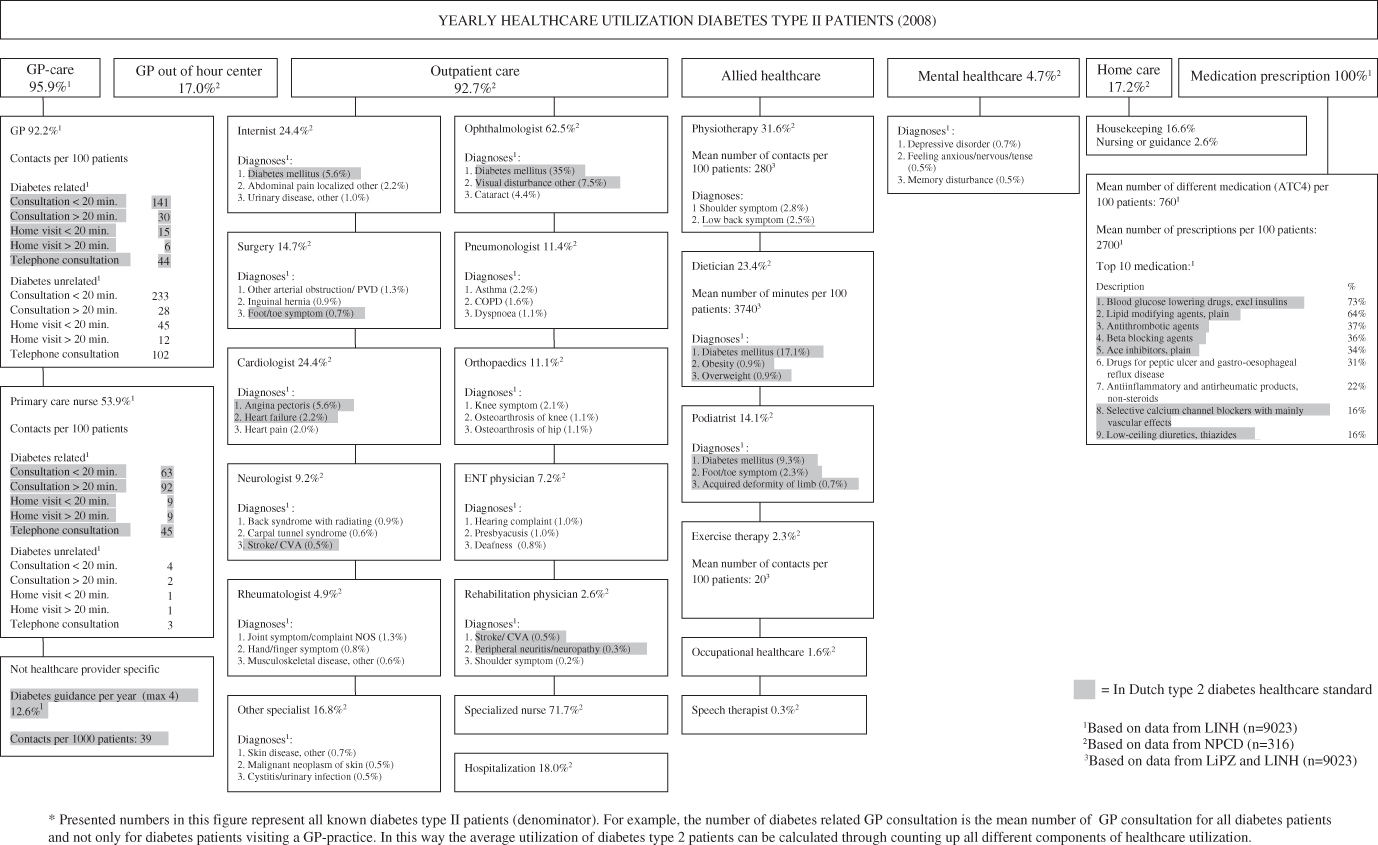
Figure 1.
Yearly healthcare utilization of diabetes mellitus type II patients, 2008*.
Table 1.
Top-10 of other chronic diseases in type 2 diabetes patients based on LINH (n=9023), 2008
| Chronic disease | Percentage of type 2 diabetes patients |
| Coronary heart disease | 15.3% |
| Dermatitis | 13.5% |
| Osteoarthritis | 8.7% |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | 8.6% |
| Chronic neck or back syndrome | 7.7% |
| Asthma | 6.9% |
| Visual disorder | 6.9% |
| Heart failure | 6.7% |
| Cancer | 6.7% |
| Transient cerebral ischaemia/cerebrovascular accident | 6.3% |
Table 2.
ICPC-codes included as ‘diabetes-related’ according to the Dutch Diabetes Federation type 2 diabetes healthcare standard
| F05: Visual disturbance other |
| F83: Retinopathy |
| F94: Blindness |
| K74: Angina pectoris |
| K75: Acute myocardial infarction |
| K76: Ischemic heart disease w/o angina |
| K86: Hypertension uncomplicated |
| K87: Hypertension complicated |
| K89: Transient cerebral ischemic |
| K90: Stroke/cerebrovascular disease, |
| K99.06: Peripheral diabetic angiopathy |
| L98: Acquired deformity limb |
| N94: Peripheral neuritis/neuropathy |
| P07: Sexual desire reduced |
| P08: Sexual fulfillment reduced |
| P17: Tobacco abuse |
| S06: Rash localized |
| S11: Other local infection skin |
| T02: Excessive appetite |
| T03: Loss of appetite |
| T05: Feeding problem of adult |
| T07: Weight gain |
| T08: Weight loss |
| T82: Obesity |
| T83: Overweight |
| T90: Diabetes mellitus |
| T93: Lipid disorder |
| X24: Fear of sexual dysfunction female |
| Y07: Impotence NOS |
| Y24: Fear of dysfunction male |
Appendix 1
Table A1. List of chronic diseases with ICPC-code and percentage of type 2 diabetes patients with the chronic disease
| Chronic disease | ICPC-code | Percentage of type 2 diabetes patients |
| Tuberculosis | A70 | 0.0% |
| HIV-infection/AIDS | B90 | 0.0% |
| Cancer | A79, B72, B73, D74, D75, D77, L71, N74, R84, R85, S77, T71, U75, U76, U77, W72, X75, X76, X77, Y77, Y78 | 6.7% |
| Peptic or duodenal ulcer | D85, D86 | 0.9% |
| Chronic enteritis/ulcerative colitis | D94 | 0.5% |
| Visual disorder | F83, F84, F92, F93, F94 | 6.9% |
| Hearing disorder | H84, H85 | 1.5% |
| Congenital anomaly cardiovascular | K73 | 0.0% |
| Coronary heart diseases | K74, K75, K76 | 15.3% |
| Heart failure | K77 | 6.7% |
| Transient cerebral ischaemia/ cerebrovascular accident | K89, K90 | 6.3% |
| Chronic neck or back syndrome | L83, L84, L85, L86 | 7.7% |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | L88 | 1.8% |
| Osteoarthritis | L89, L90, L91 | 8.7% |
| Osteoporosis | L95 | 3.2% |
| Congenital anomaly neurological | N85 | 0.0% |
| Multiple sclerosis | N86 | 0.1% |
| Parkinson | N87 | 0.6% |
| Epilepsy | N88 | 0.8% |
| Chronic alcohol abuse | P15 | 0.9% |
| Dementia | P70 | 1.6% |
| Schizophrenia | P72 | 0.3% |
| Anxiety disorder, other neurosis | P74, P79 | 2.0% |
| Depression | P76 | 5.8% |
| Mental retardation | P85 | 0.1% |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) | R91, R95 | 8.6% |
| Asthma | R96 | 6.9% |
| Dermatitis | S87, S88 | 13.5% |
| Anorexia | T06 | 0.0% |
Box 1.
Health care utilization for known type 2 diabetes patients based on Dutch Diabetes Federation type 2 diabetes healthcare standard
| Check-ups by GP and primary care nurse |
| 3-montly check-up: wellbeing, hypo- or hyperglycemia, nutritional problems or exercise advice and medication, body weight, fasting blood glucose levels, blood pressure (if patient uses antihypertensive drugs), foot examination (if patient had ulcus, acquired deformity of limb or serious neuropathy foot) |
| Yearly check-up: possible visual problems, cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy or sexual problems, lifestyle aspects as smoking status, exercise and alcohol use, blood pressure, body weight, foot examination, inspection insuline injection sites (if patients uses insuline), eye fundus examination. Laboratory measures: fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, creatinine levels, potassium levels (if patient uses diuretic or RAS inhibitor), creatinine clearance, albumin creatinine-ratio or albumin urine levels (if patients has a life expectancy of minimal 10 years), fasting lipids spectrum |
| Medication |
| Diabetes: oral blood glucose lowering drugs, insulin |
| Risk factor cardiovascular diseases: lipid modifying agents (recommended for almost all type 2 diabetes patients), diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-ii-antagonists, beta blocking agents, calcium channel blockers, antithrombotic agents |
| Superficial foot ulcer: oral antibiotic |
| Consultation other healthcare providers |
| Internist (including nephrologistadjustment insulin (when knowledge not available in GP-practice), insufficient correction postprandial blood glucose levels with two-times daily insulin, diabetes ulcer, low creatinine clearance, serious hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic coma, pregnant women or women with pregnancy wish |
| Dietician: for extensive nutrition advice |
| Ophthalmologist: retinaphotography (if not available in GP-practice), assessment of retinaphotography (if expertise not available in GP-practice), deviations eye fundus |
| Podotherapist: callous and/or pressure sites without signs of peripheral vascular disease |
| Surgeon: diabetes ulcer |
| Orthopedic: diabetes ulcer |
| Dermatologist: diabetes ulcer |
| Based on the described healthcare utilization the following ICPC-codes were coded as ‘according to the healthcare standard’ see Table 2. |
