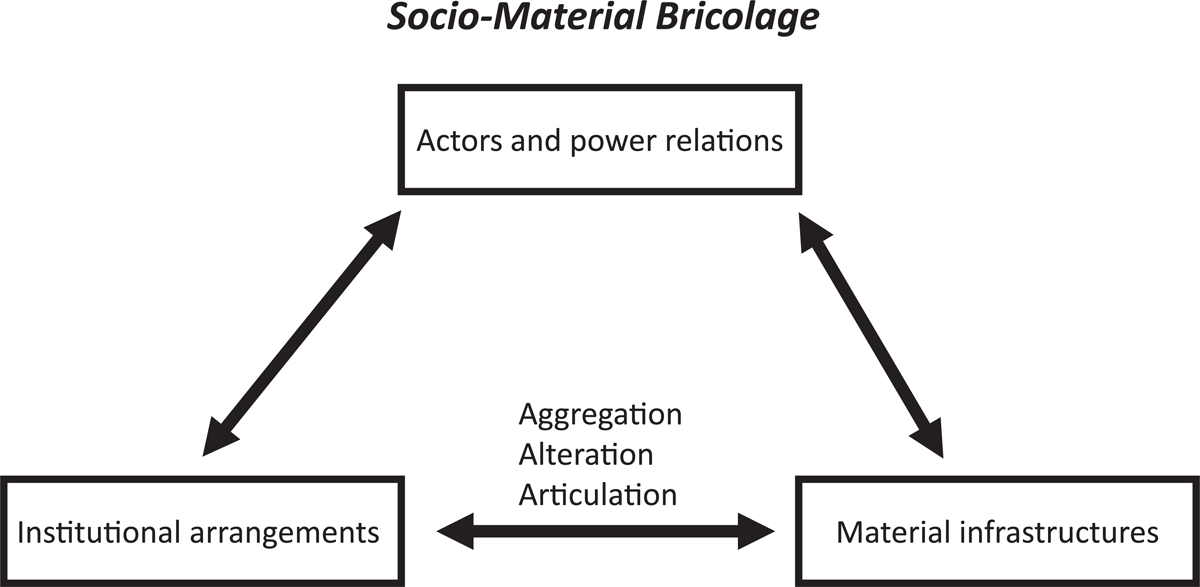
Figure 1
Conceptual framework of socio-material bricolage (Source: authors).
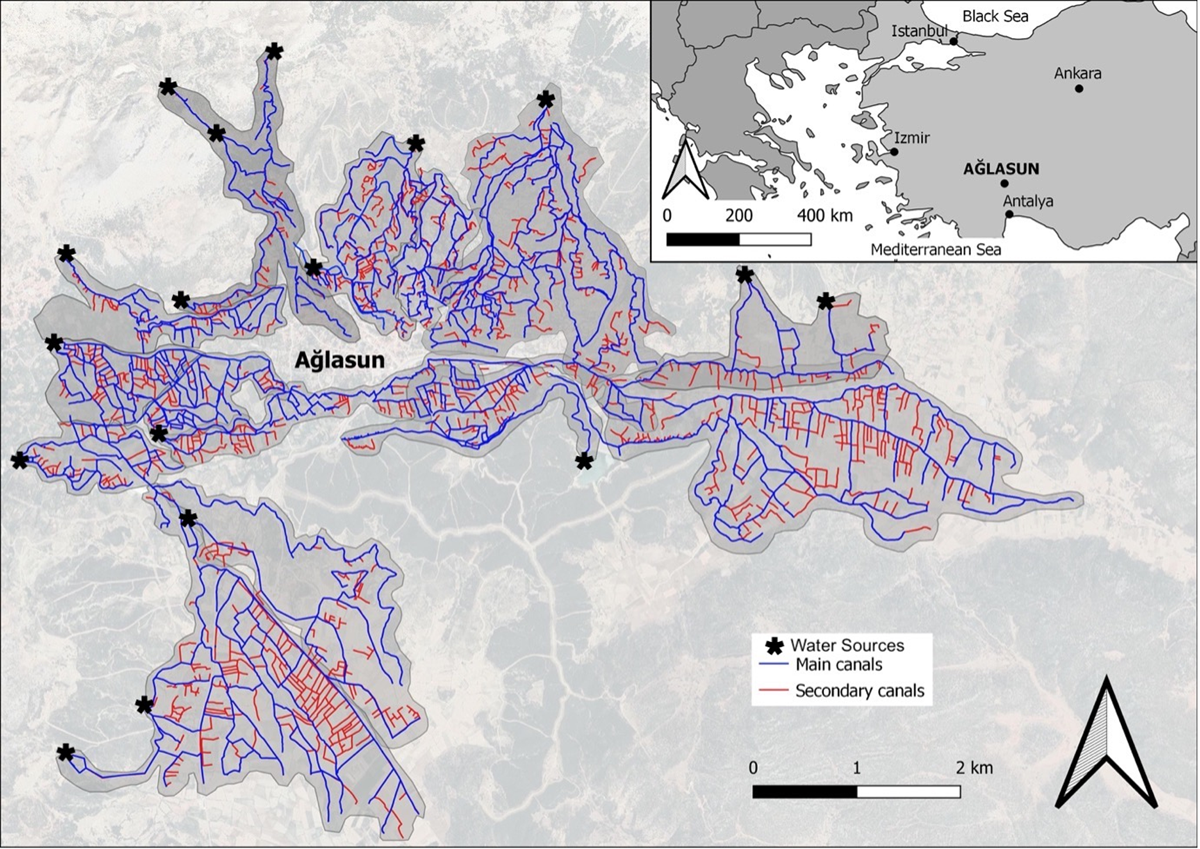
Figure 2
Map of the Ağlasun irrigation network (Source: Adnan Mirhanoğlu & Enrico Roets).3
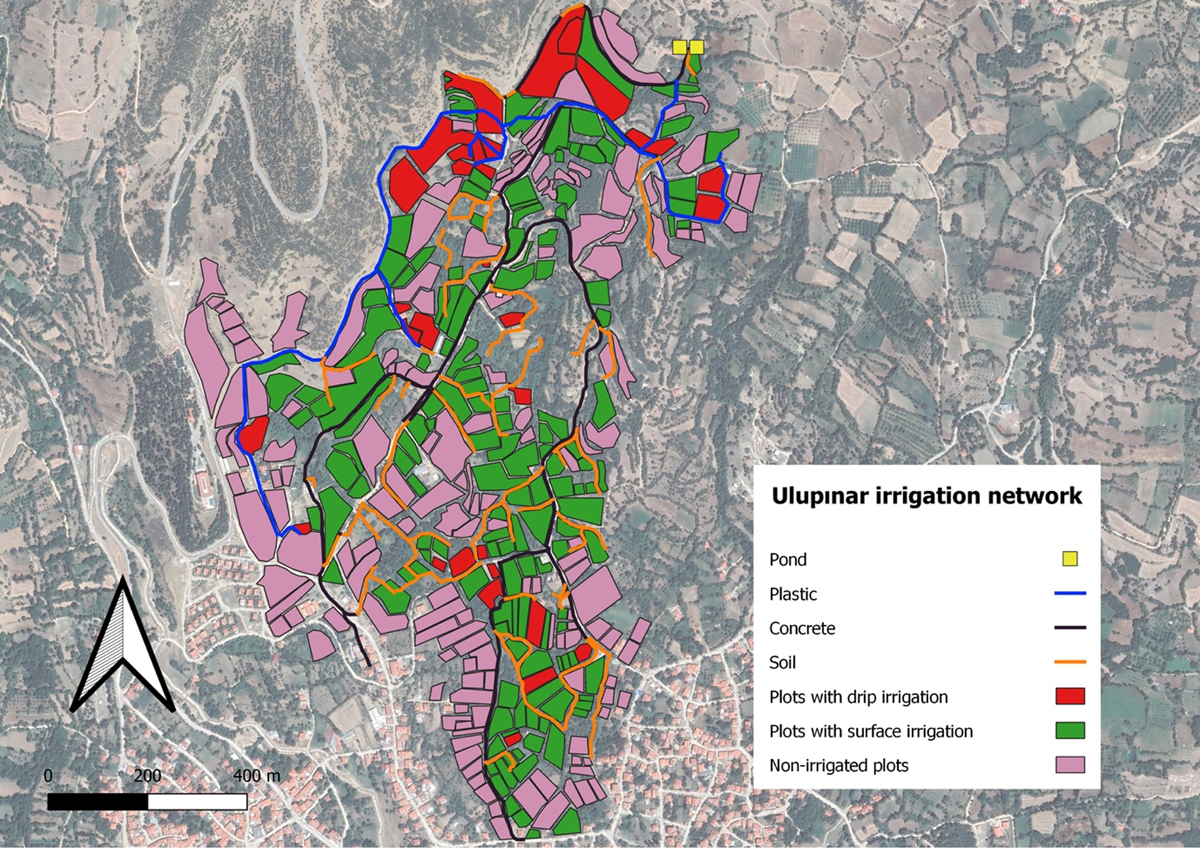
Figure 3
Map of the case study (Source: Adnan Mirhanoğlu & Enrico Roets).
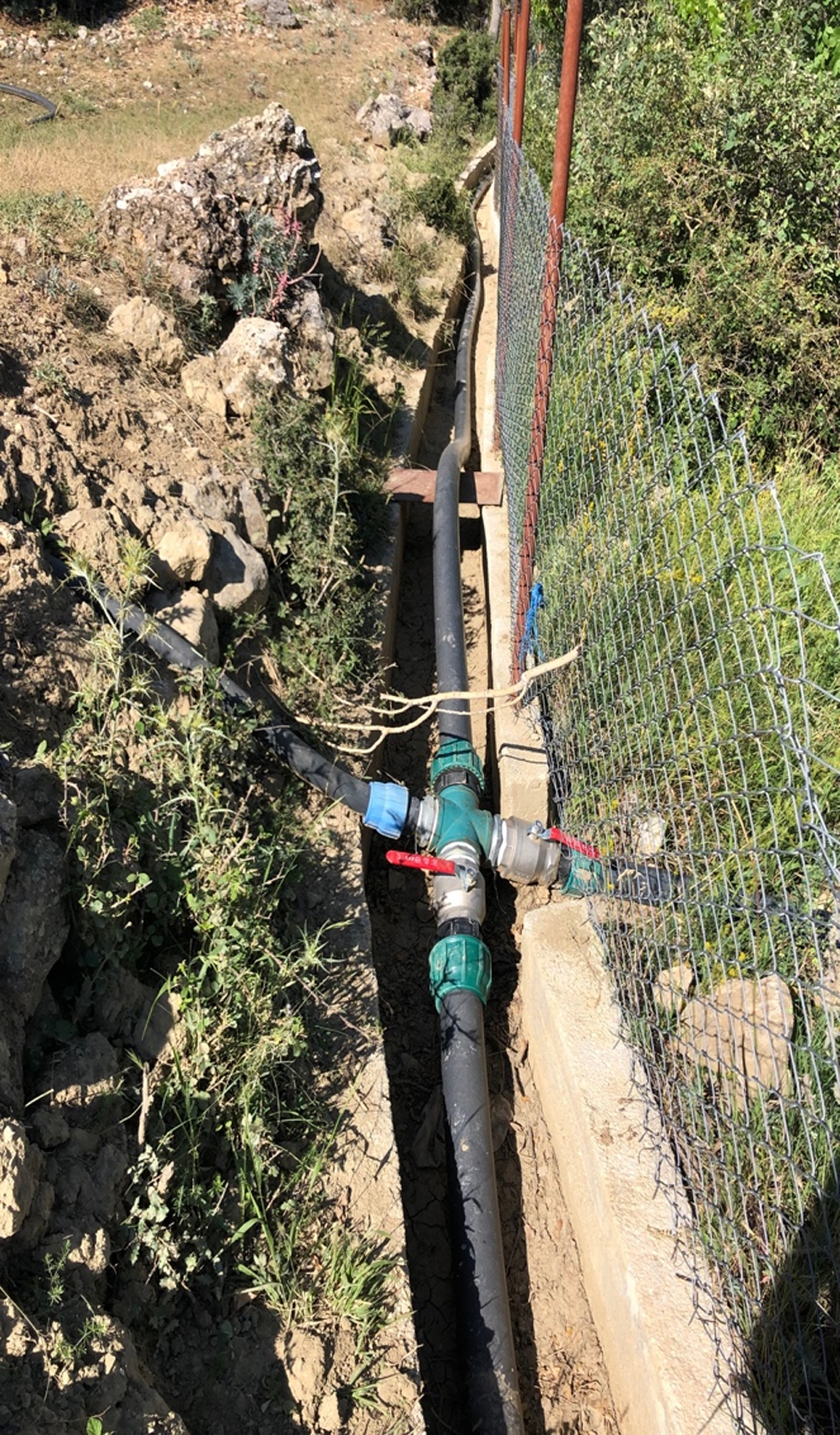

Figure 4
Most of the pressurized drip irrigation pipes were placed inside the existing main concrete canals.
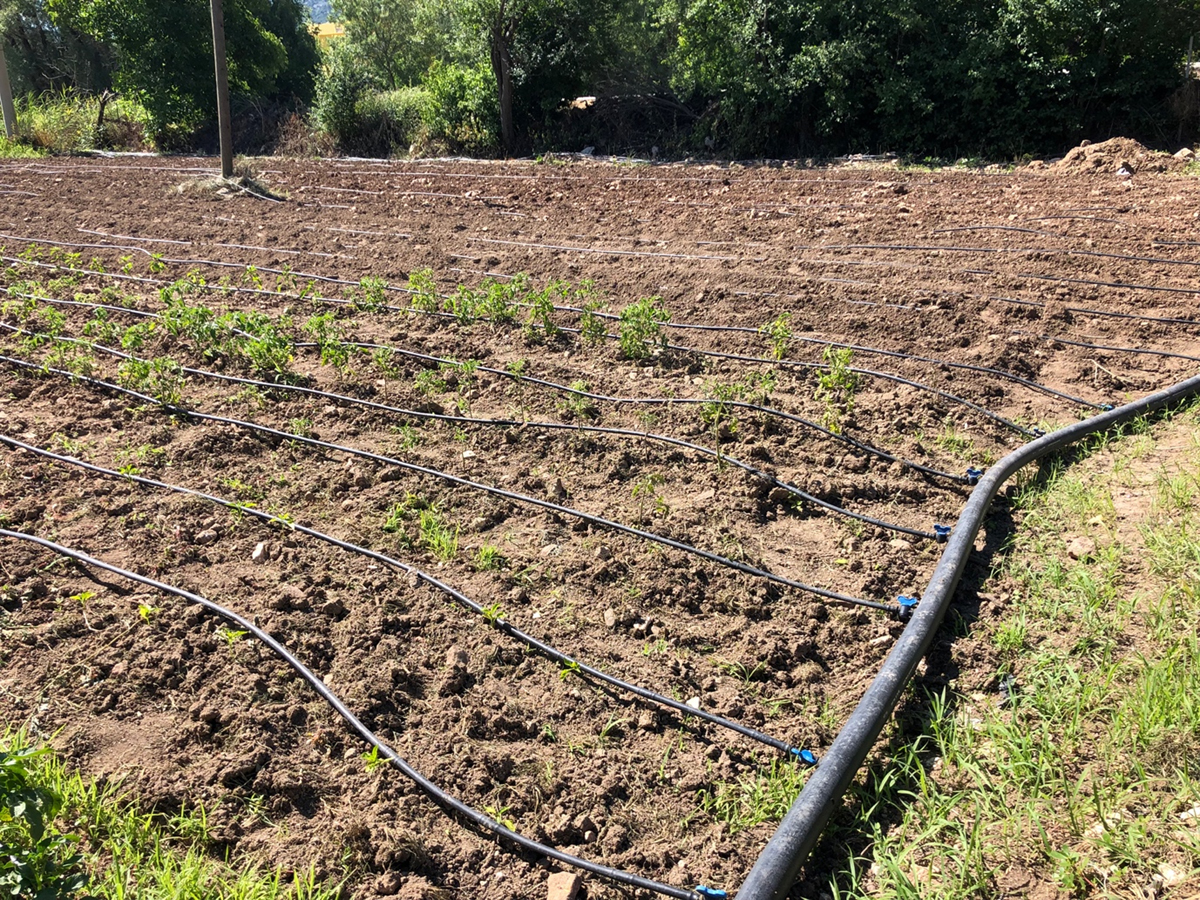

Figure 5
Farmers must redesign the irrigation infrastructure in their own field to switch to drip irrigation.
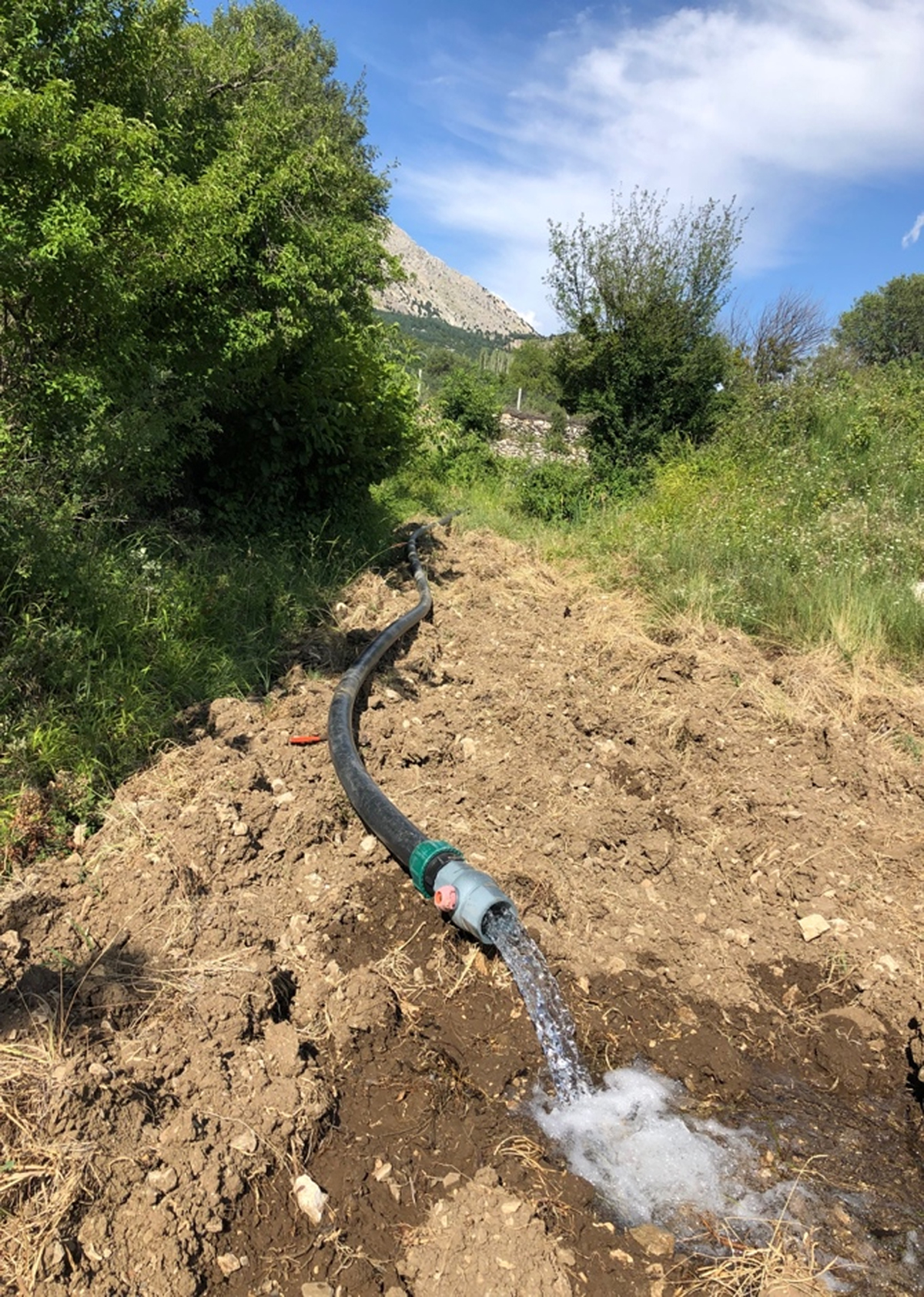

Figure 6
The farmers hesitating to switch to drip irrigation receive water via drip irrigation pipes but they continue surface irrigation.
Table 1
Levels and processes of socio-material bricolage in Ağlasun’s irrigation system.
| LEVEL | PROCESS | AGGREGATION | ALTERATION | ARTICULATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual | Infrastructural bricolage | Combination of drip irrigation infrastructure with surface irrigation at plot level (section 4.2) Redesigning irrigation infrastructure (building ponds) at plot level to switch to drip irrigation (section 4.2) | ||
| Livelihood (land/labour use) bricolage | Less supervision of drip irrigation allowing alternative income strategies combined with farming (section 4.2) | Switching to less-labour intensive crops after the introduction of drip irrigation (section 4.2) | Rejecting drip because the soil type is not suitable for it and the crops will not get enough water (section 4.2) | |
| Collective | Infrastructural bricolage | Adding pressurized pipes to an existing open canal network (section 4.1) | Pressurized pipes placed inside existing canals, which obtained a protective function rather than a waterbearing one (section 4.1) | Rejecting pressurized pipes to protect green areas along the main irrigation canal and to make water accessible for wild animals (section 4.1) |
| Formal institutional bricolage | The decentralization of the water distribution rules related to the priority use of water by drip irrigation users (section 4.4) | Shifting responsibility for the maintenance and cleaning of collective infrastructure from the users to the municipality (section 4.3) | Resistance against the priority use of water by drip irrigation users (section 4.4) | |
| Informal institutional bricolage | Increased power of water guard as farmers can no longer perform a visual check of the flow rate (section 4.4) Informal priority for drip-using social head-enders (section 4.4.) |
