Figure 1.

Figure 2.
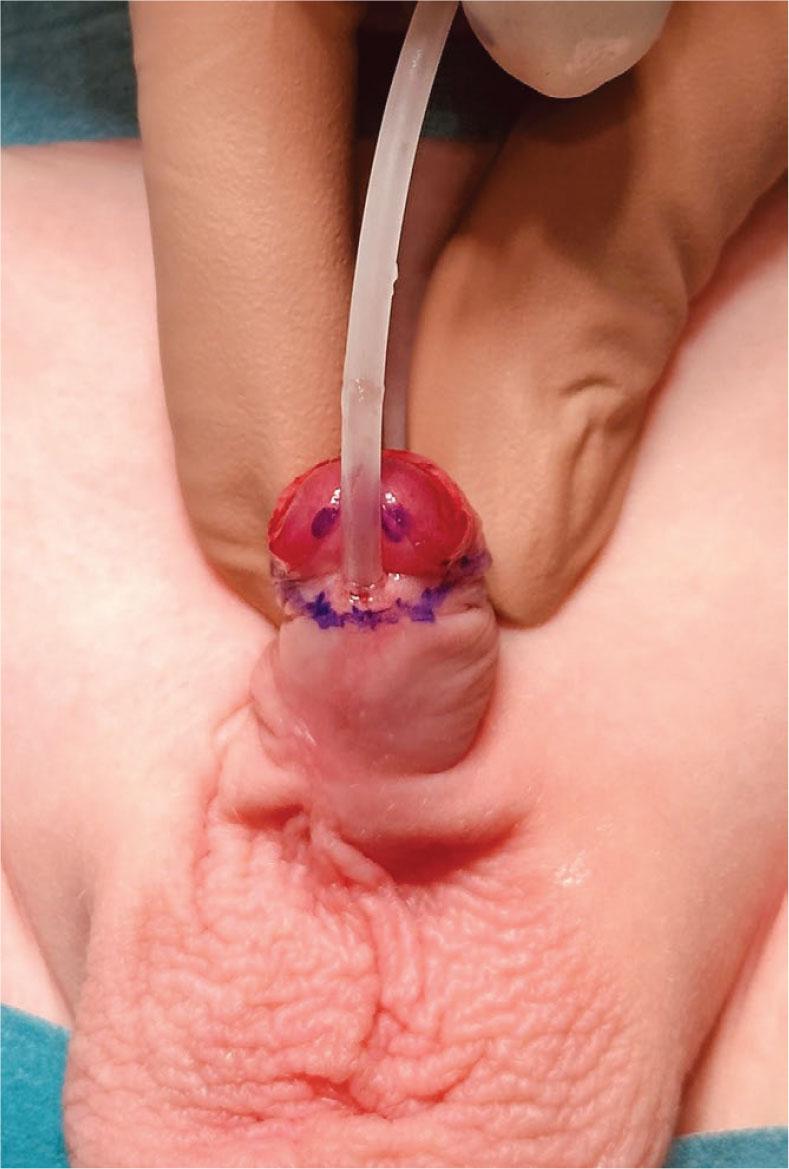
Figure 3.

Figure 4.
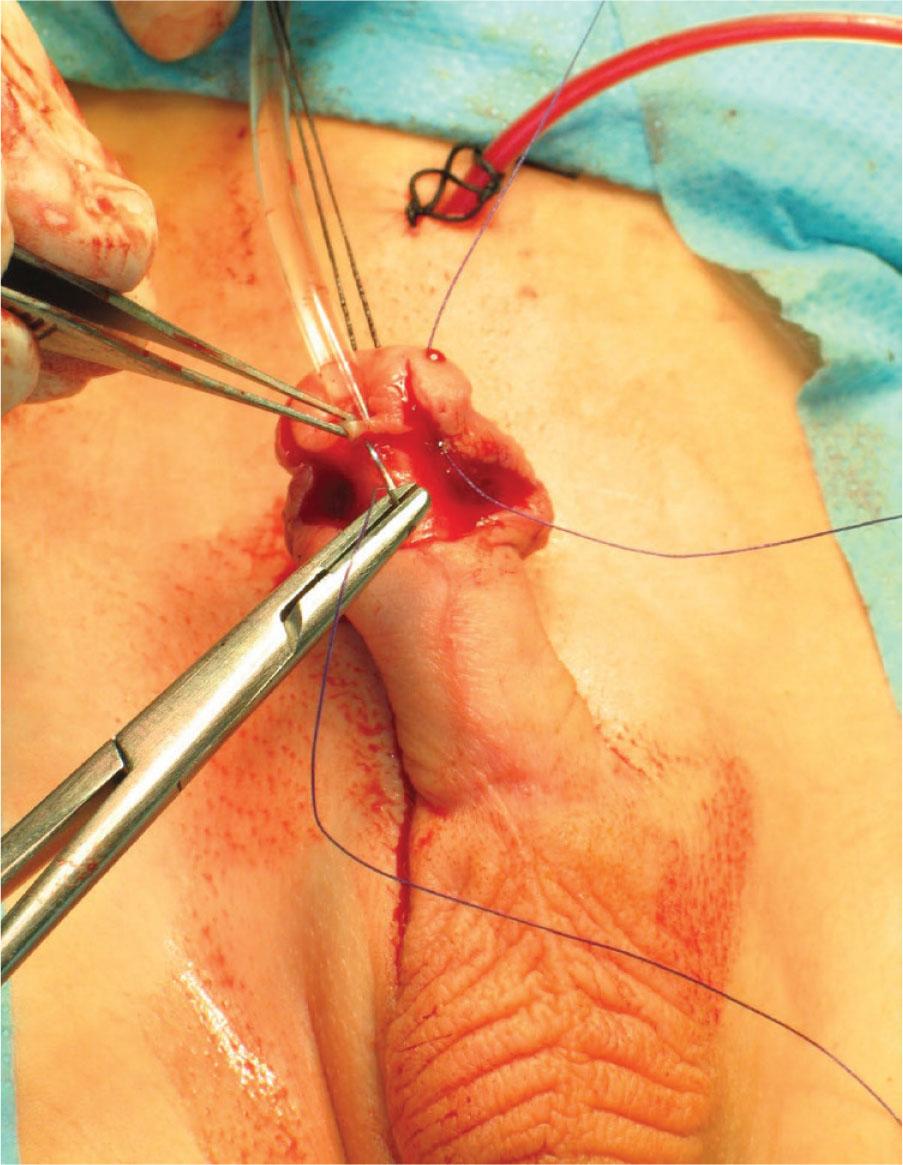
Figure 5.
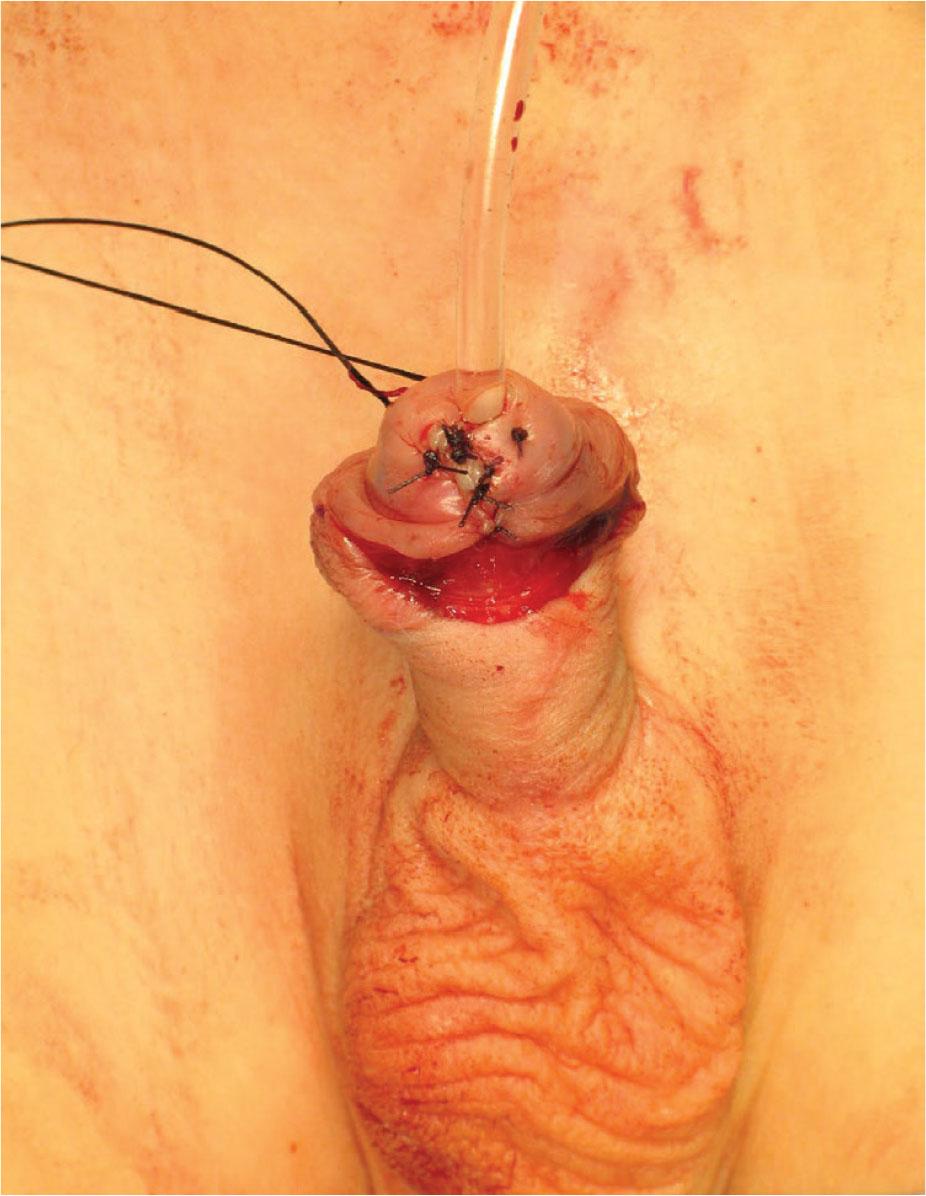
Figure 6.

Late complications after coronal hypospadias treatment_
| Study participants | |
|---|---|
| 265 | |
| Late complications: | |
| Abnormal morphology of the foreskin (separation, atrophy, asymmetry) | 9 (3.39%) |
| Retraction of the external urethral meatus | 8 (3.01%) |
| Urethral fistula | 3 (1.13%) |
Late complications after coronal hypospadias surgery requiring surgical treatment_
| Study participants | |
|---|---|
| 265 | |
| Late complications: | |
| Abnormal morphology of the foreskin (separation, atrophy, asymmetry) | 4 (1.51%) |
| Retraction of the external urethral meatus | 8 (3.01%) |
| Urethral fistula | 3 (1.13%) |
Early complications after coronal hypospadias treatment_
| Study participants | |
|---|---|
| 265 | |
| Early complications during hospitalisation: | |
| Catheter problems, including: | 8 (3.01%) |
| - suprapubic urinary drainage tube obstruction | 5 (1.88%) |
| - premature catheter removal | 3 (1.13%) |
| Haematoma and swelling requiring dressing change | 18 (6.79%) |
| Early complications after hospitalisation: | |
| Persistent haematoma and swelling | 9 (3.39%) |
| Dysuria | 6 (2.26%) |