Figure 1
Overview of a PCMH HDU bed with essential standards of care provided (see text).
Table 1
Health-related quality-of-life weights.
| Quality of Life weights | Health-related reasons |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | Deaths |
| 0.30 | Referral to Intensive Care Unit |
| 0.40 | Hysterectomy in patients <30 years |
| 0.80 | B-Lynch surgical procedure in patients <30 years |
| 0.90 | Uterine ruptures in patients <30 years |
| 0.90 | Sepsis (29) |
| 0.95 | Pre-eclampsia/eclampsia (30) |
| 0.50 | Other severe diagnosis (disseminated intravascular coagulation, emiparesis) |
| 1.0 | Full recovery at discharge |
Table 2
Use of key procedures and treatments provided in the HDU compared between survivors and non-survivors.
| Treatment | All patients (n = 523) | Alive cases (n = 468) | Dead cases (n = 55) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 116 (22.2%) | 84 (72.4%) | 32 (27.6%) |
| Vasopressors | 68 (13.0%) | 45 (66.2%) | 23 (33.8%) |
| Transfusions | 263 (50.3%) | 241 (91.6%) | 22 (8.4%) |
| Antibiotics | 109 (20.8%) | 103 (94.5%) | 6 (5.5%) |
| Magnesium Sulphate protocol | 72 (13.8%) | 63 (87.5%) | 9 (12.5%) |
| Hydralazine protocol | 74 (14.1%) | 68 (91.9%) | 6 (8.1%) |
Table 3
Values for investment and one-year running costs of the HDU in the study.
| Value in € | % | |
|---|---|---|
| INVESTMENT COSTS | 64.064,65 | 100 |
| Drugs, medical materials and consumable | 6.763,50 | 11 |
| Equipment | 16.355,31 | 26 |
| Human resources | 7.644,44 | 12 |
| Other – extra generator | 9.182,12 | 14 |
| Renovation work | 15.971,35 | 25 |
| Training | 8.147,92 | 13 |
| ONE-YEAR RUNNING COSTS | 56.017,28 | 100 |
| Equipment, medical materials, and drugs | 33.956,54 | 61 |
| Human resources | 5.094,95 | 9 |
| Maintenance | 13.182,83 | 24 |
| Training | 3.782,95 | 7 |
| TOTAL COSTS | 120.081,93 |
Table 4
Values of QALY and cost per QALY per main admission diagnosis in the HDU.
| Main Admission Diagnosis | n. patients n (%) | QALY (mean) | Cost per QALY (€) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ante-Partum Haemorrhage (APH) | 85 (16.3) | 23.4 | 9.8 |
| Post-Partum Haemorrhage (PPH) | 66 (12.6) | 21.7 | 10.6 |
| Pre-Eclampsia (PE)/eclampsia | 117 (22.4) | 23.6 | 9.7 |
| Complications of abortion | 12 (2.3) | 26.2 | 8.8 |
| Ectopic Pregnancy | 53 (10.1) | 25.5 | 9.0 |
| Obstructed labour | 28 (5.4) | 25.2 | 9,1 |
| Puerperal Sepsis | 49 (9.4) | 21.0 | 10.9 |
| Uterine Rupture (UR) | 55 (10.5) | 24.3 | 9.4 |
| Others | 58 (11.1) | 18.3 | 12.5 |
| Overall | 523 | 22.9 | 10.0 |
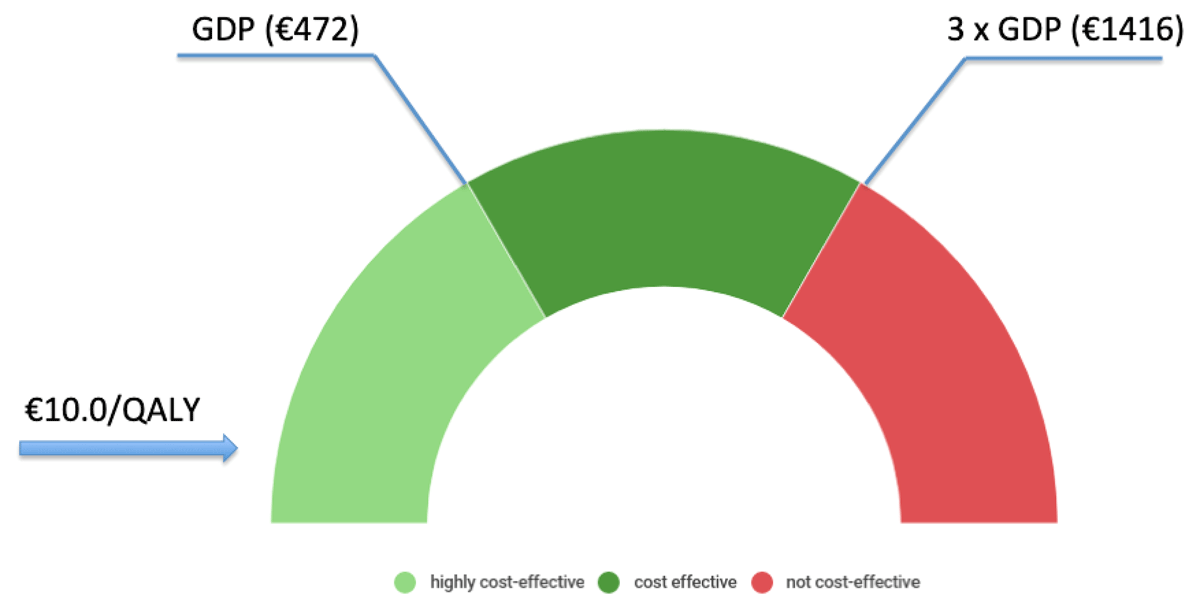
Figure 2
Cost for QALY of the implementation and one-year running of HDU within the framework of the World Health Organization interpretation of the cost-effectiveness of health care interventions. If the value of cost per QALY is less than the Country’s GDP per capita, then the intervention is considered very cost-effective. If the value of cost per QALY falls between one and three times GDP per capita, then the intervention is cost-effective, and if the cost per QALY is more than three times GDP per capita, the intervention is considered not cost-effective [12].
