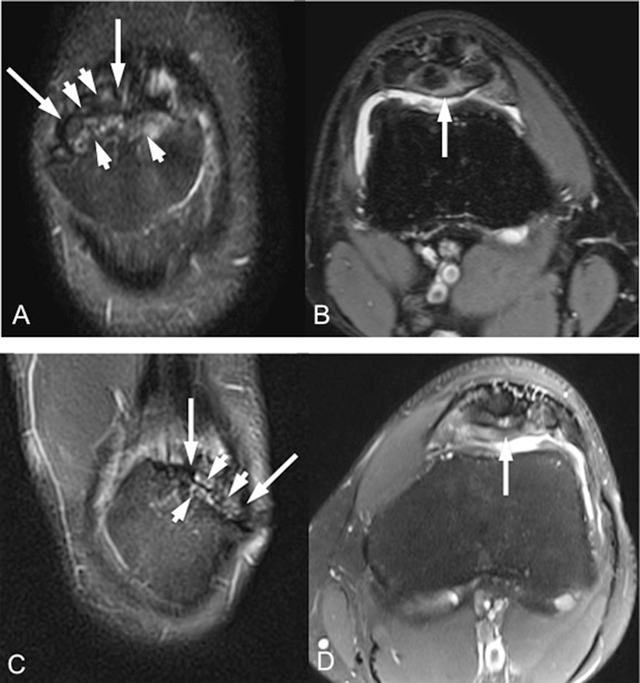
Figure 1
Coronal fat-saturated T2-weighted (A, C) and axial fat-saturated proton-density-weighted (B, D) MR images (respectively for right and left knee) show bilateral multipartite patella variation (long arrows) with bone marrow edema-like signal changes within the bony fragments (short arrows).
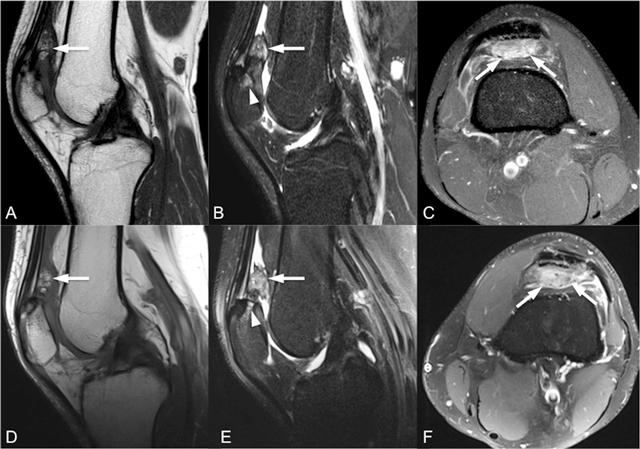
Figure 2
Sagittal T1-weighted (A, D), sagittal fat-saturated T2-weighted (B, E) and intravenous contrast-enhanced axial fat-saturated T1-weighted (C, F) MR images (top row for right knee, bottom row for left knee) show enlarged and inflamed quadriceps fat pad indicated by increased signal intensity with convex posterior border and contrast enhancement by intravenous contrast administration (arrows).
Table 1
Common Causes of Anterior Knee Pain.
| Traumatic Disorders | Nontraumatic Disorders | |
|---|---|---|
| Patellar disorders | Patellar fractures, patellar dislocation, post-traumatic osteochondral lesions | Patellofemoral osteoarthritis, chondromalacia/articular cartilage lesions, tumours, infection, osteochondritis dissecans, multipartite-bipartite patella |
| Quadriceps/patellar tendon disorders | Quadriceps tendon tear, patellar tendon tear | Quadriceps tendinosis, patellar tendinosis (jumper’s knee), Osgood-Schlatter, Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease |
| Supra- and infrapatellar fat pad disorders | – | Hoffa’s disease, excessive patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome (superolateral Hoffa’s fat pad edema), quadriceps fat pad edema inflammation, tumours |
| Bursae, plica, and recesses disorders | – | Bursitis, synovial plica syndrome, tumours |
