Figure 1
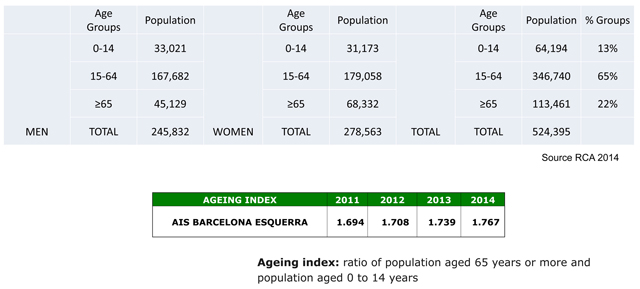
Population of the AIS Barcelona Esquerra (–).
Table 1
Main healthcare suppliers in the AIS Barcelona Esquerra.
| Primary Care |
|
| Specialty Care |
|
| Mental Health and Addictions |
|
| Social Health Care |
|
|
Table 2
Organisation of the AIS Barcelona Esquerra (AISBE).
| Integrated Healthcare Committee Barcelona Esquerra (CAISBE) |
|
| Standing Committee (SC) |
|
| Technical Office (TO) |
|
| Operational Committees (OC) |
|
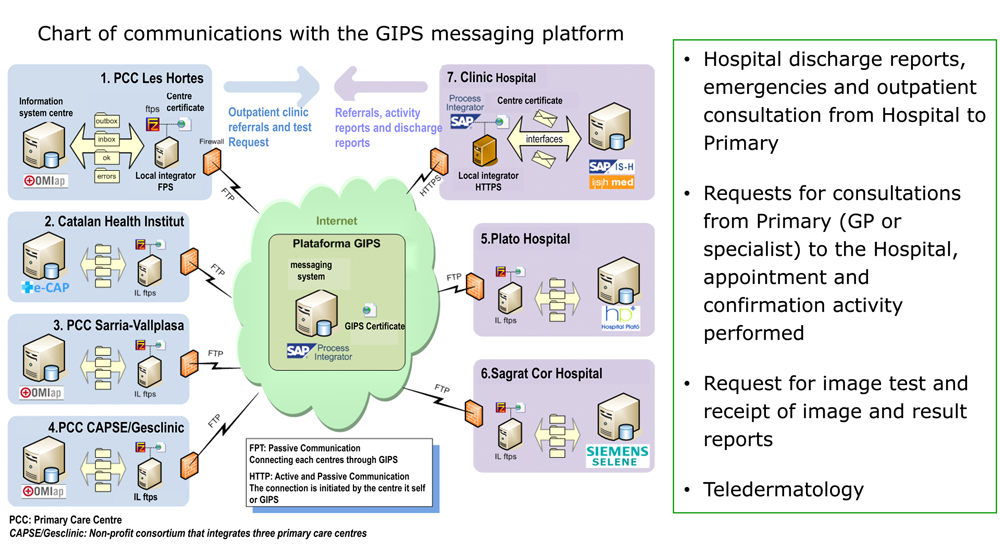
Figure 2
Interoperability platform and communication between the Information Systems of the suppliers of the AIS Barcelona Esquerr.
Table 3
Operational Committees of the AIS Barcelona Esquerra.
| Mental Health and Addictions | Locomotor Apparatus |
| Chronic Patient Care | Pain Clínic |
| Emergencies | Oncology and Haematology |
| Cardiology | Breast Cancer |
| General Surgery | Palliative Care |
| Vascular Surgery | Prevention and Community Health |
| Dermatology | Epidemiological Surveillance |
| Digestive | Sexually Transmitted Infections |
| Pneumology | Tropical Medicinal |
| Allergy | Ulcers |
| Neurology | Pharmacy |
| Endocrinology | Accessibility |
| Ophthalmology | Information Systems |
Table 4
Main activities of the Endocrinology Operational Committee.
|
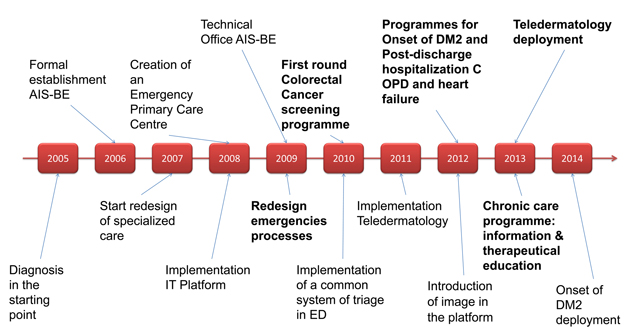
Figure 3
AIS-BE 2005–2016 10-year timeline key milestones.
Table 5
Evolution of Emergencies consultations in the Barcelona Esquerra AIS: Activity and complexity.
| A) Activity (Number of visits) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL 2008 | TOTAL 2009 | TOTAL 2010 | TOTAL 2011 | TOTAL 2012 | TOTAL 2012 – 2008 Value % | ||
| Hospital Clínic | 145,868 | 135,702 | 124,721 | 113,497 | 103,991 | –41,877 | –28.71% |
| H. Sagrat Cor | 12,623 | 13,742 | 15,461 | 16,693 | 18,914 | 6,291 | 49.84% |
| H. Plató | 7,953 | 9,207 | 9,847 | 12,299 | 12,964 | 5,011 | 63.01% |
| Total Hospitals | 166,444 | 158,651 | 150,029 | 142,489 | 135,869 | –30,575 | –18.37% |
| CUAP Manso | 43,067 | 59,177 | 60,090 | 63,634 | 53,867 | 10,800 | 25.08% |
| Global | 209,511 | 217,828 | 210,119 | 206,123 | 189,726 | –19,785 | –9.44% |
| B) Evolution of the complexity level of the emergencies dealt with in the Hospital Clínic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| % level 4 and 5 emergencies (low complexity) | 54% | 38% | 32% |
