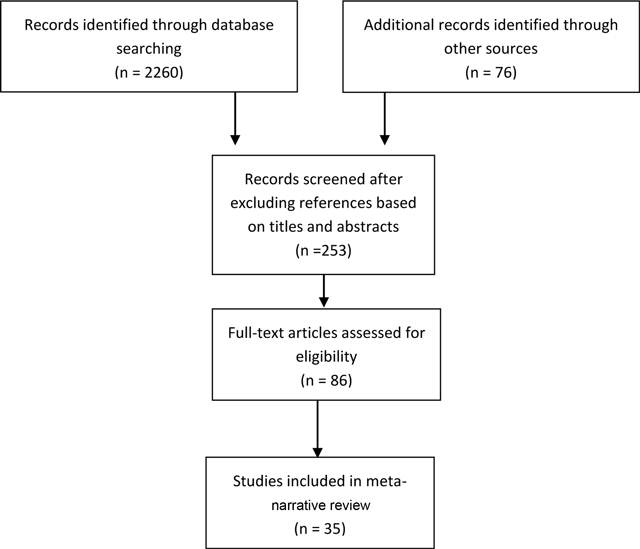
Figure 1
Search and selection strategy.
Table 1
Further questions posed of the included literature [adapted from Greenhalgh et al [9]].
|
Table 2
Reviews included in Each Meta-narrative.
| Metanarrative | Reviews primarily associated | Year of publication | Literature sources | Review methods as stated by authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Implementation should be Informed by Theoretical Constructs | Francke AL, Smit MC, Veer AJ, and Mistiaen P. | 2008 | 12 | Systematic meta-review |
| Liaw ST, Lau P, Pyett P, Furler J, Burchill M, Rowley K, et al. | 2011 | 17 | Literature review | |
| Stirman SW, Kimberly J, Cook N, Calloway A, Castro F, and Charns M. | 2012 | 125 | Literature review | |
| Flottorp SA, Oxman AD, Krause J, Musila NR, Wensing M, Godycki-Cwirko M, et al. | 2013 | 12 | Systematic review | |
| Chaudoir SR, Dugan AG, and Barr CH. | 2013 | 125 | Systematic review | |
| Braithwaite J, Marks D, and Taylor N. | 2014 | 57 | Systematic review | |
| Davy C, Bleasel J, Liu H, Tchan M, Ponniah S, and Brown A. | 2015 | 77 | Systematic review | |
| 2. The Relationships Between Theoretical Constructs and the Ways in Which they Impact Implementation | Davies P, Walker AE, and Grimshaw JM. | 2010 | 285 | Systematic review |
| Thomas A, Menon A, Boruff J, Rodriguez AM, and Ahmed S. | 2010 | 35 | Scoping review | |
| Wilson PM, Petticrew M, Calnan MW, and Nazareth I. | 2012 | 33 | Systematic scoping review | |
| Wisdom JP, Chor KHB, Hoagwood KE, and Horwitz SM. | 2014 | 20 | Review of theories and constructs | |
| Tabak RG, Khoong EC, Chambers DA, and Brownson RC. | 2014 | 61 | Narrative review | |
| 3. Developing New frameworks from Theories, Constructs and Key Factors | Greenhalgh, Robert, Macfarlane, Bate and Kyriakidou. | 2004 | 495 | Metanarrative review |
| Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, and Lowery JC. | 2009 | 19 | Consolidated framework | |
| Ward V, House A, and Hamer S. | 2009 | 28 | Narrative review | |
| Gagliardi AR, Brouwers MC, Palda VA, Lemieux-Charles L, and Grimshaw JM. | 2011 | 18 | Conceptual framework | |
| Meyers DC, Durlak JA, and Wandersman A. | 2012 | 27 | Synthesis of frameworks | |
| Taylor MJ, McNicholas C, Nicolay C, Darzi A, Bell D, and Reed JE. | 2014 | 73 | Systematic review | |
| Schell SF, Luke DA, Schooley MW, Elliott MB, Herbers SH, Mueller NB, et al. | 2013 | 85 | Comprehensive literature review | |
| Moullin JC, Sabater-Hernández D, Fernandez-Llimos F, and Benrimoj SI. | 2015 | 49 | Systematic review | |
| 4. Applying Existing Frameworks in Many Ways | Helfrich CD, Damschroder LJ, Hagedorn HJ, Daggett GS, Sahay A, Ritchie M, et al. | 2010 | 24 | Critical synthesis |
| Gaglio B, Shoup JA, and Glasgow RE. | 2013 | 71 | Systematic review | |
| Field B, Booth A, Ilott I, and Gerrish K. | 2014 | 146 | Systematic review | |
| Kadu MK, and Stolee P. | 2015 | 22 | Systematic review | |
| Kirk MA, Kelley C, Yankey N, Birken SA, Abadie B, and Damschroder L. | 2016 | 26 | Systematic review | |
| 5. Evaluating Effectiveness of Interventions within Frameworks/Models | Wensing M, and Grol R. | 1994 | 75 | Literature review |
| Grimshaw J, Thomas R, MacLennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay C, Vale L, et al. | 2004 | 235 | Systematic review | |
| Wensing M, Wollersheim H, and Grol R. | 2006 | 36 | Structured review of reviews | |
| HakkennesS, and Dodd K. | 2008 | 27 | Systematic review | |
| Prior M, Guerin M, and Grimmer-Somers K. | 2006 | 33 | Synthesis of systematic reviews | |
| Boaz A, Baeza J, and Fraser A. | 2011 | 13 | Overview of systematic reviews | |
| Scott SD, Albrecht L, O’Leary K, Ball G, Hartling L, Hofmeyer A, et al. | 2012 | 32 | Systematic review | |
| Baker R, Camosso-Stefinovic J, Gillies C, Shaw E, Cheater F, Flottorp S, et al. | 2015 | 32 | Systematic review | |
| Lau R, Stevenson F, Ong BN, Dziedzic K, Treweek S, Eldridge S, et al. | 2015 | 91 | Synthesis of systematic reviews |
Table 3
Research traditions reflected in included articles [adapted from Greenhalgh et al.[9]].
| Positivist, assumes an external and knowable reality that is objectively measured; researcher is impartial; generalizable statements the natural and social world are producible. | Interpretivist, assumes a socially constructed reality, informed reconstruction; researchers are co-constructors of knowledge, of understanding and interpretation of the meaning of lived experiences; researcher’s identity and values are inevitably implicated in the research process. | Critical, assumes an inherently unstable social order with domination of some groups by others, e.g. patients by health professionals. Aims to (in part) help dominated groups challenge their position in society. | Recursive (or integrative), assumes subject and object, micro and macro, social structure and human agency, are reciprocally related and that the purpose of research is to explore dynamics of such relationships. |
Table 4
Overview of Key Features of Metanarratives.
| Metanarrative | Disciplinary and Philosophical roots | Definition and Scope of Implementation | General Format of Review Questions | Implementation Conceptualised as… | End-users/Beneficiaries Conceptualised as | Implementation Context conceptualised as… |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Implementation should be Informed by Theoretical Constructs | Cognitive, ecological, socio-cultural, communication, change, adult learning and improvement theories. Social diffusion theory, organizational theory. Interpretivist, critical and recursive roots. | Necessitates the exploration of theoretical constructs embedded in healthcare to uncover the multiple factors that influence professional practice. | What theory base or constructs underpin implementation and how can they be used to guide all of its phases? | Seeks an understanding of evidence use through theory-based reasoning and decisions. | Researchers, health system decision-makers, and health care providers. Scarce mention of consumers. | Is complex and is a potent influence on how a theory may operate within a particular project or programme. |
| 2. The Relationships Between Theoretical Constructs and the Ways in Which they Impact Implementation | Social diffusion theory and organizational theory. Quality and safety. Based on positivist, interpretive, critical and recursive research. | Consists of multiple layers, intersections, and interdependent elements that create complex adaptive system that typifies healthcare. | What are the influences, measures, and outcome aspirations that may predict success (or failure)? | Captures the factors impacting on achievement, accomplishment and execution of translating research findings effectively and rapidly into policy and practice. | Researchers, health system decision-makers, and health care providers. Scarce mention of consumers. | The context, the nature of innovation/s, and the capacity to sustain are interacting dynamics of a complex and unstable phenomenon. |
| 3. Developing New frameworks from Theories, Constructs and Key Factors | Psychology, sociology, biomedical science, public health, sociology, business and management studies. Primarily positivist roots with pragmatist and interpretivist influences. | Implementation is to be understandable and usable for a broad audience aided by simplifying complexity, specifying relationships, for use in various contexts. | What are the key factors influencing implementation processes and outcomes, and how do they relate to one another? | A collection of activities designed to alter the behaviour of health care providers, under the influence of a variety of contextual factors. | Researchers, health system decision-makers, and health care providers. | Context exists within and outside an organization and fundamentally influences implementation. |
| 4. Applying Existing Frameworks in Many Ways | Primarily positivist approaches, some interpretivist influence. | Implementation is a process through which knowledge/evidence is disseminated and adopted into practice. | How are implementation frameworks being used and to what effect? | A process which occurs within a particular context involving barriers and facilitators. | Researchers and individuals seeking to disseminate knowledge. | Related to the type of evidence/intervention being implemented, and micro, meso and macro level factors that can support or hinder implementation. |
| 5. Evaluating Effectiveness of Interventions within Frameworks/Models | Psychology, sociology, biomedical science, public health, sociology, business and management studies. Positivist research base. | Implementation involves what works. Efficacy and safety are paramount. Change is more likely if strategies address contextual barriers and enablers. | What are the most effective ways to improve health care practice and health outcomes? | Use of research evidence involves employing strategies to implement improvements in patient care. | Researchers, health system decision-makers, and health care providers and ultimately patients when health outcomes are improved. | Context determines important factors and directs the approaches used to select interventions. |
