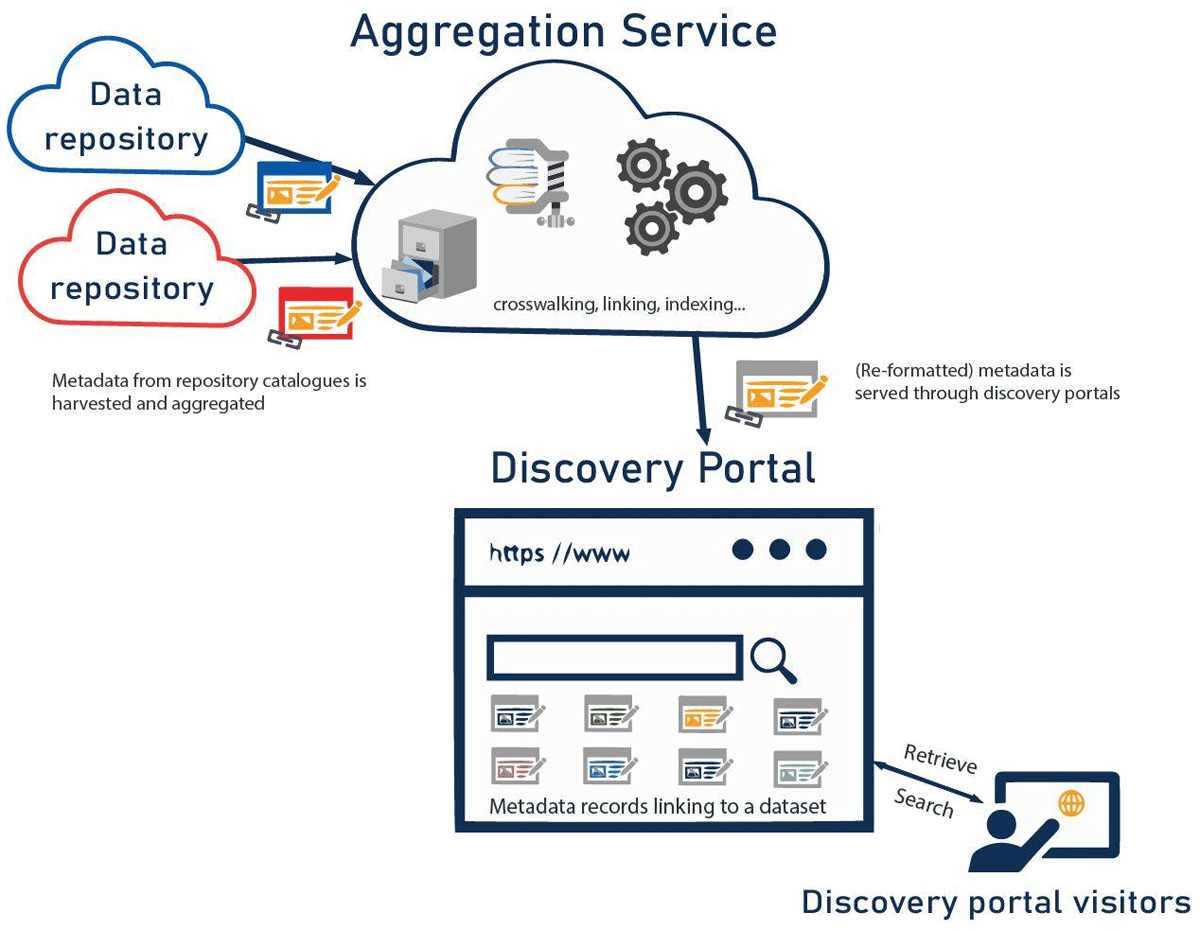
Figure 1
The metadata harvesting process. Standardized metadata is harvested from repository catalogues, then processed by an aggregation service. The service disseminates the metadata records through a search and discovery portal and/or by serving it to further aggregation services for distribution.
Table 1
HMetS-WG participants, with WDS membership type and host institutions.
| WDS MEMBER | TYPE | HOST INSTITUTION(S) |
|---|---|---|
| Centre de Données Astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS) | Regular | Strasbourg Astronomical Observatory (ObAS); University of Strasbourg; French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) |
| Global Change Research Data Publishing and Repository (GCdataPR) | Regular | Institute of Geographical Sciences and Natural Resources Research (IGSNRR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); Geographical Society of China |
| International Real-time Magnetic Observatory Network (INTERMAGNET) | Network | Multiple institutions (worldwide) |
| International Service of Geomagnetic Indices (ISGI) | Regular | School and Observatory of Earth Sciences (EOST); University of Strasbourg; French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) |
| International GNSS Service (IGS) | Network | Multiple institutions |
| National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC) | Regular | National Space Science Center (NSSC), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) |
| Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC) | Regular | Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN), Columbia University; Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) |
| World Data Center for Geomagnetism (Edinburgh) | Regular | British Geological Survey (BGS) |
| World Data Centre for Renewable Resources and Environment (WDC-RRE) | Regular | IGSNRR; CAS |
Table 2
Subject areas represented by repositories and target users groups. Subject areas were provided to WDS-ITO by the repositories.
| REPOSITORY | SUBJECT AREAS | USER GROUPS |
|---|---|---|
| GCdataPR | Agriculture, Area studies, Earth sciences, Economics, Environmental studies, forestry, Geo-ecosystems Geography, and History | Global change students, researchers policy makers and society in China and worldwide |
| IGS | Earth sciences, Geodesy, GNSS, GPS, Precise positioning, Navigation, Timing, and Space sciences | Mainly IGS staff, project and working group participants. More broadly: worldwide users of modern mapping, orientation and navigation systems, enterprises, non-profits, institutions and government actors |
| INTERMAGNET | Earth sciences, Geomagnetism, Space sciences | Scientific community, geomagnetism community, members of IAGA,1415 commercial users |
| ISGI | Solar-Terrestrial physics, Space weather-Space Climate, Space sciences, Earth sciences, Geomagnetism | Academia (including behavioral biology), members of IAGA communities, private and public sectors (military, telecommunications, satellite operators) |
| NSSDC | Astronomy, Computer sciences, Planetary science, Space physics, Space sciences, Space weather | Typical users are Chinese and international researchers in subject areas |
| SEDAC | Agriculture, Architecture and design, Anthropology, Area studies, Business, Chemistry, Climate science, Computer sciences, Cultural and ethnic studies, Earth sciences, Economics, Engineering, Environmental science, Environmental and forestry studies, Geography, Health sciences, Information system science, Political science, Sociology, Statistics, Sustainability science, Systems science, Transportation | User community interested in studying human interactions in the environment |
| WDC-RRE | Earth sciences, Ecology, Environmental studies and forestry, Geography, Geoinformatics, Natural resources | Mainly academic researchers and students, also scientific staff and technicians, general public, government agencies, policy makers, and international organizations |
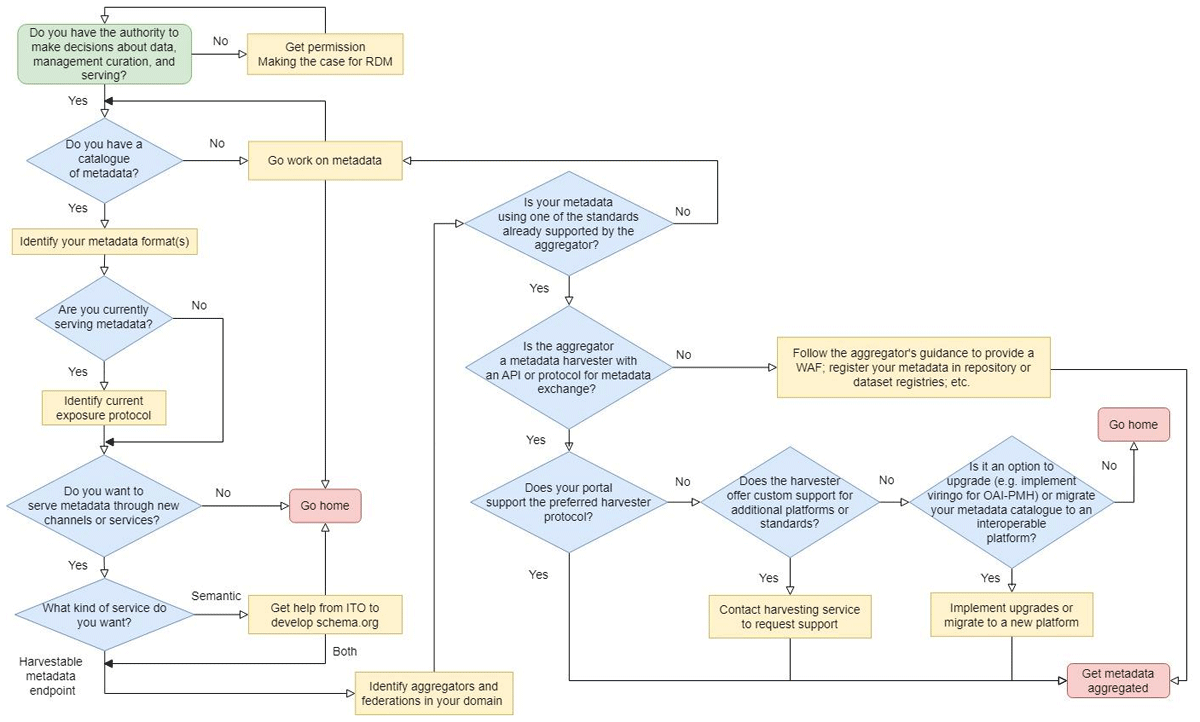
Figure 2
Flow-chart diagram of a typical harvestable metadata services implementation (Payne, Urquidi Diaz & Li 2021). This diagram gives a schematic representation of the steps involved in creating a harvestable metadata service. The HMetS-WG used these steps to scaffold the group’s initial work.
Table 3
Use Case Infrastructures: Summary of Features.
| REPOSITORY | REPOSITORY PLATFORM & CATALOGUE | METADATA STANDARDS | METADATA SERVICE PROTOCOLS | KNOWN AGGREGATORS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCdataPR | Custom GCdataPR 2.0 | DCI16, DataCite | OpenSearch | CrossRef, China-GEOSS, CNKI, DCI, CSTR, ScienceEngine |
| IGS | Catalogue via NASA CMR
| DIF 10, ECHO 10, ISO 19115-2:2009 (MENDS and SMAP dialects), UMM-C | CMR CSW, CMR public APIs, OpenSearch | via NASA’s CMR |
| INTERMAGNET | Custom repository, with some datasets on GFZ Potsdam data repository | Via INTERMAGNET: IAGA2002, CDF; Via GFZ: GeoJSON, DataCite, ISO 19115 | Via homepage: HTTP, FTP; Via GFZ: request to DataCite’s API | DataCite, FIDGEO17 |
| ISGI | Custom
| IAGA2002
| Via homepage: HTTPS; request to DataCite’s API | |
| NSSDC | Custom | NSSDC Core Metadata Specification, SPASE
| OpenSearch, OGC-CSW (via WDS China), Data search platform,
| National Science and Technology Data Sharing Network of China, Scientific Data Center, CAS |
| SEDAC | Vital Digital Asset Mgt. System (Fedora)
| FGDC CSDGM, ISO 19115, DataCite | IDN OGC CSW, NASA CMR CSW, CMR public APIs, OpenSearch | DataCite, GEOSS (via EOSDIS/CMR) |
| WDC-RRE | Custom: Debian OS, OSS NGNIX, PostgreSQL, TorCMS | Dublin Core, ISO 19115, custom Data Identification and Metadata Standards
| OpenSearch, OGC-CSW 3.0.0, OAI-PMH 2.0, SRU 1.1.,
| WDS-China, CNKI |
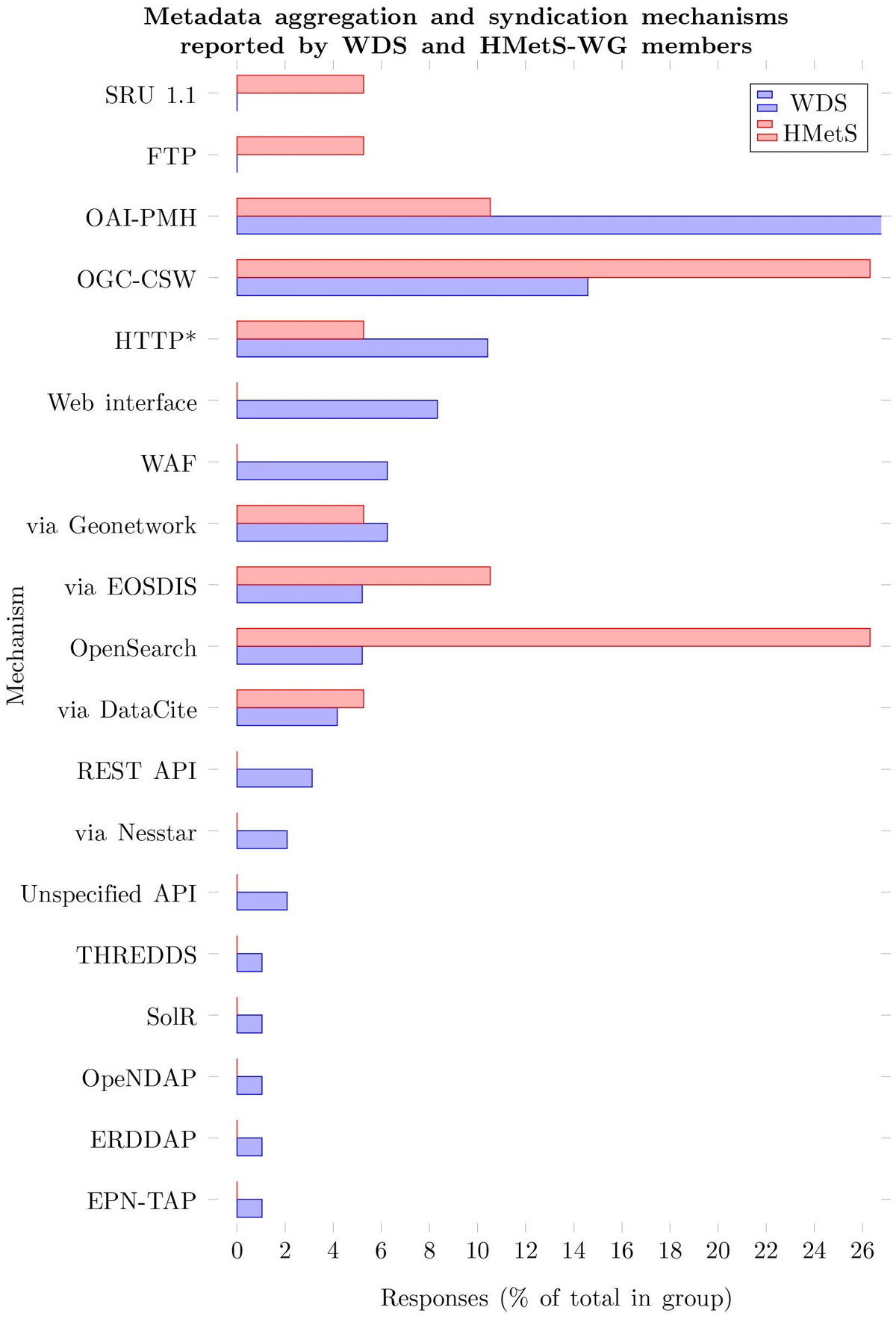
Figure 3
This bar chart compares the mechanisms for metadata exposure (aggregation, discovery, etc.) that were reported by the HMetS-WG repositories with those reported by the WDS repositories in a 2019 member survey (Payne & Urquidi Diaz 2020: 11, 15). Since some repositories reported serving their metadata via third-party services, these services also have been included (e.g. DataCite, EOSDIS, etc.). *Includes schema.org.
