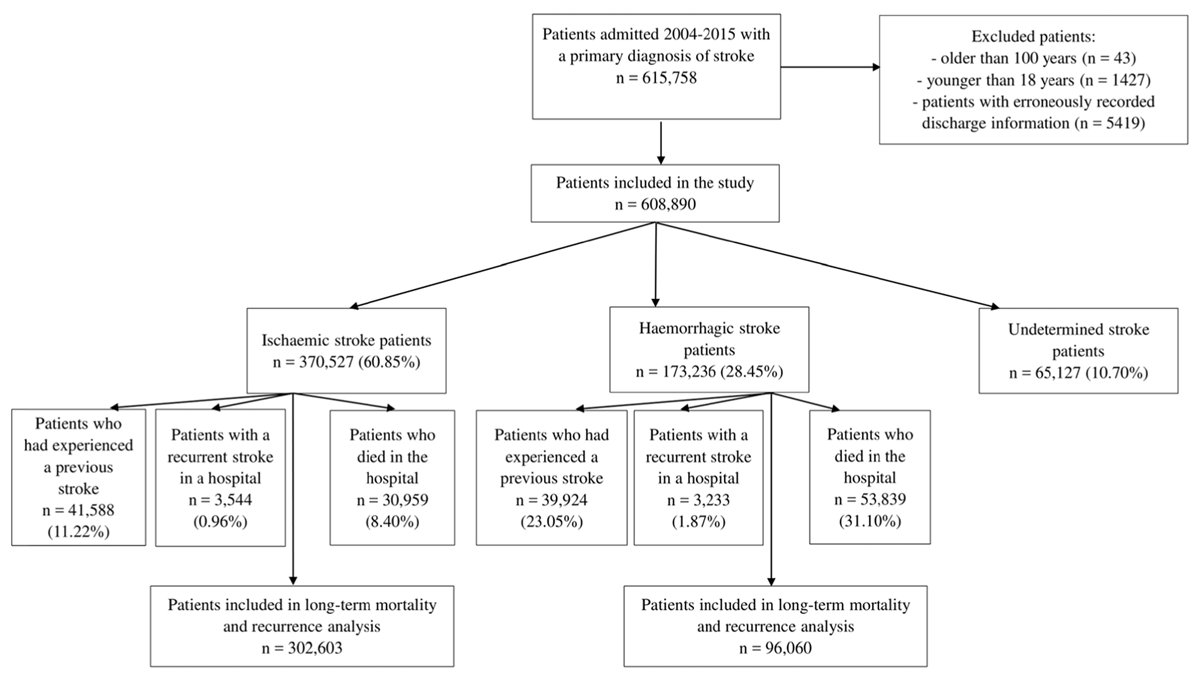
Figure 1
Patient population flowchart. Patients may be classified in one or more exclusion groups and thus the total number of excluded patients does not equal the sum across individual groups.
Table 1
Characteristics of hospitalized ischaemic stroke patients in Thailand.
| Variable | No diabetes mellitus (295,093) | Diabetes mellitus (75,434) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± Standard Deviation | 65.8 ± 13.7 | 64.6 ± 11.3 | <0.001 |
| Length of Stay, median (interquartile range) | 3 (2–6) | 4 (2–7) | <0.001 |
| Post-discharge mortality, N (%) | 110,800 (37.5) | 30,657 (40.6) | <0.001 |
| Recurrent strokes, N (%) | 27,353 (9.3) | 8141 (10.8) | <0.001 |
| Female, N (%) | 129,152 (43.8) | 43,648 (57.9) | <0.001 |
| Male, N (%) | 165,941 (56.2) | 31,786 (42.1) | |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 121,183 (41.1) | 55,061 (73.0) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure, N (%) | 8793 (3.0) | 2729 (3.6) | <0.001 |
| Atrial Fibrillation, N (%) | 28,436 (9.6) | 5034 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| Anaemia, N (%) | 17,361 (5.9) | 6934 (9.2) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidaemia, N (%) | 80,909 (27.4) | 34,303 (45.5) | <0.001 |
| Rheumatic Valve Disease, N (%) | 994 (0.3) | 79 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Ischaemic Heart Disease, N (%) | 9606 (3.3) | 4451 (5.9) | <0.001 |
| Arrhythmia, N (%) | 31,402 (10.6) | 5684 (7.5) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, N (%) | 14,109 (4.8) | 8607 (11.4) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease, N (%) | 2983 (1.0) | 836 (1.1) | 0.018 |
| Epilepsy, N (%) | 3731 (1.3) | 862 (1.1) | 0.007 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, N (%) | 6530 (2.2) | 889 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Pneumonia, N (%) | 25,679 (8.7) | 7039 (9.3) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis, N (%) | 7819 (2.6) | 3058 (4.1) | <0.001 |
| Urinary tract infection, N (%) | 986 (0.3) | 407 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular events, N (%) | 30,861 (10.5) | 9380 (12.4) | <0.001 |
| Acute Kidney Injury, N (%) | 9754 (3.3) | 4241 (5.6) | <0.001 |
| Death, N (%) | 24,266 (8.2) | 6693 (8.9) | <0.001 |
Table 2
Characteristics of hospitalized haemorrhagic stroke patients in Thailand.
| Variable | No diabetes mellitus (156,319) | Diabetes mellitus (16,917) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± Standard Deviation | 61 ± 14.5 | 62.3 ± 11.8 | <0.001 |
| Length of Stay, median (interquartile range) | 5 (2–11) | 6 (2–14) | <0.001 |
| Post-discharge mortality, N (%) | 50,232 (32.1) | 5893 (34.8) | <0.001 |
| Recurrent strokes, N (%) | 8328 (5.3) | 936 (5.53) | 0.26 |
| Female, N (%) | 60,693 (38.8) | 9135 (54.0) | <0.001 |
| Male, N (%) | 95,626 (61.2) | 7782 (46.0) | |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 80,837 (51.7) | 14,007 (82.8) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure, N (%) | 1926 (1.2) | 538 (3.2) | <0.001 |
| Atrial Fibrillation, N (%) | 2882 (1.8) | 544 (3.2) | <0.001 |
| Anaemia, N (%) | 12,069 (7.7) | 2478 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidaemia, N (%) | 11,417 (7.3) | 4070 (24.1) | <0.001 |
| Rheumatic Valve Disease, N (%) | 132 (0.1) | 17 (0.1) | 0.499 |
| Ischaemic Heart Disease, N (%) | 1851 (1.2) | 689 (4.07) | <0.001 |
| Arrhythmia, N (%) | 3863 (2.5) | 706 (4.2) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, N (%) | 4976 (3.2) | 2229 (13.2) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease, N (%) | 2896 (1.9) | 315 (1.9) | 0.93 |
| Epilepsy, N (%) | 1669 (1.1) | 207 (1.2) | 0.06 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, N (%) | 2067 (1.3) | 166 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| Pneumonia, N (%) | 19,685 (12.6) | 2865 (16.9) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis, N (%) | 5049 (3.2) | 1024 (6.1) | <0.001 |
| Urinary tract infection, N (%) | 375 (0.2) | 76 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular events, N (%) | 11,249 (7.2) | 1406 (8.3) | <0.001 |
| Acute Kidney Injury, N (%) | 4084 (2.6) | 1065 (6.3) | <0.001 |
| Death, N (%) | 48,520 (31.0) | 5319 (31.44) | 0.28 |
Table 3
Odds ratios with 99% confidence intervals of developing different stroke complications in patients with diabetes mellitus in ischaemic, haemorrhagic and undetermined stroke patients in Thailand.
| Ischaemic Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus vs. no diabetes mellitus | ||
| Complication | Odds Ratio (99% Confidence Intervals) | p-value |
| Pneumonia | 1.19 (1.15, 1.24) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 1.57 (1.47, 1.67) | <0.001 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1.34 (1.13, 1.57) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular events | 1.21 (1.16, 1.25) | <0.001 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 1.53 (1.45, 1.62) | <0.001 |
| In-hospital death | 1.13 (1.08, 1.18) | <0.001 |
| Haemorrhagic stroke | ||
| Diabetes mellitus vs. no diabetes mellitus | ||
| Complication | Odds Ratio (99% Confidence Intervals) | p-value |
| Pneumonia | 1.15 (1.08, 1.23) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 1.55 (1.40, 1.72) | <0.001 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1.25 (0.88, 1.76) | 0.099 |
| Cardiovascular events | 1.14 (1.05, 1.24) | <0.001 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 1.78 (1.60, 1.97) | <0.001 |
| In-hospital death | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) | <0.001 |
| Undetermined stroke | ||
| Diabetes mellitus vs. no diabetes mellitus | ||
| Complication | Odds Ratio (99% Confidence Intervals) | p-value |
| Pneumonia | 1.24 (1.10, 1.41) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 1.43 (1.18, 1.73) | <0.001 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1.54 (0.99, 2.42) | 0.013 |
| Cardiovascular events | 1.16 (0.87, 1.54) | 0.186 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 1.41 (1.18, 1.68) | <0.001 |
| In-hospital death | 0.93 (0.81, 1.06) | 0.13 |
Table 4
Death and recurrent stroke events and Hazard Ratios with 99% confidence intervals in ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke patients with diabetes mellitus.
| Ischaemic stroke | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus | No diabetes mellitus | ||
| Events (%) | Hazard Ratio (99% Confidence Intervals) | Events (%) | |
| Death | 29,135 (44.3%) | † | 99,715 (42.1%) |
| Recurrent stroke | 7679 (11.7%) | 1.52 (1.26, 1.84) | 23,539 (9.9%) |
| Haemorrhagic stroke | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | No diabetes mellitus | ||
| Events (%) | Hazard Ratio (99% Confidence Intervals) | Events (%) | |
| Death | 4841 (50.1%) | † | 40,495 (46.9%) |
| Recurrent stroke | 758 (7.8%) | † | 6546 (7.6%) |
[i] † Proportional hazards assumption not met (see Figure 2).
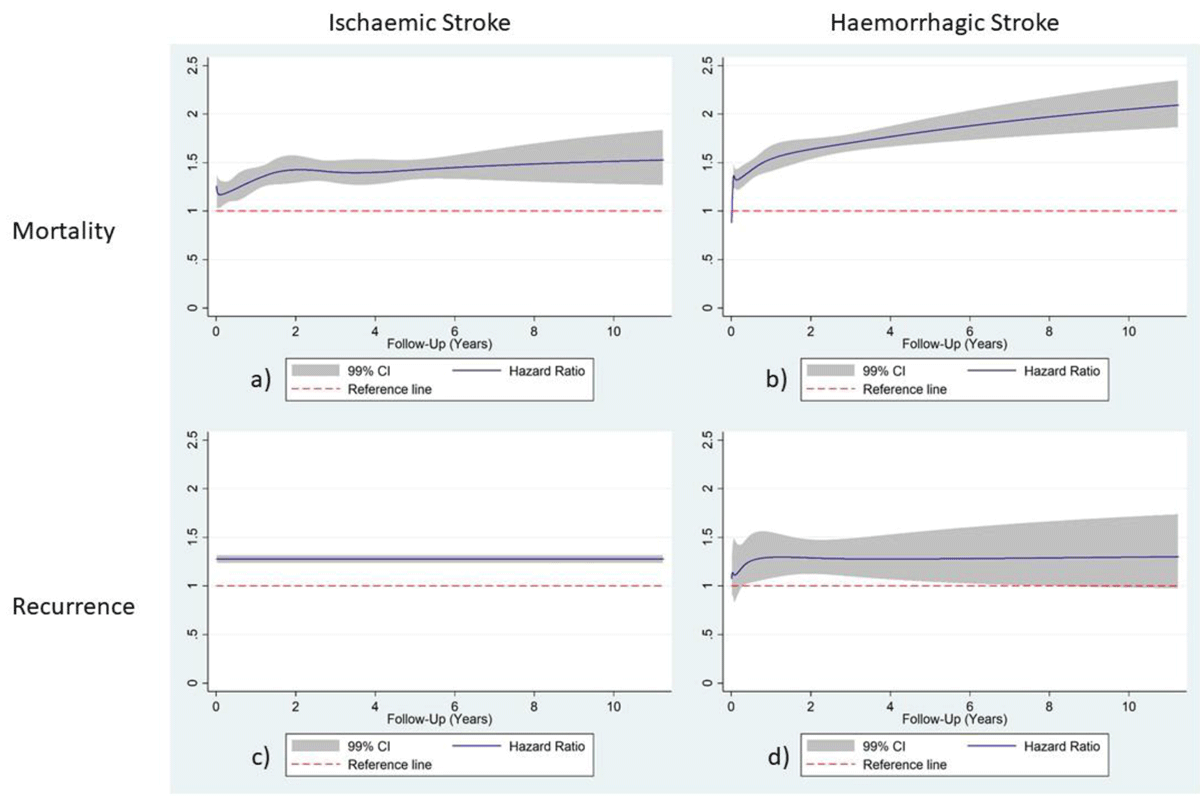
Figure 2
Hazard Ratio functions have been plotted against post-discharge follow-up time (days) using RCS modelling with 99% confidence intervals for mortality in ischaemic stroke diabetes mellitus patients (a), mortality in haemorrhagic stroke diabetes mellitus patients (b), recurrence in ischaemic stroke patients (c) and recurrence in haemorrhagic stroke diabetes mellitus patients (d) in Thailand; patients without diabetes were used as a reference category.
