Table 1
Basic details for the iPhone and Samsung smartphone sensor systems.
| iPhone 6S | Samsung | |
|---|---|---|
| Release Date | September 9, 2015 | Note 5: August 13, 2015 |
| Galaxy 8s: April 21, 2017 | ||
| Phones in circulation | 773 million (ca 2015) | Note 5: 11 million (ca 2017) |
| Galaxy 8s: Over 20 million | ||
| Operating System | iOS 11.2.5 (2018 release) | Note 5: Android v5.1.1 (Lollipop) |
| Galaxy 8S: Android 8.8.0 | ||
| Camera | 12.2 megapixel f/2.2 | Note 5: 16 megapixel f/1.9 |
| Galaxy 8s: 12.2 megapixel f/1.7 | ||
| Magnetometer | Alps Electric HSCDTD007 | Note 5: Asahi Kasei AK09911C |
| Galaxy 8s: AKM: AK09916C | ||
| Camera array | Sony iSight 1.22 mm pixels A = 18 mm2 | Note 5: SonyExmor RS-IMX240 1.2 mm pixels A = 23 mm2 |
| Galaxy 8s: LSI S5K2L2 or Sony IMX333, 1.4 mm pixels. A = 24 mm2 | ||
| Light Sensor | AMS #TSL2586 | Note 5: AMS TMD4903 |
| Galaxy 8s: AMS #TMD4906 |
Table 2
Representative environmental radiation dosages with smartphone back cameras.
| Source | Mazur | Radiation Counter | Smart Geiger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor table top | 36 CPM, 0.12 mSv/h | 2.1 CPM, 0.07 mSv/h | 1.0 CPM, 0.05 mSv/h |
| Outdoor back yard | 49 CPM, 0.14 mSv/h | 1.6 CPM, 1.5 mSv/h | 0.1 CPM, 0.05 mSv/h |
| Airport indoors | 32 CPM, 0.13 mSv/h | 1.3 CPM, 0.06 mSv/h | 0 CPM, 0.05 mSv/h |
| 26,000-foot altitude | 100 CPM, 1.3 mSv/h | 2.2 CPM, 0.08 mSv/h | 6 CPM, 0.54 mSv/h |
| Granite counter top | 100 CPM, 0.28 mSv/h | 3.8 CPM, 0.07 mSv/h | 1.5 CPM, 0.12 mSv/h |
| 30,000-foot altitude | 745 CPM, 2.4 mSv/h | 6.0 CPM, 5.0 mSv/h | 80 CPM, 2.0 mSv/h |
Table 3
Flight measurements and platform comparisons with the back camera.
| Altitude | Mazur | iPhone | Samsung | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPM | μSv/hr | CPM | μSv/hr | CPM | μSv/hr | |
| 0 – SFO | 30 ± 5 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 8.0 ± 1.0 | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| 0 – ORD | 35 ± 5 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 3.0 ± 0.5 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 19.3 ± 2.0 | 0.5 ± 0.05 |
| 31,000 (ORD-SFO) | 730 ± 100 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 0.08 ± 0.03 |
| 31,000 (SFO-ORD) | 745 ± 25 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.2 | 8.1 ± 1.0 | 28.0 ± 5.0 | 1.0 ± 0.3 |
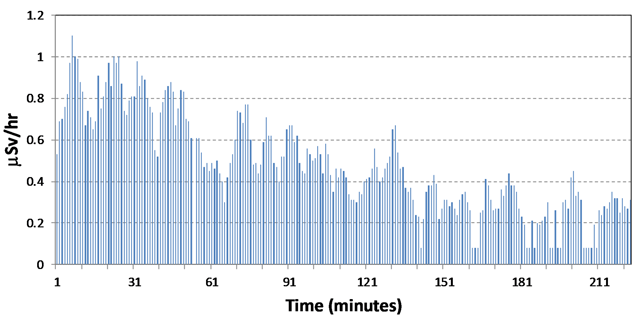
Figure 1
Radiation measurements with Samsung platform back camera for a temperature change from 29.9°C to 30.8°C.
Table 4
Comparison of ground radiation levels measured by multiple Samsung phones.
| Run | Samsung Galaxy 8s | Galaxy Note 5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | |
| Front-1 | 8.4 | 17.6 | 7.2 | 9.4 | 9.9 | 11.6 | 3 | 7.2 |
| Front-2 | 7.9 | 14.2 | 8.4 | 9.6 | 11.3 | 11.6 | 4.2 | 7.6 |
| Front-3 | 6.9 | 14.8 | 7.9 | 10.2 | 10.6 | 10.2 | 3.6 | 6 |
| Ave: | 7.7 | 15.5 | 7.8 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 11.1 | 3.6 | 6.9 |
| Back-1 | 50.4 | 21.6 | 29.3 | 34.0 | 1.6 | 9.9 | 2.4 | 12.4 |
| Back-2 | 56.1 | 22.1 | 32.6 | 36.8 | 1.4 | 8.4 | 3.4 | 24.2 |
| Back-3 | 62.8 | 19.4 | 37.4 | 52.4 | 1.4 | 5.8 | 4.7 | 17.7 |
| Ave: | 56.4 | 21.0 | 33.1 | 41.1 | 1.5 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 18.1 |
Table 5
Detected counts for the smartphones after 20 minutes with Cs-137 sample.
| Device | CPM (1 minute) | CPM (20 minutes) |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung Galaxy 8s | ||
| Phone 1 | 75 | 90.8 ± 0.5 |
| Phone 2 | 30 | 91.4 ± 1.0 |
| Phone 3 | 49 | 54.6 ± 0.7 |
| Phone 4 | 126 | 83.6 ± 0.5 |
| Ave = 70 ± 40 | Ave = 80 ± 17 | |
| Samsung Note 5 | ||
| Phone 1 | 23 | 15.6 ± 0.4 |
| Phone 2 | 39 | 26.8 ± 1.0 |
| Phone 3 | 29 | 30.3 ± 0.1 |
| Phone 4 | 23 | 37.9 ± 0.3 |
| Ave = 29 ± 8 | Ave = 28 ± 9 | |
| iPhone 6s | 16 | 28.2 ± 0.5 |
| Mazur | 1050 | 1085 ± 20 |
Table 6
Comparison of CPMs for apps on different platforms.
| Model | App | CPM-1 | CPM-2 | CPM-3 | CPM-4 | Average | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iPhone | Radioactivity Counter | 35 | 31 | 37 | 33 | 34 | 1.9 |
| Smart Geiger | 26 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | |
| Note 5 | Radioactivity Counter | 34 | 32 | 47 | 38 | 38 | 6.7 |
| Smart Geiger | 22 | 23 | 29 | 23 | 24 | 3.2 | |
| Galaxy 8s | Radioactivity Counter | 115 | 117 | 127 | 84 | 111 | 18.6 |
| Smart Geiger | 14 | 18 | 23 | 18 | 18 | 3.7 |
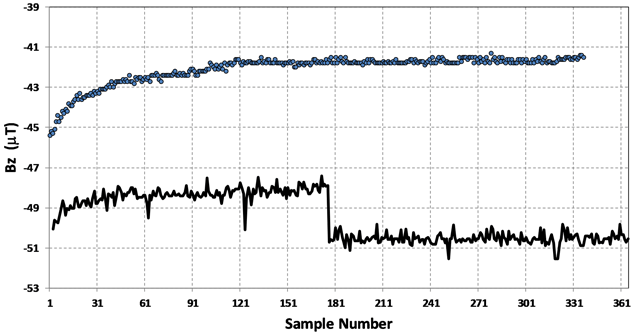
Figure 2
Glitch artifacts, DC level jumps, and asymptotic settling seen in side-by-side tests of the iPhone and Samsung platforms. Samsung data (solid line), iPhone data (dots). Credit Odenwald (2018).
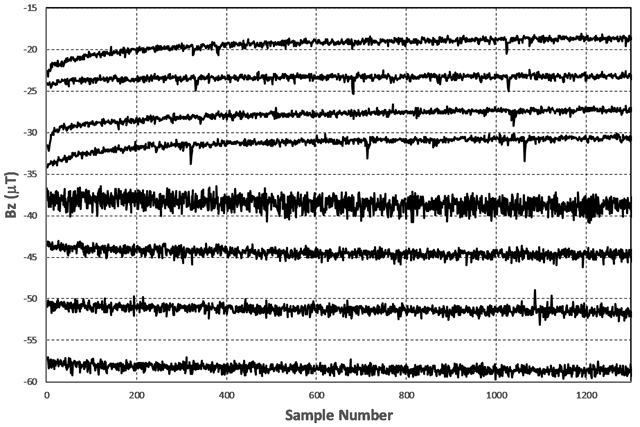
Figure 3
Display of continuous 2-hour Bz data for smartphones: Samsung Note 5 (Top four) and Samsung 8S (Bottom four). Bz values are shifted by arbitrary amounts to improve display visibility.
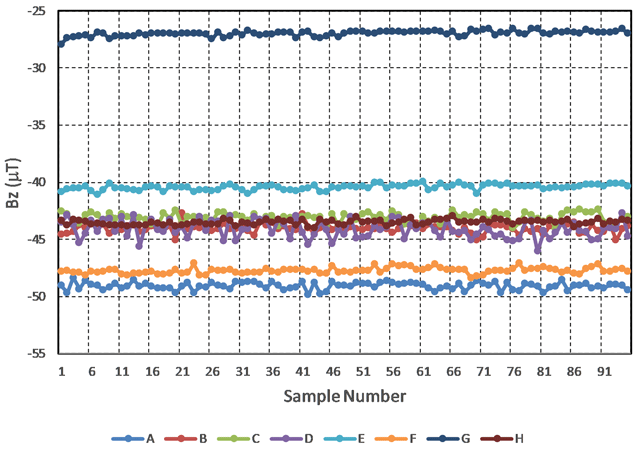
Figure 4
Samsung phone data showing dissimilar measurement values under identical conditions. Plot symbols A–D are for the four Samsung Galaxy 8S phones. Symbols E–H are for the Samsung Note 5 phones.
Table 7
Comparison of magnetic bearings with eight Samsung phones.
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardinal Angle | Bx (μT) | By (μT) | Bz (μT) | |Bh| (μT) | |B| (μT) | θxy (deg) | Magnetic (deg) | True-Mag (deg) | |
| Samsung Note 5 | |||||||||
| 0 | N | –0.8 | 21.4 | –36.2 | 21.5 | 42.1 | 362 | 361 | 1 |
| 90 | E | –26.1 | –3.3 | –35.8 | 26.3 | 44.4 | 97 | 95 | 5 |
| 180 | S | 4.1 | –29.2 | –36.5 | 29.6 | 47.1 | 187 | 185 | 5 |
| 270 | W | 24.7 | 0.6 | –35.5 | 24.7 | 43.4 | 271 | 265 | –5 |
| Galaxy 8s | |||||||||
| 0 | N | 1.5 | 24.4 | –43.1 | 24.4 | 49.6 | 357 | 355 | –6 |
| 90 | E | –22.6 | 0.1 | –42.1 | 22.6 | 47.8 | 90 | 90 | –1 |
| 180 | S | 3.9 | –25.6 | –42.6 | 25.9 | 49.9 | 188 | 187 | 7 |
| 270 | W | 26.7 | 4.4 | –42.4 | 27.1 | 50.3 | 280 | 278 | 8 |
[i] Note: The values in each cell are the averages of the four phone measurements. The 1-σ uncertainties in the magnetic measurements in each table cell are ±2.5 μT (Note 5) and ±1.8 μT (Galaxy 8s). The uncertainties in the angular measures for each cardinal direction are ±3.8° (Note 5) and ±4.7° (Galaxy 8s).
Table 8
Comparison of Platforms and Apps with the FRD Absolute Measurement.
| iPhone: | Bz | Bh (H) | |B| (F) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teslameter 11th | –46.9 | 20.2 | 51.1 |
| Sensor Kinetics | –46.9 | 20.3 | 51.1 |
| Teslameter | –46.8 | 20.3 | 51.0 |
| Magnitude | –47.1 | 20.1 | 51.2 |
| Magnetscape | –47.2 | 20.3 | 51.4 |
| Tesla Field Recorder | –46.9 | 20.1 | 51.0 |
| Average | –47.0 | 20.2 | 51.1 |
| Samsung: | |||
| Teslameter 11th | –41.3 | 20.8 | 46.2 |
| Sensor Kinetics | –40.9 | 20.1 | 45.6 |
| Physics Toolbox | –41.3 | 20.4 | 46.1 |
| Richi AMI Magnetometer | –41.5 | 20.3 | 46.2 |
| Advance Sensor | –41 | 20.6 | 45.9 |
| MagLog | –41.5 | 20.3 | 46.2 |
| Average | –41.3 | 20.4 | 46.0 |
| FRD | –45.5 | 21.6 | 51.0 |
| IGRF at FRD | –46.1 | 21.0 | 50.8 |
Table 9
Comparison of Samsung magnetic field values in Kensington, MD.
| Phone | Bz | Bh | |B| |
|---|---|---|---|
| Samsung Note 5 – Copy 1 | –39.92 | 22.20 | 45.67 |
| Samsung Note 5 – Copy 2 | –47.24 | 17.42 | 50.35 |
| Samsung Note 5 – Copy 3 | –26.37 | 16.10 | 30.90 |
| Samsung Note 5 – Copy 4 | –43.40 | 22.38 | 48.84 |
| Average | –39.23 ± 9.0 | 19.52 ± 3.2 | 43.94 ± 8.9 |
| Samsung Galaxy 8s – Copy 1 | –49.34 | 23.97 | 54.85 |
| Samsung Galaxy 8s – Copy 2 | –44.24 | 22.33 | 49.56 |
| Samsung Galaxy 8s – Copy 3 | –43.39 | 17.95 | 46.95 |
| Samsung Galaxy 8s – Copy 4 | –44.33 | 21.92 | 49.46 |
| Average | –45.32 ± 2.7 | 21.54 ± 2.6 | 50.20 ± 3.3 |
| IGRF-Kensington | –46.6 | 21.1 | 51.1 |
| Estimated Actual Kensington | –46.0 | 21.7 | 51.3 |
Table 10
Comparison of smartphone measurement accuracy.
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Model | Apps | σ(A-to-A) | |||
| Radiation | Ground-level (cpm) | Flight (cpm) | Cs-137 (cpm) | |||
| iPhone 6s | ±2.0 | ±0.5 | ±0.5 | Radioactivity Counter | 34 ± 1.9 | |
| Smart Geiger | 24 ± 0.5 | |||||
| Note 5 | ±2.3 (±7) | ±1.0 | ±2 (±7) | Radioactivity Counter | 38 ± 6.7 | |
| Smart Geiger | 24 ± 3.2 | |||||
| Galaxy 8s | ±5.4 (±18) | N/A | ±5 (±18) | Radioactivity Counter | 111 ± 18 | |
| Smart Geiger | 18 ± 3.7 | |||||
| Magnetism | Geomagnetic (mT) | |||||
| iPhone 6s | ±0.2 | Teslameter 11 | –44.15 ± 0.21 | |||
| Sensor Kinetics | –43.88 ± 0.13 | |||||
| Magnetometer | –42.48 ± 0.13 | |||||
| Magnetscope | –42.85 ± 0.13 | |||||
| Teslameter | –44.10 ± 0.13 | |||||
| Note 5 | ±0.42 (±4.6) | Teslameter 11 | –44.33 ± 0.42 | |||
| Advance Sensor | –43.73 ± 0.36 | |||||
| Sensor Kinetics | –43.38 ± 0.32 | |||||
| Tesla Recorder | –44.25 ± 0.24 | |||||
| Magnetometer | –43.93 ± 0.17 | |||||
| PhyPhox | –43.98 ± 0.33 | |||||
| Galaxy 8s | ±1.54 (±2.3) | Teslameter 11 | –43.98 ± 1.54 | |||
| Sensor Kinetics | –43.65 ± 0.69 | |||||
| PhyPhox | –43.50 ± 0.71 | |||||
| Advance Sensor | –43.58 ± 0.80 |
