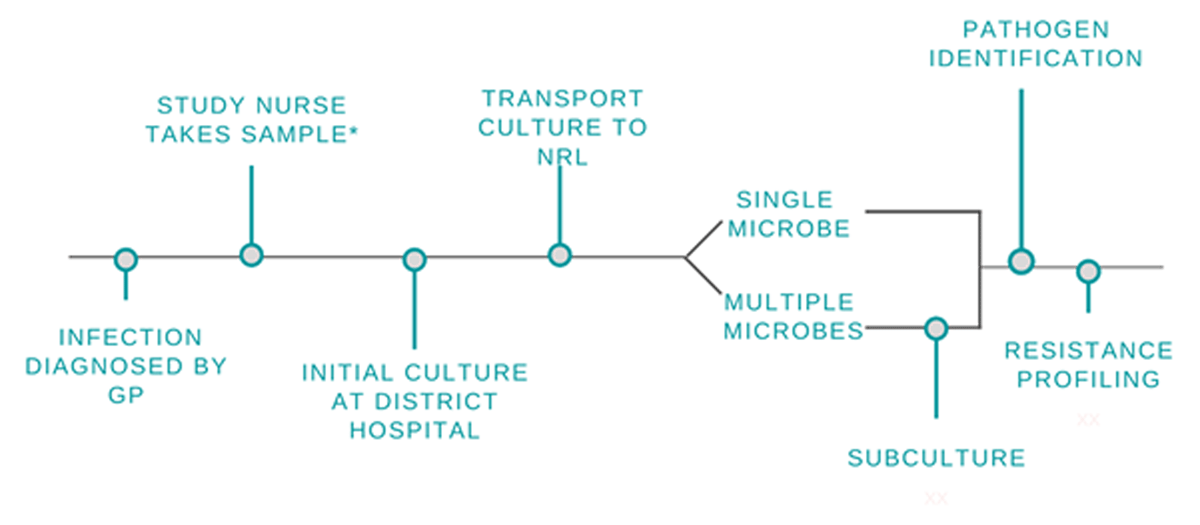
Figure 1
Overview of Study Processes.
GP = General Practitioner. NRL = National Reference Laboratory.
* The study process differed for the subgroup of women presenting with surgical-site infections enrolled in the parallel NIH-funded study where two swabs were collected: one swab was processed through this route and the other swab was sent directly to the NRL. This separate process is detailed in Figure 2.
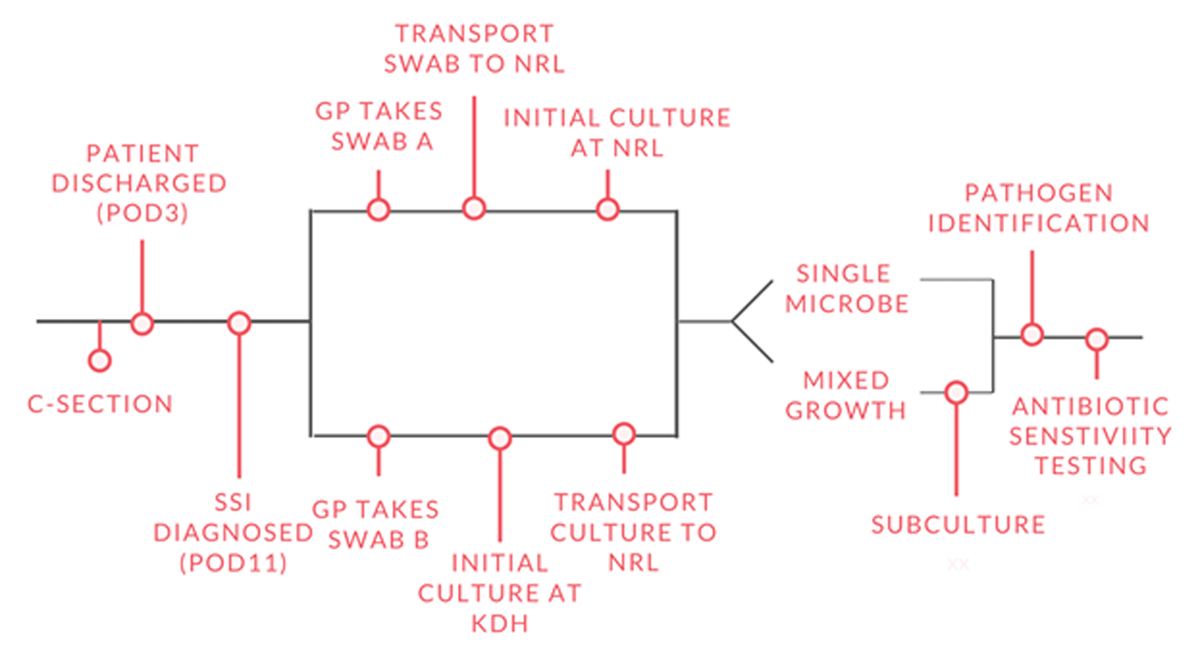
Figure 2
Processing of AMR-SSI samples from KDH.
GP = General Practitioner. NRL = National Reference Laboratory.
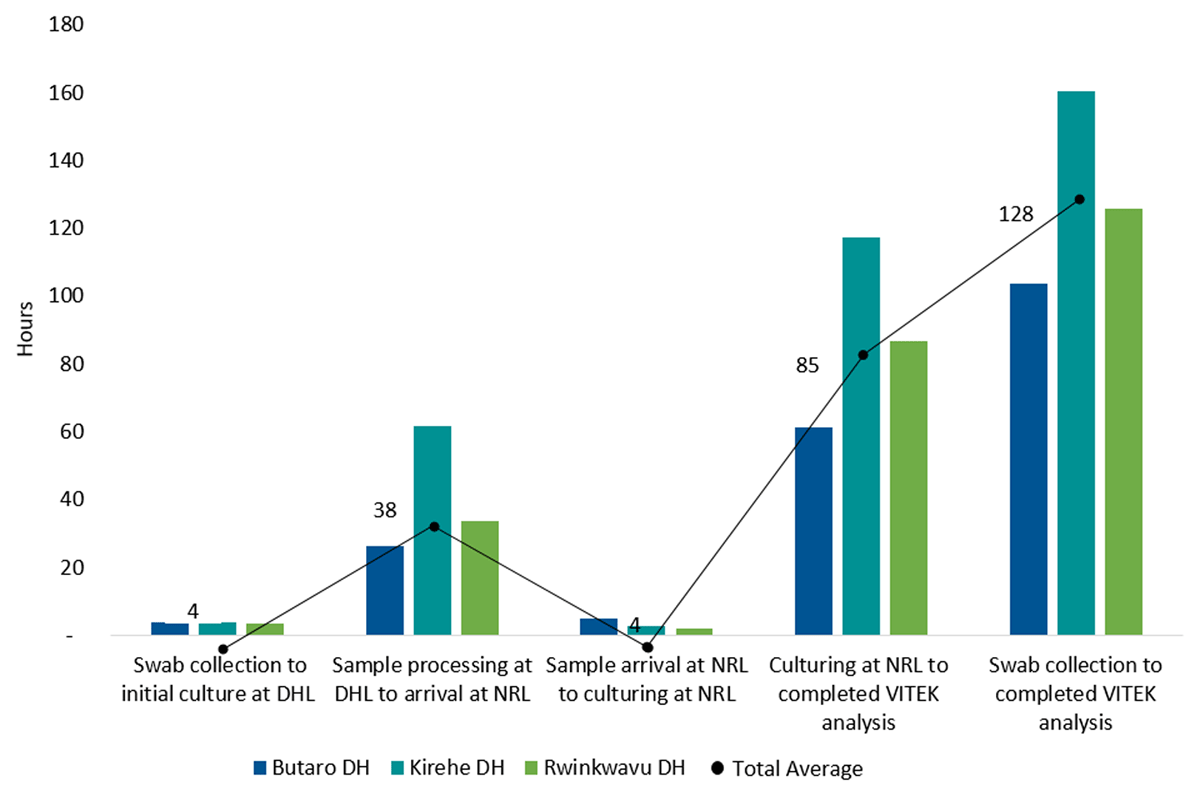
Figure 3
Turnaround Time, Disaggregated by Study Site and Sample Processing Steps.
DHL = District Hospital Laboratory. NRL = National Reference Laboratory. DH = District Hospital.
Table 1
Concordance between Quality Control samples at the District Hospital (DH) and National Reference Laboratory (NRL).
| QUALITY CONTROL AT DH LEVEL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INITIAL CULTURE (A) | INITIAL CULTURE CONTROL (B) | |||
| SINGLE MICROBE | MIXED GROWTH | NO GROWTH | TOTAL | |
| Single microbe | 12 | 2 | 0 | 14 |
| Mixed growth | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| No growth | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 22 | 5 | 2 | 20 |
| Concordance | (13+3+2)/20 = 17/20 (85%) | |||
| QUALITY CONTROL FOR SAMPLE A AT THE NRL | ||||
| INITIAL CULTURE (AA) | INITIAL CULTURE CONTROL (BA) | |||
| SINGLE MICROBE | MIXED GROWTH | NO GROWTH | TOTAL | |
| Single microbe | 14 | 1 | 0 | 15 |
| Mixed growth | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| No growth | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 15 | 3 | 2 | 20 |
| Concordance | (14+2+2)/20 = 18/20 (90%) | |||
| QUALITY CONTROL FOR SAMPLE B AT THE NRL | ||||
| INITIAL CULTURE (AB) | INITIAL CULTURE CONTROL (BB) | |||
| SINGLE MICROBE | MIXED GROWTH | NO GROWTH | TOTAL | |
| Single microbe | 14 | 1 | 0 | 15 |
| Mixed growth | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| No growth | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 15 | 2 | 2 | 20 |
| Concordance | (14+2+2)/20 = 19/20 (90%) | |||
[i] Culture A: cultures prepared by the study laboratory technician at the DH.
Culture B: cultures prepared by another laboratory technician at the DH.
Culture AA: cultures prepared by the study laboratory technician at the DH and processed by the study laboratory technician at the NRL.
Culture AB: cultures prepared by the study laboratory technician at the DH and processed by another laboratory technician at the NRL.
Culture BA: cultures prepared by another laboratory technician at the DH and processed by the study laboratory technician at the NRL.
Culture BB: cultures prepared by another laboratory technician at the DH and processed by another laboratory technician at the NRL.
Table 2
Concordance between AMR-SSI swabs processed through regular study processes and those taken directly to the National Reference Laboratory (NRL, N = 44).
| LEVEL OF CONCORDANCE (N, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FULL CONCORDANCE | HIGH CONCORDANCE | PARTIAL CONCORDANCE | LOW CONCORDANCE | NO CONCORDANCE |
| 4 (9.1%) | 21 (47.7%) | 10 (22.7%) | 6 (13.6%) | 3 (6.8%) |
[i] Full concordance = full agreement of all pathogen findings and antibiotic susceptibility.
High concordance = full agreement of all pathogen findings but discrepancies in antibiotic susceptibility.
Partial concordance = full agreement of some pathogen findings.
Low concordance = agreement of gram-stain.
No concordance = no agreement of pathogen findings in the two samples.
Table 3
Costing estimates for processing 600 wound swabs from one district hospital (DH).
| OPTION A: COST USING MANUAL TESTING AT DH | OPTION B: COST USING VITEK2 SYSTEM AT DH | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | ||
| Equipment | 13,695 | 13,695 |
| Laboratory supplies | 9,686 | 72,777* |
| Reagents | 6,1193 | 6,119 |
| Total cost | 29,500 | 92,591 |
| B. | ||
| Equipment and supplies at DH | 4,638 | |
| Reagents for NRL tests (pathogen identification and AST) | 29,814 | |
| Total cost | 34,452 | |
| C. | ||
| Equipment and supplies at DH | 1,569 | |
| Reagents for NRL tests (pathogen identification and AST) | 32,201 | |
| Total cost | 33,770 | |
[i] a: Scenario 1: Cost (USD) of having all pathogen identification and sensitivity testing done at DH.
* This includes the cost of a VITEK machine to have tests done at DH.
Costs not included:
1. Cost of one additional laboratory technician for sample processing.
2. Electricity, water, and other utility cost.
b: Scenario 2: Cost (USD) of having initial cultures done at DH but samples sent to the NRL for pathogen identification and sensitivity testing.
Costs not included:
1. Cost of one additional laboratory technician for sample processing at DH and NRL.
2. Cost of electricity, water, and other utility cost.
3. Cost for sample transportation.
If culture media are prepared at the DHL, logistics for blood transportation from the national transfusion center to DHL should be taken into account.
c: Scenario 3: Cost (USD) of having swabs sent from DH to the NRL for all pathogen identification and sensitivity testing.
Costs not included:
1. Cost for having one additional laboratory technician for sample processing at the NRL.
2. Cost for electricity, water, and other utility cost.
3. Cost for sample transportation to NRL.
