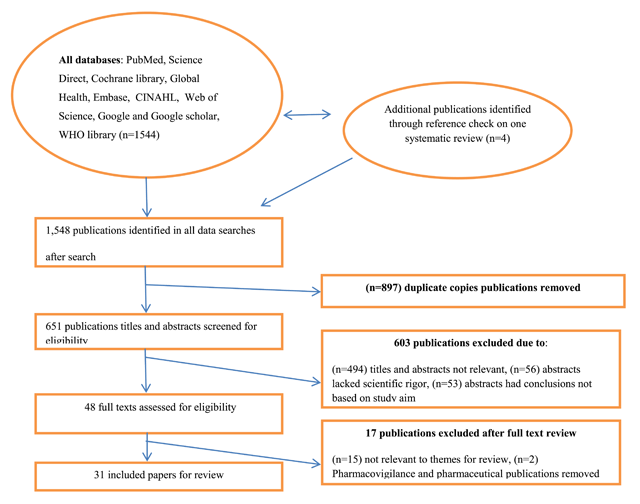
Figure 1
PRISMA flow diagram showing how publications were screened for eligibility for inclusion.
Table 1
List and origins of publications reviewed.
| SSA Region | Number of publications |
|---|---|
| East Africa | 9 |
| West Africa | 10 |
| Southern Africa | 6 |
| Global perspective with focus on SSA | 6 |
| Total | 31 |
Table 2
Health workforce-related publications included in review.
| Reference Publication | Study Title | Design/Setting/Data/Analytical Approach | Main findings on local health system strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ledikwe et al. 2013 [34], Botswana | Establishing a health information workforce: innovation for low- and middle-income countries | Mixed method approach with qualitative and quantitative data was used. Tools included pre and post-test, interviews during stakeholder site visits, a survey focusing on achievements, focus group discussions, and an attrition assessment |
|
| Otu et al. 2016 [35], Nigeria | Using a mHealth tutorial application to change knowledge and attitude of frontline health workers to Ebola virus disease in Nigeria: A before-and-after study | Quantitative cross-sectional survey in 14 health facilities in Ondo state, Nigeria |
|
| Sayinzoga et al. 2016 [33], Rwanda | Drivers of improved health sector performance in Rwanda: A qualitative view from within | Web-based survey among district health managers on opinions that drive performance in the health sector |
|
Table 3
Surveillance and data management-related publications reviewed.
| Reference Publication | Study Title | Design/Setting/data/Analytical Approach | Main findings on local health system strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Martha Gyansa-Lutterodt 2013 [39], Ghana | Antibiotic resistance in Ghana | Comment on antibiotic use and its growing resistance in Ghana |
|
| Justine Davis et al. 2017 [40], Africa | Sustainable clinical laboratory capacity for health in Africa | Comment on laboratory capacities across Africa |
|
| Lancet Editorial 2017 [41], Africa | Global health security: How can laboratories help? | Editorial comment with focus in Africa |
|
| Jones et al. 2008 [36], Kenya and Uganda | District-based malaria epidemic early warning systems in East Africa: Perceptions of acceptability and usefulness among key staff at health facility, district and central levels | Development and testing of a district-based malaria surveillance system in four pilot districts of Kenya and Uganda. Health staff interviews conducted among 52 health staff at districts and Ministries of Health in Kenya and Uganda |
|
| Cox et al. 2007 [37], Africa | Early warning systems for malaria in Africa: From blueprint to practice | Review of evidence in Africa |
|
| Peckham et al. 2017 [38], West Africa | Satellite and the new war on Infection: Tracking Ebola in West Africa | Data synthesis of available evidence of study aim |
|
| Haskew et al. 2015 [42], Kenya | Implementation of a Cloud-Based Electronic Medical Record to Reduce Gaps in the HIV Treatment Continuum in Rural Kenya | Project evaluation of an electronic medical record systems for HIV cases in rural Kenya |
|
| Kiberu et al. 2014 [43], Uganda. | Strengthening district-based health reporting through the district health management information software system: The Ugandan experience | Training facilitation for cadre of health professional on the use of the district health management information software system version 2 (DHIS2) across 112 districts. |
|
| Mate et al. 2009 [44], South Africa | Challenges for Routine Health System Data Management in a Large Public Programme to Prevent Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission in South Africa | A survey conducted between January-December 2007 on completeness and accuracy of HIV data for decision making in South Africa |
|
| Wong et al. 2009 [45], Ethiopia | Developing patient registration and medical records management system in Ethiopia | Pre-post intervention study in large referral hospital |
|
Table 4
Health Governance-related publications included in review.
| Reference Publication | Study Title | Design/Setting/Data/Analytical Approach | Main findings on local health system strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heymann et al. 2016 [4], Lancet, West Africa | Global Health security: Wider lessons from the West African Ebola Virus disease epidemic | Historical and secondary review of Ebola events in West Africa during and post Ebola |
|
| Drobac et al. 2013 [76], Rwanda | Comprehensive and integrated district health systems strengthening: The Rwanda population Health Implementation and Training (PHIT) Partnership | Impact evaluation using population level outcome data from demographic health surveys (DHS) in Rwanda (protocol) |
|
| Sherr et al. 2013 [48], Mozambique | Strengthening integrated primary health care in Sofala, Mozambique | Evaluation design technique employing a quasi-experimental controlled time-series design to assess impact of partnership strategy on under-5 mortality rates in study setting |
|
| Cho et al. 2014 [85], Global Editorial | Out of Africa, Into Global Health Security Agenda | Editorial comment |
|
| Cho et al. 2015 [86], Global Editorial | Two Epidemics and Global Health Security Agenda | Editorial comment |
|
| GHSA Task Force Team 2015 [87], Brief Report | Global Health Security: The Lessons from the West African Ebola Virus Disease Epidemic and MERS outbreak in the Republic of Korea | Retrospective assessment of Ebola and MERS |
|
| Patel et al. 2015 [49], West Africa | Health security and political and economic determinants of Ebola | Correspondence on global health security and its needs |
|
| Wang et al. 2013 [52], Global Review | New vaccine introductions: Assessing the impact and the opportunities for immunization and health systems strengthening | Mixed approaches that includes a review of published and grey literature, in-depth case studies in three countries, interviews with key informants from countries and WHO Regional Offices, and a multivariable analysis examining impact of NVI on coverage for 3rd dose of diphtheria–tetanus–pertussis vaccine (DTP3). |
|
| Buseh et al. 2015 [53], West Africa | The Ebola Epidemic in West Africa: Challenges, opportunities and policy priority areas | Literature review of peer-reviewed journals on disease burden and health reforms in developing countries with focus on West Africa |
|
| Gostin et al. 2015 [88], Lancet West Africa | A retrospective and prospective analysis of the West African Ebola virus disease epidemic: Robust national health systems at the foundation and an empowered WHO at the apex | A synthesis of public policy issues in post-Ebola outbreak in West Africa |
|
| Siekmans et al. 2017 [89], Liberia | Community-based health care is an essential component of a resilient health system: Evidence from Ebola outbreak in Liberia | A descriptive observational study design using mixed methods to collect data among community health workers. |
|
| Kongnyuy et al. 2008 [50], Malawi | Criteria-based audit to improve a district referral system in Malawi: A Pilot study | A criteria-based audit by conducting a retrospective review of 60 obstetric emergencies from 12 health centres |
|
| Topp et al. 2015 [51], Zambia | The impact of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) service scale-up on mechanisms of accountability in Zambian primary health centres: A case-based health systems analysis | Guided by the Mechanisms of Effect framework and Brinkerhoff’s work on accountability. In-depth multi-case study with case data interviews collected among providers. Direct observation and key informant interviews were also used |
|
| Coovadia et al. 2009 [54], South Africa | The health and health system of South Africa: Historical roots of current public health challenges | Historical review of South African Health Care Systems |
|
| Kieny et al. 2014 [10], Western Africa | Health-system resilience: Reflections on the Ebola crisis in western Africa | Perspectives on the health systems in affected West African countries |
|
| WHO 2010 [25] | Monitoring the building blocks of health systems: A handbook of indicators and their measurement strategies | A published book on the essential building blocks in health systems strengthening |
|
| WHO 2007 [3] | Everybody’s business: Strengthening health systems to improve health outcomes: WHOs framework for action | A published book on making health systems strengthening a priority for all citizens, academics, WHO staff, governments, and donors. |
|
