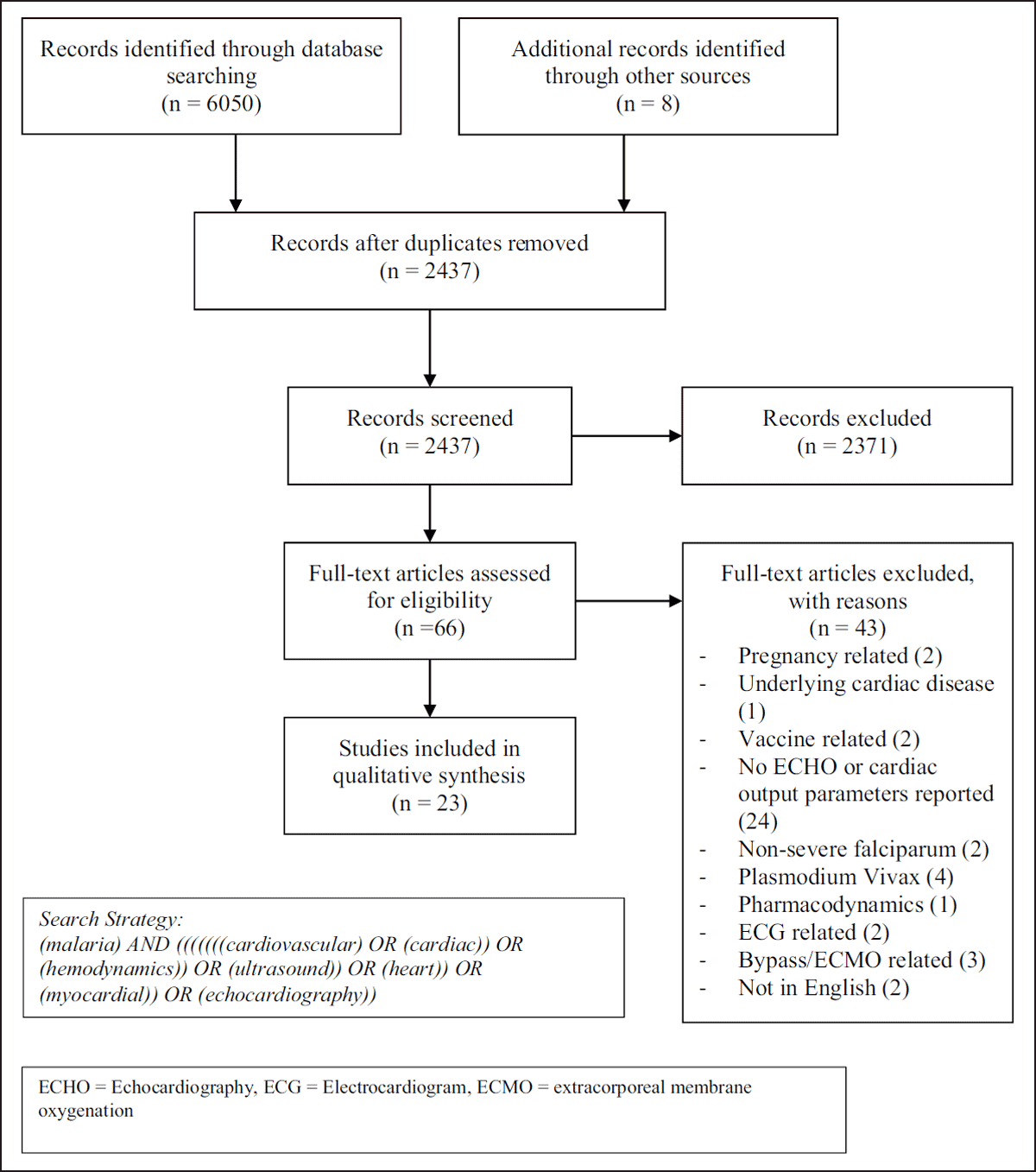
Figure 1
PRISMA Flow Diagram.
Table 1
Descriptive characteristics of all included trials.
| Trial | Type of Study | Location | Patient Population | No of participants | Study used to assess cardiac function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charoenpan (1990) [14] | Prospective Cohort | Thailand | Adult with SFM | 13 | Echo and PAC |
| Beards (1994) [15] | Case Report | South Africa | Adult with SFM undergoing exchange transfusion | 1 | PAC |
| Bruneel (1997) [16] | Retrospective study | France | Adult with SFM and shock | 14 | PAC |
| Lagudis (2000) [17] | Case Series | Brazil | Adult | 2 | PAC and ECHO |
| Saissy (2000) [18] | Prospective observational | Senegal | Adult with SFM | 29 (control group=systemic vascular resistance of 800 dyne s–1 cm–5 or higher. Hyperkinetic group with a level lower than this) | PAC |
| Mohsen (2001) [19] | Case Report | UK | Adult with SFM | 1 | Echo, cardiac biomarkers |
| Janka (2010) [20] | Prospective observational | Mali | Pediatric with SM and those without. 1–5yrs with SM (excluded if CM though) | 53 with SM | Echo, cardiac biomarkers |
| Yacoub (2010) [21] | Prospective observational as part of interventional trial | Kenya | Pediatric with severe malaria (>6m)–SM with metabolic acidosis, children without | 30 | Echo |
| Hanson (2011) [22] | Prospective observational | Bangladesh and India | Adult with SFM admitted to ICU | 28 (same cohort of patients as in Hanson 2013 paper below) | CVP and PiCCO, (Transpulmonary thermodilution) |
| Herr (2011) [23] | Prospective Case control | Germany | Adult, complicated and uncomplicated FM | 28 | Non-invasive method based on the re-breathing technique |
| Mocumbi (2011) [24] | Prospective observational | Mozambique | Pediatric, 5–15yrs with FM | 47, 10 with SM | Echo |
| Murphy (2011) [25] | Pilot observational | Uganda | Pediatric, SFM and non-severe | 17 with SM | Echo |
| Nguyen (2011) [26] | Retrospective analysis of prospectively collected hemodynamic data from interventional trials | Vietnam | Adults with SFM | 43 (managed with fluid loading or inotropes) | PAC |
| Sanklecha (2011) [27] | Case Series | India | Pediatric | 3 (cardiac involvement in one only) | Echo |
| Nguah (2012) [28] | Prospective observational | Ghana | Pediatric | 183 | Echo |
| Hanson (2013) [29] | Interventional | Bangladesh and India | Adult | 28 | PiCCO (transpulmonary thermodilution) |
| Nayak (2013) [30] | Prospective observational | India | Adult and Pediatric (13–75yr), severe vivax and SFM | 100 with SM, 28/100 with SFM. 9/28 had cardiac involvement | Echo |
| Sulaiman (2014) [31] | Case Report | Malaysia | Adult with SFM | 1 | Echo |
| Colomba (2017) [32] | Case Reports | Italy | Adults with SFM | 2 | Echo |
| Ray (2017) [33] | Prospective observational | India | Adult > 15 < 70yr with SFM | 23/27 SFM. 7 had circulatory failure | Echo |
| Kotlyar (2018) [34] | Prospective observational–comparison of SM and SMA | Uganda | Pediatric with SFM (3m–12yr) | 13 with SM | Echo and cardiac biomarkers (trop I and BNP) |
| Leopard (2018) [35] | Prospective observational–sepsis and SM | Bangladesh | > 12 years, SFM or sepsis | 102, 13 with SFM | Lung ultrasound |
| Kingston (2019) [36] | Prospective observational | Bangladesh and India | Adult with SFM or sepsis | 46 with SM | ECHO and Expired gas collection |
[i] SFM = Severe falciparum malaria, Echo = Echocardiogram, PAC = Pulmonary Arterial Catheter, CVP = Central Venous Pressure, PiCCO = Pulse Contour Cardiac Output, SMA = Severe Malaria Anemia.
Table 2
Selected clinical and cardiovascular findings in pediatric studies.
| Trial | Mean Age (months) | Mean Hb (dg/L) | Preload D0 | Cardiac Function | Structural | Pulmonary Artery Pressures mmHg | Cardiac Biomarkers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF D0 | CI (l/min/m2) DO | |||||||
| Janka (2010) [20] | 30.1 | 4.2 | – | 64% | – | – | 31 TRV = 2.5m/s (controls 2m/s) | CK-MB 4.31 ng/mL and Troponin T 10 pg/mL |
| Yacoub (2010) [21] | 46(median) | 7.5 (median) | IVC collapsibility index 43.8 LVEDD 3.17 | 63.1% | 4.6 Ultrasound Cardiac Output Monitor (USCOM) stroke volume index improved after fluid bolus in 80% of acidotic patients from an average of 36.7 mL/m2 (95% CI, 30.9–42.5) to 41.5 mL/m2 (95% CI, 37.19–45.8; p = .007) | – | – | – |
| Mocumbi (2011) [24] | 84 | 9.3 | – | “Preserved systolic and diastolic function” | ‘Left ventricular dimensions indexed for body surface were abnormal in two children with severe anemia’(4.4%) | – | – | cTNT undetectable |
| Murphy (2011) [25] | 36 | 7 | – | “Good” LV function | – | No pericardial effusions seen | 2 patients demonstrated a low-velocity, tricuspid, regurgitant jet (1.5 m/sec and 2.4 m/sec. 3 trace TR. Nil had RV enlargement | – |
| Sanklecha (2011) [27] | Case report of 3 patients with Myocarditis 24,120, 144 of age | 7.2 | – | – | Patient two only: Myocardial dysfunction with serial ejection fractions of 45%, 35% and 25% | – | – | – |
| Nguah (2012) [28] | 36 (median) | 7.4 | LV-EDDI (mm/m2) 53.15 | 66% | 5.8 | – | – | – |
| Kotlyar (2018) [34] | 19.2 (median) | 5.12 | 58% | 6.4 (T0 all), SM 5.28 T0, SMA 6.89 T0 | – | – | Trop I 0.08 (ng/mL) BNP 69.1 (pg/mL) | |
[i] Data presented as means unless otherwise indicated.
Blank = no value given, HR = heart rate, MAP = mean arterial pressure, SMA = severe malaria anemia, LVEF = Left ventricular ejection fraction, CI = Cardiac Index, TRV= Tricuspid regurgitant velocity, LV-EDDI = left ventricular end diastolic diameter index, cTNT = Cardiac Troponin.
Table 3
Adult echocardiogram findings of myocarditis, pericarditis or myocardial ischemia.
| Trial | Proposed SM induced cardiac diagnosis | Age (years) | Hemoglobin g/dL | Dimensions | EF % | Structural | Pulmonary artery pressures mmHg | Cardiac Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohsen (2001) [19] | Myocarditis | 30 | 11.2 | – | D0 admission echo normal. Cardiac Output was supra-normal at 11l/min. Echo on d10 demonstrated severe global left ventricular dysfunction with no regional wall abnormalities (EF 38%) | Normal RAP and PWP (12–18mmHg) | Normal creatinine phosphokinase | |
| Nayak (2013) [30] | – | 13–75years | – | (LVEDD) of 4.04 (LVESD) of 2.55 | 56% with cardiac involvement (59% without cardiac involvement) | 9 patients had mitral regurgitation, mild tricuspid regurgitation, mild aortic regurgitation and mild pulmonary regurgitation; these findings were present at the time of admission, on the day of discharge as well as on Day 21 of follow up. None of these patients had any valvular thickening. No patient had any evidence of pericardial effusion and regional or global hypokinesia | Both Troponin-I and CPK-MB were increased in 14% cases and were found normal in 3 out of 17 patients who presented with cardiovascular involvement | |
| Sulaiman (2014) [31] | Myocardial Ischemia | 51 | 10.7 | – | Hyperdynamic contractility with preserved LV systolic function | Normal (and normal coronary angiography) | ||
| Colomba (2017) [32] | Pericarditis | 19 and 52 | 8.2/8.6 | – | Pt 1. Revealed an anterior non-compressive pericardial effusion (6 mm behind the right atrium, 9 mm in lateral) and a congenital intra-atrial and intra-ventricular communication with left-to-right shunt Pt 2. Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy with preserved global systolic function, absence of any segmental wall-motion abnormalities of the left ventricle; right sections were of normal size with preserved right ventricular function. It also showed pericardial effusion | - | ||
| Ray (2017) [33] | – | – | – | <55% in 3, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in 1 | mild pericardial effusion (1) | mild TR with mild PAH (1) | – | |
| Leopard (2018) [35] | – | 33 | LVFS % 41 IVC collapsibility % 18 Uncomplicated 31% LVFS 26% IVCC Sepsis 31% LVFS 26% IVCC (all medians) | – | – |
[i] Data presented as means unless otherwise indicated.
Blank = no value given, LVEF = Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction, LVEDD = Left Ventricular End Diastolic Diameter, LVESD = Left Ventricular End Systolic Dysfunction, TR = Tricuspid Regurgitation, PAH = Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
Table 4
Adult invasive cardiac output monitoring findings.
| Trial | Invasive Monitoring | Preload: CVP | Cardiac Index (L/min/m2) | SVR (dyne/s/cm–5m2) | PAOP mmHg | Cardiac Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charoenpan (1990) [14] | PAC | – | 4.66 | 832 reported as low as (normal values 900–1100 in paper) low PVR | – | – |
| Beards (1994) [15] | PAC | 12 (prior to exchange) | 4.42 | 586 | – | – |
| Bruneel (1997) [16] | PAC–7 patients only | – | – | Peripheral vasodilatation with elevated cardiac output | – | – |
| Lagudis (2000) [17] | PAC – hyperdynamic pattern and normal LV stroke work index | Normal echo | 1st patient 6 2nd patient 4.3 | SVRI 1st patient 1049 2nd patient 1078 | 1st patient 17 2nd patient 15 | – |
| Saissy (2000) [18] | PAC | 3.9 control group 6.1 hyperkinetic group | 1098 control group 536 hyperkinetic group | 6 control group 9 hyperkinetic group | – | |
| Hanson (2011) [22] | CVP and PiCCO | 5.2 (median) | 3.08 (median) | SVRI 2155 (median) | – | – |
| Herr (2011) [23] | Non-invasive method based on the re-breathing technique | - | 2.9 9SM cases (healthy controls 3.4) (median) | SVRI 29.2 l/min (median) | – | Pro-BNP 139.3 pg/ml Myoglobin 43.6 μg/l Trop T and CK-MB similar to controls H-FABP 1.9ng/ml (1.7 in uncomplicated) |
| Nguyen (2011) [26] | PAC | 2 fluid load, 4.5 no fluid load | 4 (with and without fluid load) | 1633/without fluid 1589 | 6 fluid load/10 no fluid loading | – |
| Hanson (2013) [29] | PiCCO | 4.5 (median) | 3.08 (median) | 2155 (median) | – | – |
| Kingston (2019) [36] | ECHO and Expired gas collection | – | 4.1 (median) | – | – | – |
[i] Data presented as means unless otherwise indicated.
SFM = Severe falciparum malaria, Echo = Echocardiogram, PAC = Pulmonary Arterial Catheter, CVP = Central Venous Pressure, PAOP = Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure, PiCCO = Pulse Contour Cardiac Output, SMA = Severe Malaria Anemia, SVR = Systemic Vascular Resistance, SVRI = Systemic Vascular Resistance Index, DO2 = Oxygen delivery, VO2= Oxygen consumption. NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; CK-MB = creatine kinase-muscle brain; TnT = troponin T; H-FABP = heart-type fatty acid-binding.
