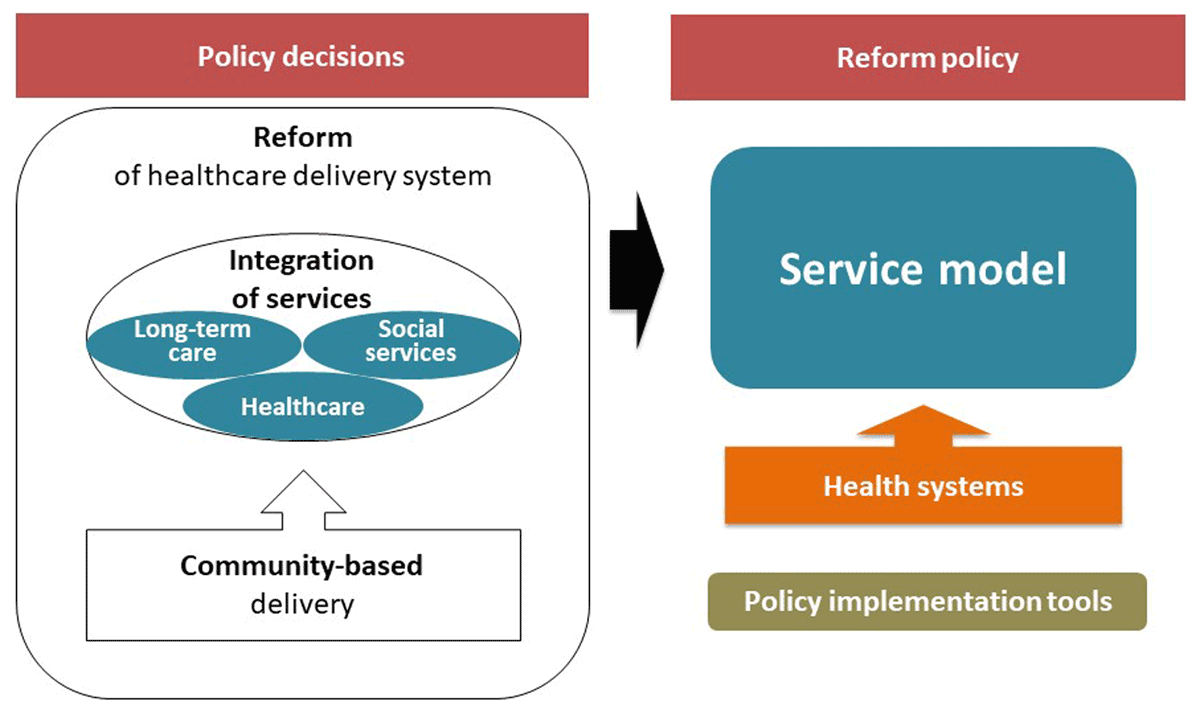
Figure 1
A conceptual framework developed to compare policies.
Table 1
Question items.
| ASPECTS | AREAS | NO. | QUESTION ITEMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy decisions | Reform | Item 1 | Is there any policy decision to reform current healthcare service delivery system to adapt to the ageing society? |
| Integrtion | Item 2 | Does the healthcare service reform policy aim at integration of healthcare and long-term care? | |
| Does it aim at integration of healthcare and welfare services? | |||
| Community-based | Item 3 | Does it aim at more community-based care? | |
| Reform policy | Service model | Item 4 | Name of service delively model |
| Item 5 | Services (What kind of services are provided through the model?) | ||
| Item 6 | Unit of a service delivery system (Geopgraphical area in which a delivery system of the model is established. E.g. adminisrative unit, school unit, etc) | ||
| Item 7 | Models referred (Which service delivey models were used as a reference to develop the service delivery model?) | ||
| Item 8 | Who developed the model? | ||
| Health systems | Item 9 | Type of financial source for the services Self help: individual & family, Mutual help: informal network based on locality or co-belongingness, Social solidarity: insurance, Public assistance: tax [22] | |
| Item 10 | New special heatlh workforces introduced for the model | ||
| Item 11 | New special other workforces introduced for the model | ||
| Item 12 | New information system introduced for the model | ||
| Item 13 | New coordination mechanism introduced to facilitate collaboration between health care service providers and welfare service providers | ||
| Policy implementation tools | Item 14 | Name of the policy document to introduce the model | |
| Item 15 | Issuing body/institution | ||
| Item 16 | Date of officially approved | ||
| Item 17 | Policy goal | ||
| Item 18 | Policy objective | ||
| Item 19 | Policy timeframe | ||
| Item 20 | Name of the strategies | ||
| Item 21 | Name of the laws or decrees | ||
| Item 22 | Name of the program | ||
| Item 23 | Source of finance for the program | ||
| Item 24 | Incentive to implement the policy | ||
| Item 25 | M&E system to check implementation status of the policy |
Table 2
Policy decisions on reform of healthcare delivery.
| QUESTION ITEMS | JAPAN | KOREA | THAILAND | CHINA | INDONESIA | PHILIPPINES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Is there any policy decision to reform current healthcare service delivery system for ageing? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Does it aim at integration of healthcare and long-term care? | Yes | Not yet | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not applicable |
| Does it aim at integration of healthcare and welfare services? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not applicable |
| Does it aim at more community-based care? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Not applicable |
Table 3
Services covered by delivery models in Asian countries.
| COUNTRY | DELIVERY MODEL | SERVICES COVERED BY THE MODEL |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | Community- based integrated care systems |
|
| Korea | Reach in g-Out Community Service Centre |
|
| Thailand | Home care model |
|
| China | Integrated health and social care | Atlong-term care facilities or the service area for acommunity health centre
|
| Indonesia | Community service centre for elderly (Posyandu lansia, Pos pelayanan terpadu, Puskesmas santun lansia) |
|
| The Philippines | There is no health service reform specific for elderly care; however, the following services are provided by the government |
|
Table 4
Building blocks of the health systems that are introduced for implementation of the models.
| COUNTRY | TYPE OF FINANCIAL SOURCES | NEW SPECIAL WORKFORCES | NEW INFORMATION SYSTEMS | NEW COORDINATION MECHANISMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan |
| Livelihood support coordinator | There is not a single standardised network system of patient and in-home care information, which is expected to facilitate information sharing among different care providers. However, many municipalities introduced a unique cloud-based network by themselves |
|
| Korea |
| None |
|
|
| Thailand |
| Elderly caregiver | None (theThai government plans touse the individual identification number to facilitate sharing of information, including medical records and income, welfare service usage, but thisis not only introduced forth is model) | The National Commissionon the Elderly underthe cabinet and new Ministry of SocialDevelopment and Human Security |
| China |
| None | The central policies encourage local governments to establish asingle information systemto facilitate information sharing among different care providers, but it is not mandatory. Some companies establish such informationsystems by themselves |
|
| Indonesia |
| None |
| None |
| The Philippines |
| None | None | None |
