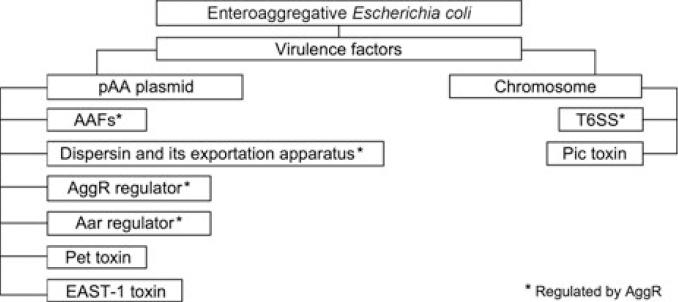
Fig. 1.
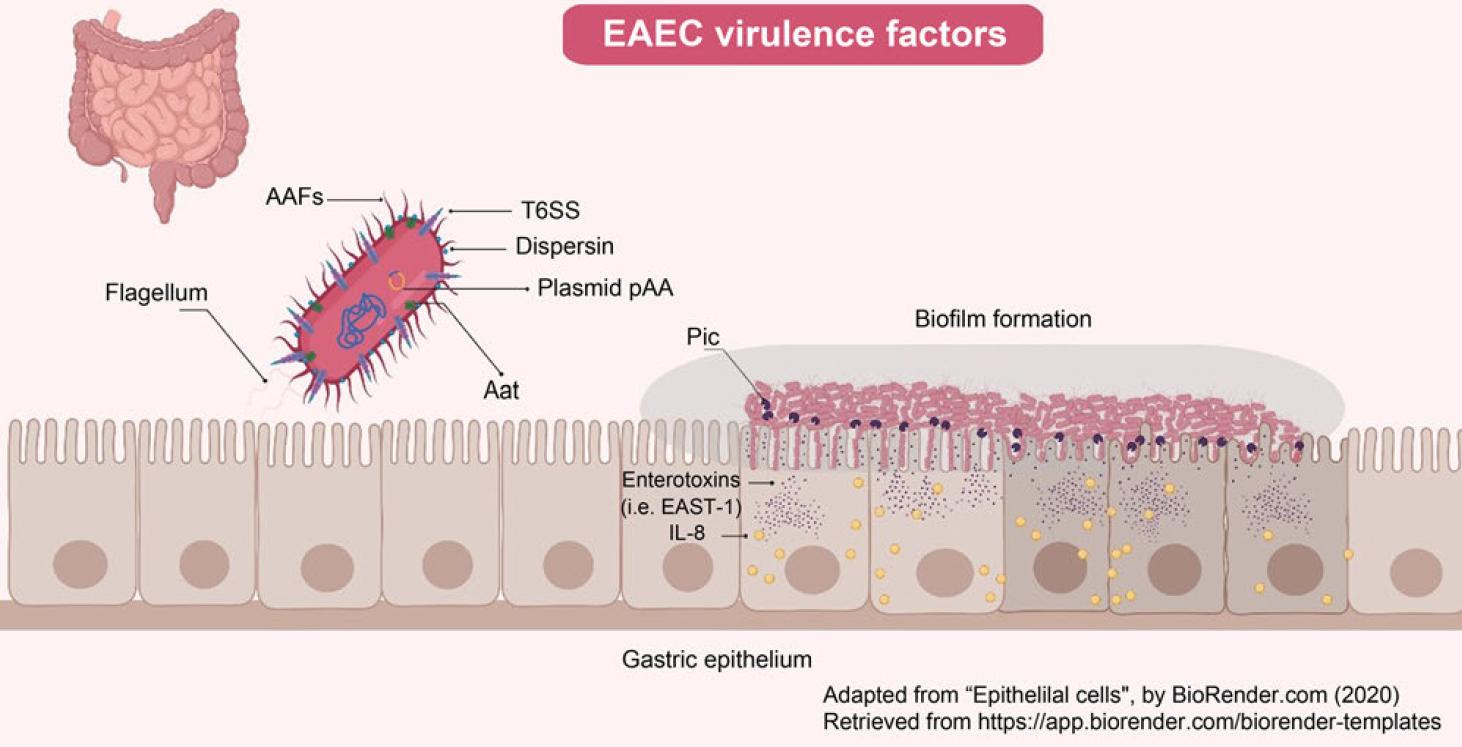
Fig. 2.
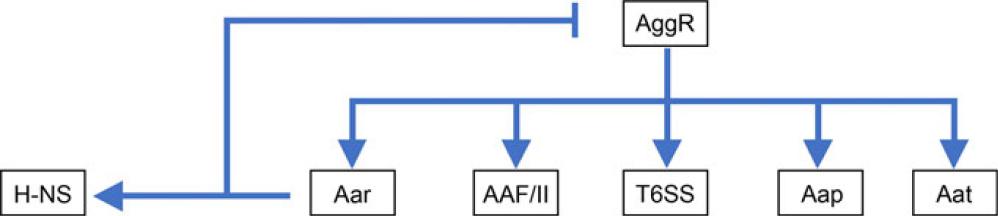
Virulence genes regulated by AggR*_
| Location | Virulence factor | Regulated genes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| pAA2 plasmid | AAF/II | aafA, aafB, aafC, aafD | major subunit, minor subunit, usher protein, chaperone of AAF/II |
| dispersin | aap | dispersin (antiaggregation protein) | |
| dispersin export apparatus | aatA, aatB, aatC, aatD, aatP | TolC-like outer membrane protein, hypothetic protein, ABC transporter, N-acyltransferase, permease protein | |
| AggR | aggR | AraC/XylS-type transcriptional regulator | |
| Aar | aar | ANR-family regulator | |
| ORF3 | EC042_RS26240 (pAA003) | isoprenyl diphosphate synthase | |
| Idi (ORF4) | idi | isopentenyl-diphosphate delta-isomerase | |
| Shf | shf | polysaccharide deacetylase | |
| EC042_RS30880 (pAA005A), EC042_RS26330 (pAA0020), (pAA0047), (pAA0056) | hypothetical proteins | ||
| Chromosome | Type VI secretion system | aaiA-U (EC042_RS24360–EC042_RS24465) | T6SS putative proteins |
| EC042_RS16995 (EC042_3181) | putative transcriptional regulator | ||
| EC042_RS17000 (EC042_3182) | ParB-type nuclease | ||
| EC042_RS17030 (EC042_3187) | putative helicase | ||
| EC042_RS17005, EC042_RS17010, EC042_RS21290 (EC042_3183, EC042_3184, EC042_4006) | hypothetic proteins |