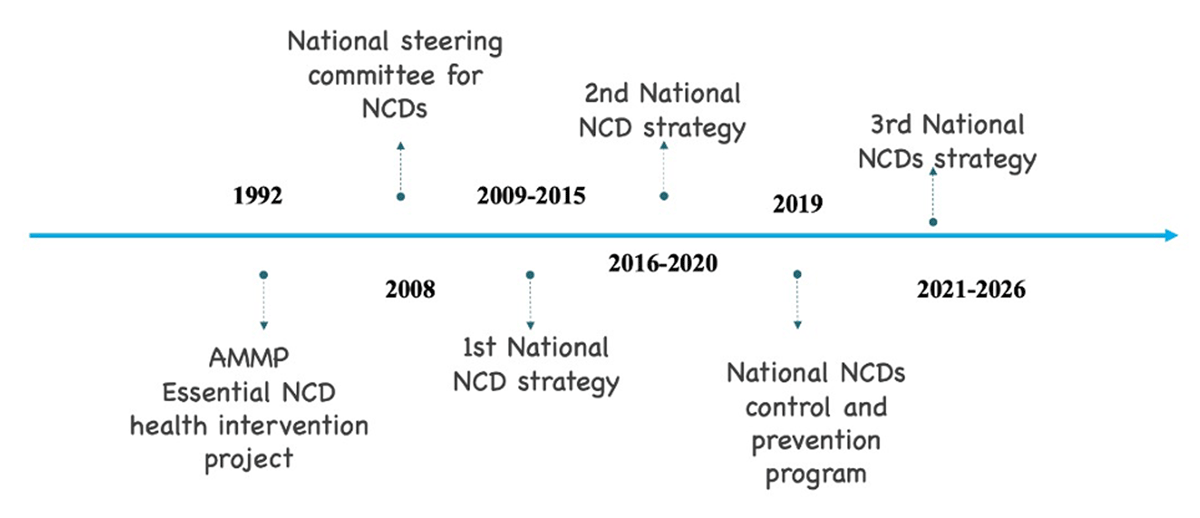
Figure 1
NCD program historical milestones in Tanzania.
Table 1
Strategies and approaches to address NCDs in Tanzania.
| STRATEGY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Multi-stakeholder engagement | Collaboration with local and international stakeholders: the Non-Communicable Diseases Alliance (TANCDA), Tanzania Diabetes Association (TDA), World Health Organization (WHO), Tanzania Cancer Association (TCA), Tanzania Association for Respiratory Diseases (TARD), Heart Foundation of Tanzania (HFT), World Diabetes Foundation (WDF), and institutions such as the Tanzania Food and Nutrition Centre (TFNC), Tanzania Food and Drug Authority (TFDA), and the Tanzania Bureau of Standards (TBS). |
| Crossing beyond health systems to engaging other sectors, including education, agriculture, communication, employment, energy, environment, finance, food. Also establishing multisectoral committees at different administrative levels, acknowledging that many determinants of NCDs are outside the health sector. | |
| Development of guidelines and policies | Working with scientists, policy makers, health personnel, and other partners to develop an NCD strategic plan, which is now being relied upon to develop and implement plans and strategies addressing the burden of NCDs in the country. |
| Advocacy, treatment, and care guidelines for specific diseases, such as sickle cell disease (SCD), hypertension, stroke, and diabetes mellitus have been developed, used for the routine care of patients with NCDs. | |
| The National NCD Research Agenda has been developed, stipulating the research areas of national interest, also serving as an important guide to scientists and potential funders to select priority areas for NCD research. | |
| Strengthened capacity of health facilities and health care workers | In collaboration with TDA and TANCDA, the NCD unit has managed to establish over 150 clinics throughout the country, which are all supplied with diagnostic guidelines and the equipment necessary for the management of NCDs. |
| Hundreds of healthcare workers from Northern Tanzania, the Lake Zone, and other parts of Tanzania have been trained on NCD prevention, diagnosis, and treatment through support from DANIDA and WDF, in collaboration with the civil society organizations. | |
| Increased community engagement and awareness on NCDs | Campaigns that focus on prevention and fostering good health-seeking behaviors, which will help ensure timely diagnosis and management of NCDs; these campaigns have been conducted through radio, TV sessions and physical seminars. |
| One hundred thousand school children have been provided with basic knowledge on risk factors for NCDs and have undergone screening for some of the NCDs. | |
| Over six million individuals were reached by outreach screening and sensitization campaigns conducted in the Lake Zone and Northern Tanzania |
