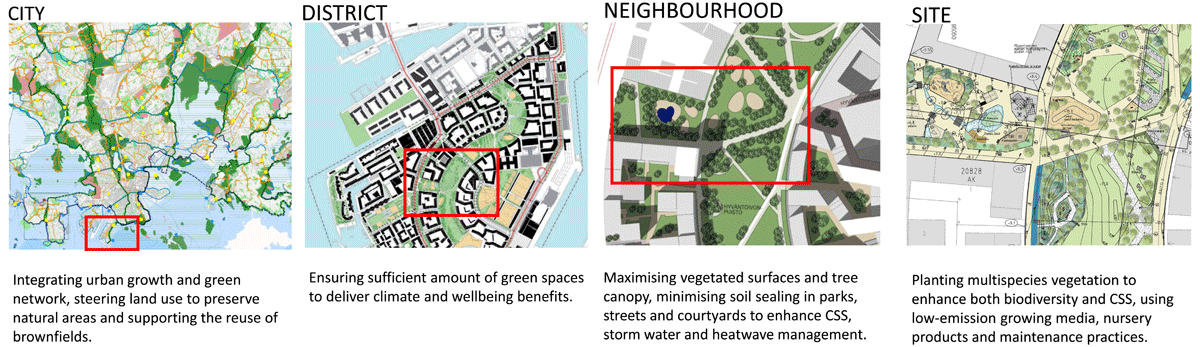
Figure 1
Carbon-smart urban green infrastructure (UGI) can be promoted across planning scales. Shown is the most effective means to enhance UGI and its climate benefits at different urban scales for a typical urban brownfield development.
Source: City of Helsinki, plans from Jätkäsaari.
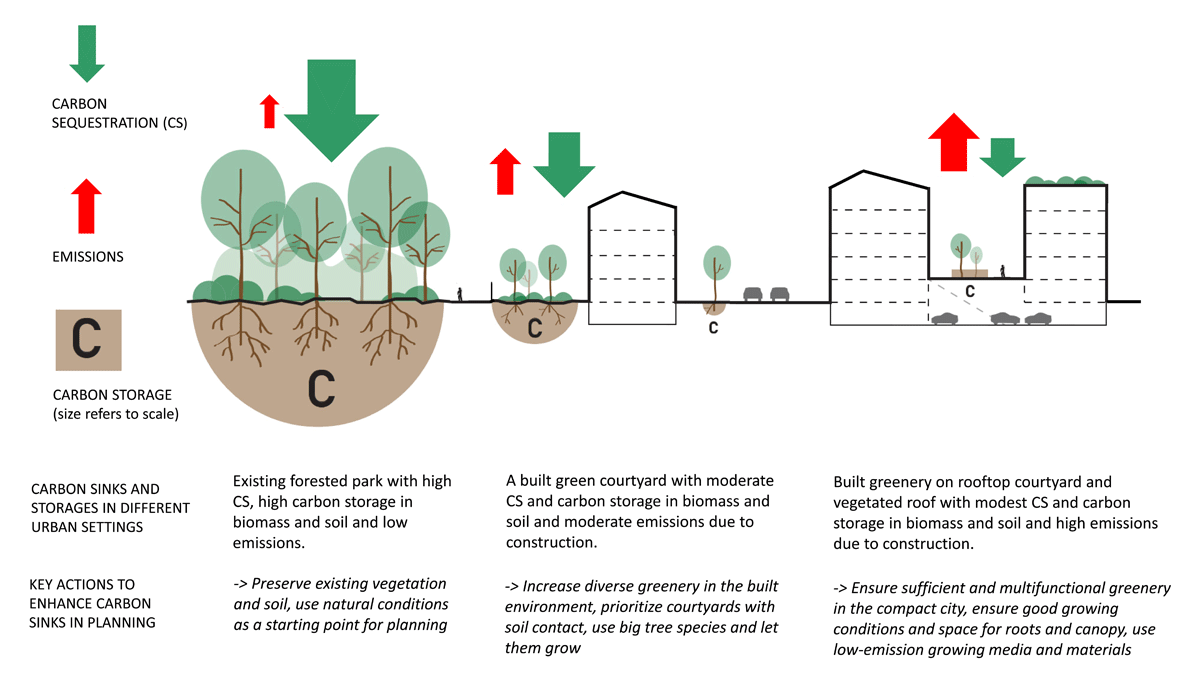
Figure 2
Different types of urban green infrastructure (UGI) have different carbon sequestration and storage (CSS) capacities and emission rates and require different methods to enhance carbon sinks. Highlighted are the carbon fluxes and key CSS actions in an existing forest, a courtyard with soil-based greening and built greening on rooftop courtyards.
Source: Hautamäki (2025).
Table 1
Key action points for carbon-smart urban green infrastructure (UGI) across different scales and actors in planning, construction, and management.
| SCALE AND ACTORS | PRESERVE UGI | CREATE A NEW UGI | LOW-EMISSION UGI |
|---|---|---|---|
| City- and district-scale urban planning and policies Urban planners |
|
|
|
| Planning neighbourhoods and plots Urban planners, architects, private-sector developers |
|
|
|
| Planning and implementing parks, courtyards and street plantings Landscape architects, architects, constructors, property owners |
|
|
|
| Maintaining UGI Landscape managers, constructors, communities, property owners |
|
|
|
