Table 1
Baseline characteristics of study participants.
| VARIABLES | RESULTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Total patients (n) | 1,152 | |
| *KRT modalities, n (%) | Hemodialysis | 785 (68.1) |
| CAPD | 86 (7.5) | |
| Kidney transplant | 281 (24.4) | |
| Male, n (%) | 674 (58.5) | |
| Age, median (IQR) years | 52 (41–61) | |
| Age at KRT presentation, median (IQR) years | 48 (37–58) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | Javanese | 341 (29.5) |
| Betawi | 258 (22.4) | |
| Sundanese | 132 (11.5) | |
| Batak | 67 (5.8) | |
| Malay | 13 (1.1) | |
| Balinese | 3 (0.3) | |
| Others | 204 (17.7) | |
| Missing data | 134 (11.6) | |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | Hypertension | 855 (74.2) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 347 (30.1) | |
| Cardiovascular disease | 133 (11.5) | |
| Stroke | 44 (3.8) | |
| Malignancy | 21 (1.8) | |
| Hepatitis B | 46 (4.0) | |
| Hepatitis C | 122 (10.6) | |
| Others | 165 (14.3) | |
| Medical history, n (%) | Family history with kidney disease | 171 (14.8) |
| Smoking | 401 (34.8) | |
| NSAID exposure | 258 (22.4) | |
| History of urolithiasis | 172 (14.8) | |
| Other nephrotoxic exposure | 210 (18.2) | |
| ¥eGFR at KRT initiation, median (IQR) ml/minute/1.73 m2 | 5.90 (4.0–8.34) | |
| <5 ml/minute/1.73 m2, n(%) | 156 (34.4) | |
| 5–10 ml/minute/1.73 m2, n(%) | 239 (52.8) | |
| >10 ml/minute/1.73 m2, n(%) | 58 (12.8) | |
| Missing data, n(%) | 699 (60.7) | |
| Duration on KRT, median (IQR) years | 3.0 (1.0–5.0) | |
| Vascular access for HD, n (%) | AV Fistula | 476 (60.6) |
| CVC | 271 (34.5) | |
| Others | 13 (1.7) | |
| Missing data | 25 (3.2) | |
[i] * The KRT initiation date was made accordingly to their current KRT modality (i.e., dialysis or kidney transplantation). Therefore, for the kidney transplant group, the time of KRT initiation was refer to the time the subjects received their kidney transplant.
¥ Data was collected from 39.3% (n = 453/1152) participants with complete initial laboratory parameters.
AV fistula arteriovenous fistula; CAPD continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis; CVC central venous catheter; eGFR estimated glomerular filtration rate; KRT kidney replacement therapy.
Table 2
Laboratory parameters at KRT initiation.
| VARIABLES | RESULTS |
|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (n = 480), median (IQR) g/dl | 8.9 (7.4–10.1) |
| Leucocyte (n = 478), median (IQR) per mm3 | 8,570 (6,592.5–11,255) |
| Thrombocyte (n = 479), median (IQR) cells/µL | 243,000 (186,000–308,000) |
| Albumin (n = 195), median (IQR) mg/dL | 3.39 (2.9–3.9) |
| Calcium (n = 166), median (IQR) mg/dL | 8.0 (7.07–8.92) |
| Phosphate (n = 157), median (IQR) mg/dL | 5.3 (4.0–7.25) |
| Sodium (n = 434), median (IQR) meq/L | 136 (132–140) |
| Potassium (n = 441), median (IQR) meq/L | 4.5 (3.8–5.1) |
| HBsAg positive (n = 332), n (%) | 15 (4.5) |
| Anti-HCV positive (n = 329), n (%) | 16 (4.9) |
| Anti-HIV positive (n = 284), n (%) | 3 (1.1) |
[i] HBsAg hepatitis B surface antigen; HCV hepatitis C virus; KRT kidney replacement therapy.
Table 3
Etiology of kidney disease in the study population.
| ETIOLOGY OF KIDNEY DISEASE | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Diabetic kidney disease | 313 (27.2) |
| Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | 132 (11.5) |
| Glomerulonephritis | 150 (13.0) |
| Primary glomerulonephritis | 128 (85.3) |
| Secondary glomerulonephritis | 22 (14.7) |
| Lupus nephritis | 20 (91) |
| Others | 2 (9) |
| Urolithiasis | 119 (10.3) |
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease | 17 (1.5) |
| Toxic Nephropathy | 5 (0.4) |
| Others: | 58 (5.0) |
| CAKUT | 7 (12.1) |
| Urinary tract and gynecology malignancy | 11 (19.0) |
| Cardiorenal syndrome | 7 (12.1) |
| Pre-eclampsia | 22 (37.9) |
| Infection* | 4 (6.9) |
| Miscellaneous | 7 (12.1) |
| Unknown | 358 (31.1) |
[i] * Infection (3 subjects: related to HIV-associated nephropathy, 1 subject: related to hepatitis C infection).
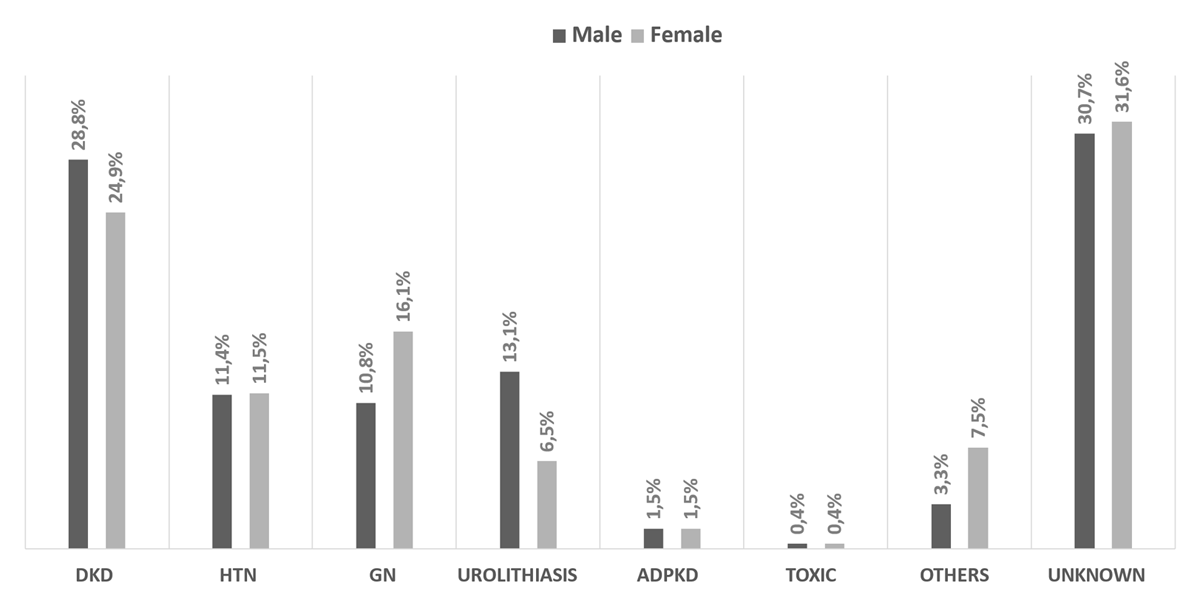
Figure 1
The distribution of ESKD etiology stratified by gender.
Notes: DKD = diabetic kidney disease; HTN = hypertensive nephrosclerosis; GN = glomerulonephritis; ADPKD = autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Toxic = toxic nephropathy.
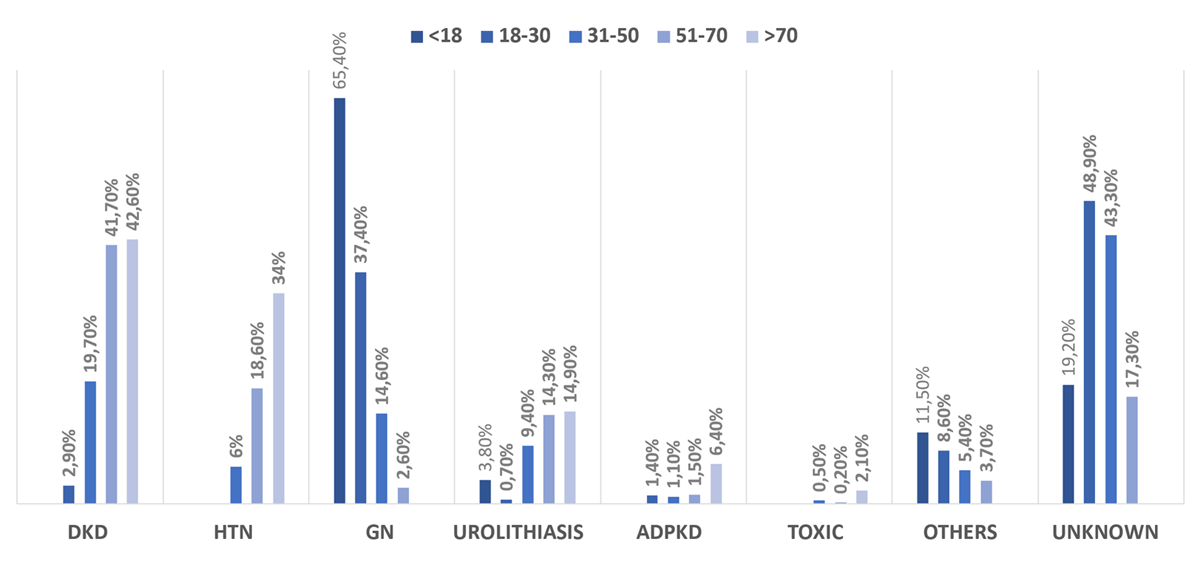
Figure 2
The distribution of ESKD etiology stratified by age groups.
Notes: DKD = diabetic kidney disease; HTN = hypertensive nephrosclerosis; GN = glomerulonephritis; ADPKD = autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Toxic = toxic nephropathy.
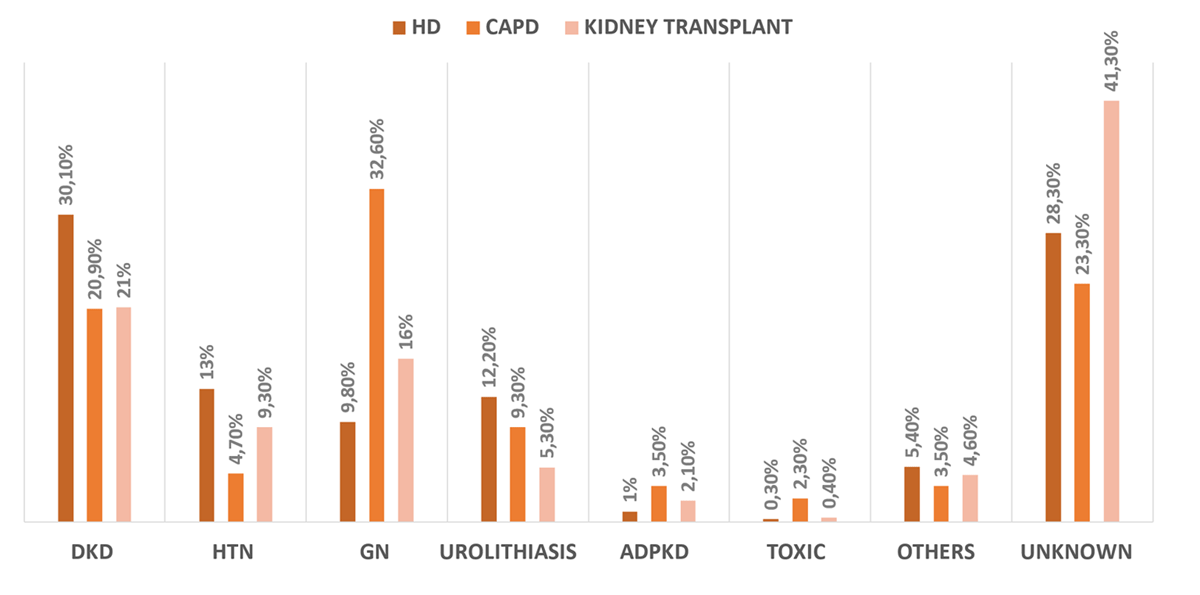
Figure 3
The distribution of ESKD etiology stratified by KRT modalities.
Notes: DKD = diabetic kidney disease; HTN = hypertensive nephrosclerosis; GN = glomerulonephritis; ADPKD = autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Toxic = toxic nephropathy.
