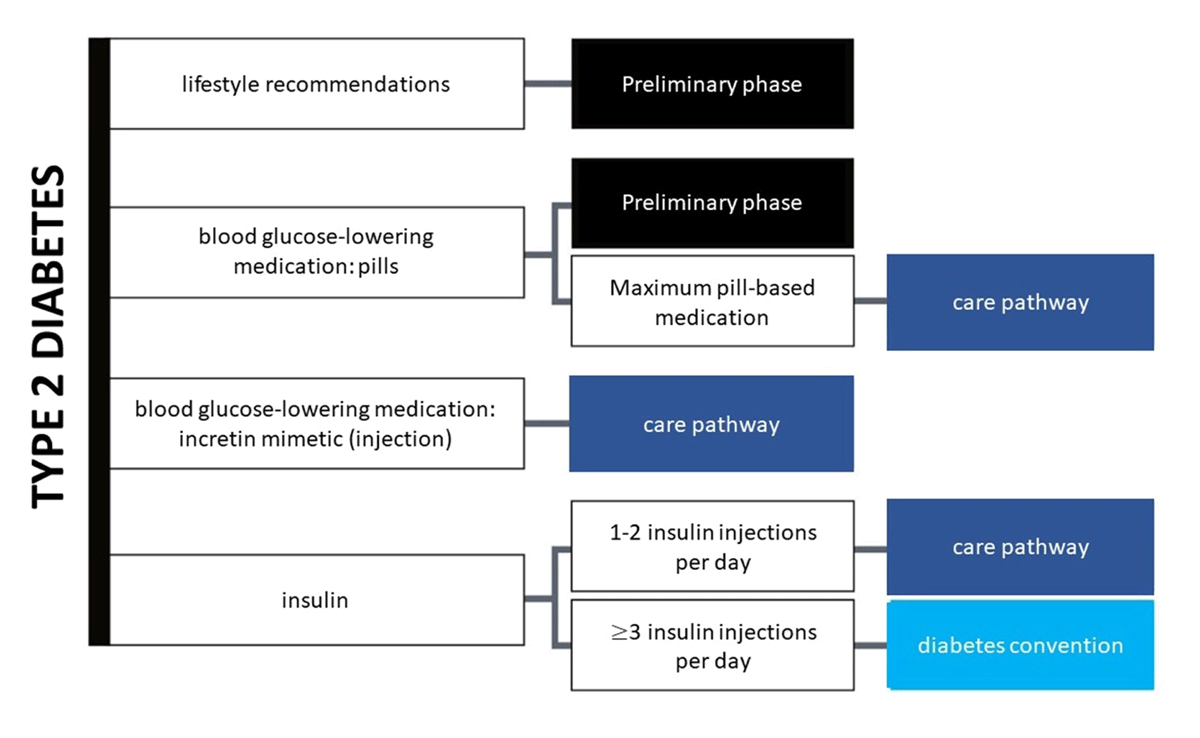
Figure 1
T2DM care systems and facilities in Belgium (www.diabetes.be).
Table 1
Characteristics of the participants and of interview methods.
| VARIABLE | VALUE | N | PER CENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 18 | 64% |
| Female | 10 | 36% | |
| Social status | Married | 15 | 54% |
| Widow | 8 | 29% | |
| Living together | 2 | 7% | |
| Divorced | 2 | 7% | |
| Single | 1 | 4% | |
| Nationality | Belgian | 24 | 86% |
| Non-Belgian | 4 | 14% | |
| Residence | Urban | 14 | 50% |
| Rural | 14 | 50% | |
| Complications | Renal | 16 | 57% |
| Ophthalmological | 12 | 43% | |
| Foot problems | 9 | 32% | |
| Cardiac | 8 | 29% | |
| Amputation lower limb | 7 | 25% | |
| Stroke | 4 | 14% | |
| Neuropathy | 4 | 14% | |
| Interview method | Live | 22 | 79% |
| Phone | 5 | 18% | |
| Videoconference | 1 | 4% | |
| Location of live interview (n=22) | Outpatient ward of hospital | 13 | 46% |
| General practitioner | 6 | 21% | |
| Home | 3 | 11% |

Figure 2
Example of a biographical–visual timeline.
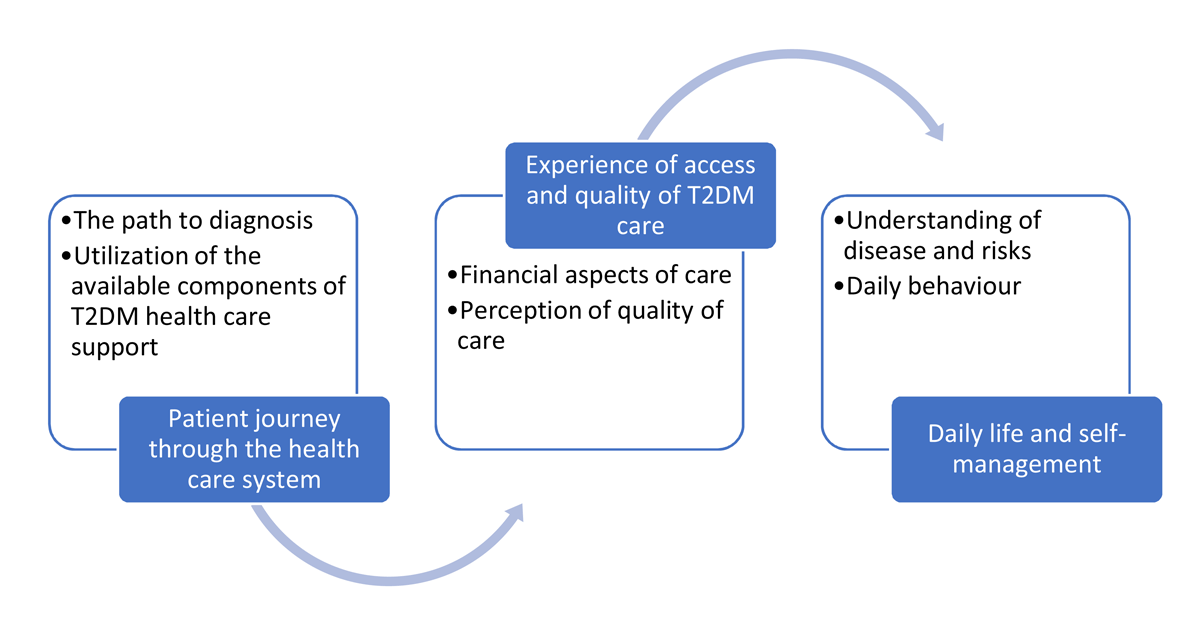
Figure 3
Chronological overview of the themes and subthemes.
Opening questions:
| |
| General topic | Specific topic |
| General information | Age Job, income and education Receiving of governmental subsidies Family situation and residency |
| Diseases | T2DM Comorbidities and other problems |
| Life with T2DM | Priorities in life Barriers in life |
| Care timeline | Overview of the providers you visit and how often Current treatment Which kind of services are linked to it? Use of health care services Barriers and facilitators Difficulties in attending services Postpone appointments |
| Financial aspects | Barriers and facilitators Government support Reimbursement of health care interventions Pharmacy and medication Transport to health care providers Expenses and costs related to T2DM Medical care Hospitalisation Other expenses Percentage expenses related to overall income Most expensive items regarding to treatment of T2DM |
| Home & living environment | Barriers and facilitators |
| Self-management of T2DM | Auto daily follow-up of T2DM Awareness of the risks and complications of T2DM Nutrition Lifestyle |
| Non-medical care | Informal care Household assistance |
| Assistive devices | Medical devices linked to T2DM Home adaptations Small assistive devices Home equipment |
| Participation in daily life | Environment Activities of daily life Social life |
| Accessibility and perceived quality of care | Language Distance to care provider Relationship with provider |
[i] T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus.
