Fig. 1

Fig. 2
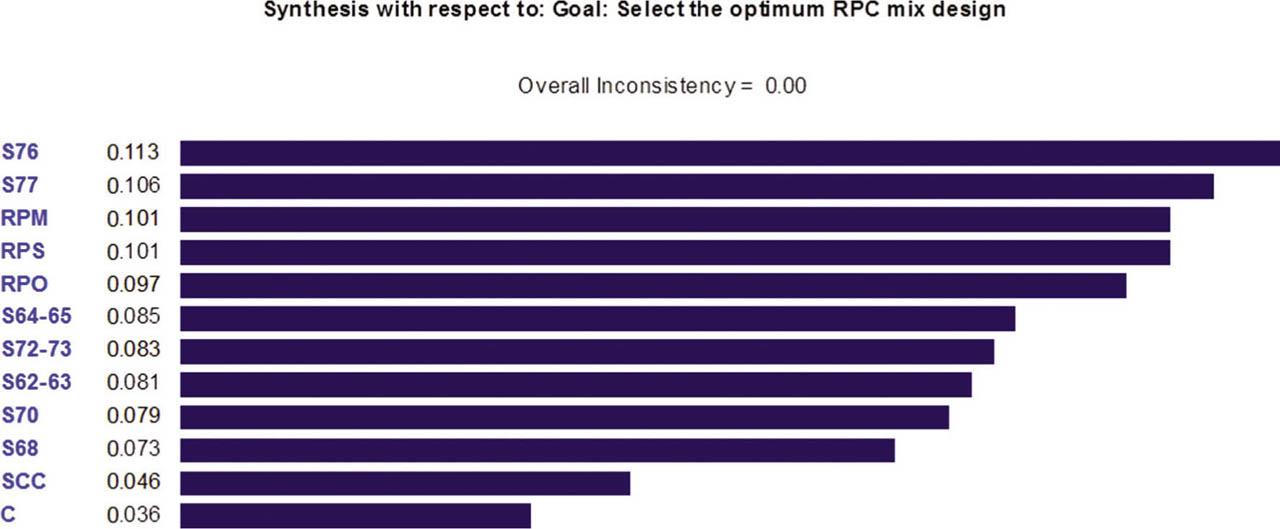
Fig. 3
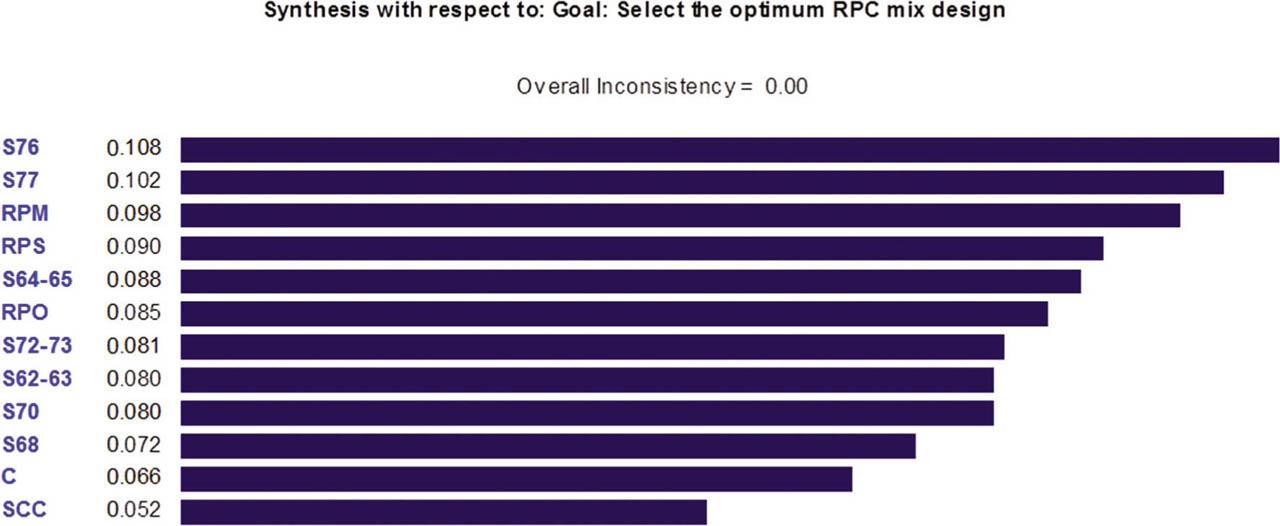
Fig. 4
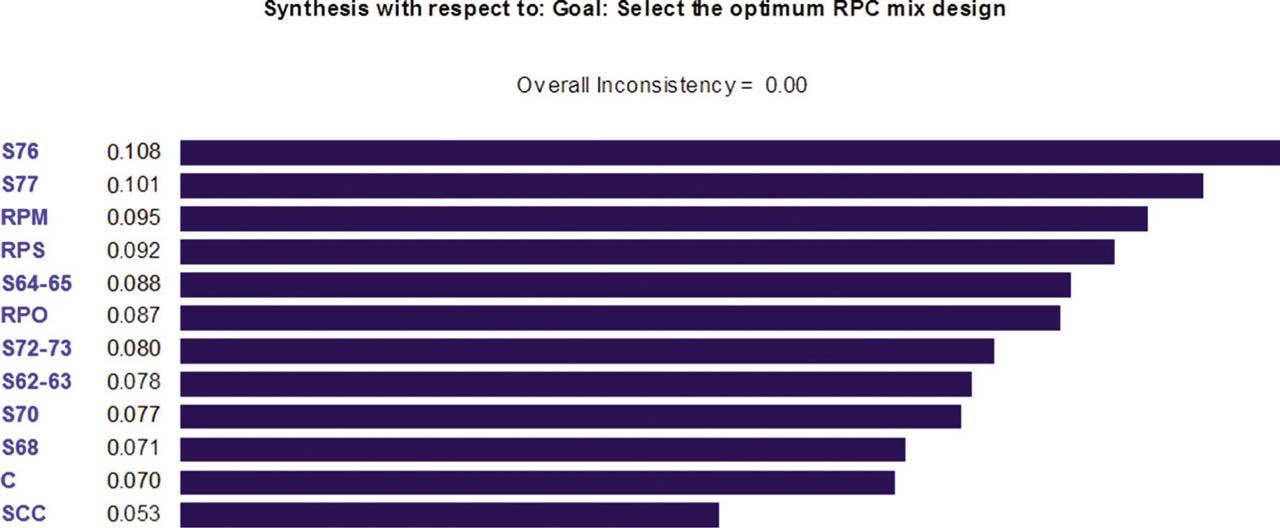
Fig. 5
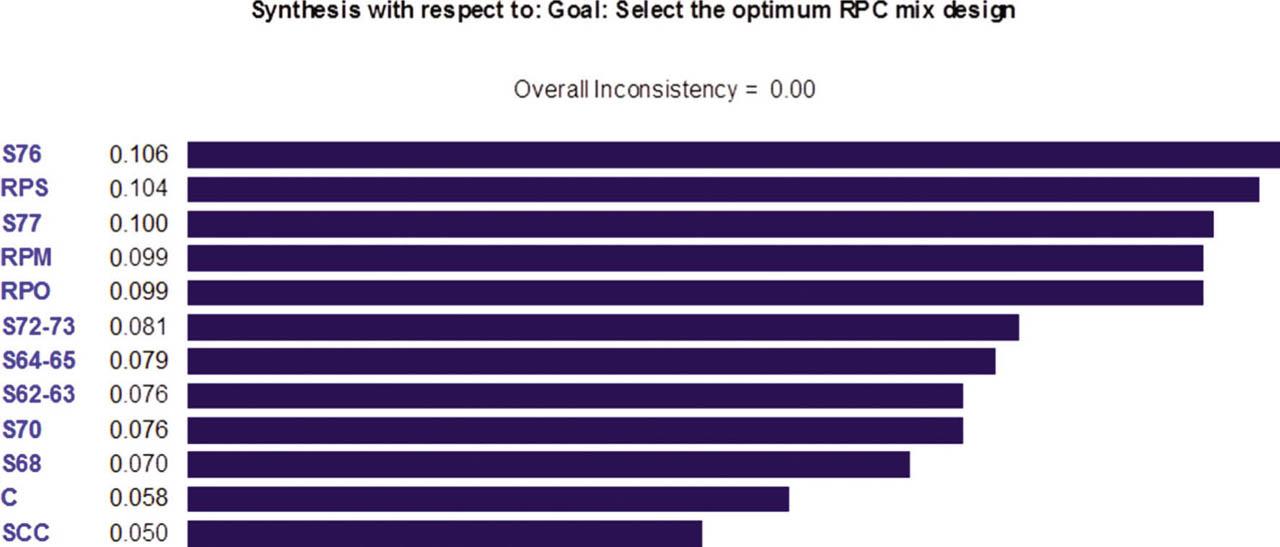
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9

Fig. 10
Mixture proportions of concrete_
| No. | Mixtures | Cement content/type (Kg) | W/CM | PCE (kg/m3) | Silica fume (kg/m3) | Colloidal nanosilica (kg/m3) | Powdered nanosilica (kg/m3) | Quartz (0–75 μm), (kg/m3) | Sand (0–75 μm), kg/m3 | Sand (0–5 mm), kg/m3 | Gravel (5–9.5 mm), kg/m3 | Gravel (9.5–19 mm), kg/m3 | Quartz (0–1 mm), kg/m3 | Quartz (75 μm to 6 mm), kg/m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S62 | 900/II | 0.28 | 48.7 | 225 | 9 | 90 | 1,000* | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2 | S63 | 900/II | 0.31 | 48.7 | 225 | 9 | 90 | 1,000* | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 3 | S64 | 900/V | 0.28 | 44 | 180 | 18 | 18 | – | 1,000 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 4 | S65 | 0.247 | 44 | 180 | 18 | 18 | – | 1,001 | – | – | – | – | – | |
| 5 | S68 | 900/V | 0.27.4 | 46.5 | 180 | 18 | 18 | – | – | 1,000 | – | – | – | – |
| 6 | S70 | 900/V | 0.27.4 | 50 | 180 | 18 | 18 | – | – | 1,000** | – | – | – | – |
| 7 | S72 | 900/II | 0.25.1 | 52 | 180 | 18 | – | – | 1,100** | – | – | – | – | – |
| 8 | S73 | 900/II | 0.27.2 | 52 | 180 | 18 | – | – | 1,100** | – | – | – | – | – |
| 9 | S76 | 900/II | 0.30.4 | 56 | 165 | 18 | – | 1,000 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 10 | S77 | 900/II | 0.27.7 | 56 | 165 | 18 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,000 | – |
| 11 | RP,S1 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | – | 139 | – | – | – | – | – | 861 |
| 12 | RP,S2 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | – | 50 | – | – | – | – | – | 950 |
| 13 | RP,S3 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | – | 100 | – | – | – | – | – | 900 |
| 14 | RP,S4 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | – | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | 1,000 |
| 15 | RP,O1 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | 165 | 268 | 567* | – | – | – | – | – |
| 16 | RP,O2 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | 165 | 567 | 268* | – | – | – | – | – |
| 17 | RP,O3 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | 85 | 315 | 600* | – | – | – | – | – |
| 18 | RP,O4 | 900/II | 0.31 | 46 | 165 | 18 | 85 | 600 | 315* | – | – | – | – | – |
| 19 | RP,M1 | 900/II | 0.25 | 40 | 165 | 18 | – | – | – | 600 | – | – | 400 | – |
| 20 | RP,M2 | 900/II | 0.25 | 40 | 165 | 18 | – | – | – | 500 | – | – | 500 | – |
| 21 | RP,M3 | 900/II | 0.25 | 40 | 165 | 18 | – | – | – | 400 | – | – | 600 | – |
| 22 | RP,M4 | 900/II | 0.25 | 40 | 165 | 18 | – | – | – | 700 | – | – | 300 | – |
| 23 | SCC1 | 400/II | 0.48 | 12 | 60 | .. | 120 | – | – | 820 | 750 | – | – | – |
| 24 | SCC2 | 400/II | 0.5 | 9 | 60 | .. | 120 | – | – | 820 | 750 | – | – | – |
| 25 | SCC3 | 400/II | 0.45 | 9 | 70 | .. | 74 | – | – | 900 | 525 | 225 | – | – |
| 26 | SCC4 | 400/II | 0.45 | 9 | 70 | .. | 74 | – | – | 800 | 450 | 400 | – | – |
| 27 | SCC5 | 400/II | 0.45 | 9 | 70 | .. | 74 | – | – | 900 | 225 | 525 | – | – |
| 28 | C1 | 400/II | 0.45 | 1.75 | .. | .. | – | – | – | 920 | 440 | 460 | – | – |
| 29 | C2 | 400/II | 0.45 | 1.75 | .. | .. | – | – | – | 900 | 220 | 700 | – | – |
| 30 | C3 | 400/II | 0.45 | 1.75 | .. | .. | – | – | – | 850 | 470 | 400 | – | – |
Chemical compositions (%) of quartz sand and silica fume_
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | Na2O | K2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz sand | 96–98.8 | 0.151–1.65 | 0.2–0.7 | 0.2–0.5 | 0.03–0.08 | 0.03–0.1 |
| Silica fume | 90 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
Optimal framework for mixing design of the concrete_
| No. | Optimum mixture | Aggregate | Cement (kg)/type | Silica fume (kg) | Powdered nanaosilica (kg) | Colloidal nanosilica (kg) | Concrete |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S76 | Quartz (0–75 μm) | 900/II | 165 | – | 18 | RPC |
| 2 | S77 | Quartz (0–1 mm) | 900/II | 165 | – | 18 | MRPC |
| 3 | RPM | Quartz + sand (0–1 mm) | 900/II | 165 | – | 18 | |
| 4 | RPS | Quartz (75 μm–6 mm) | 900/II | 165 | – | 18 | |
| 5 | RPO | Quartz + Ottawa (0–75 μm) | 900/II | 165 | 85–165 | 18 | RPC |
| 6 | S64–65 | Sand (0–75 μm) | 900/V | 180 | 18 | 18 | |
| 7 | S72–73 | Crystal sand (0–75 μm) | 900/II | 180 | – | 18 | |
| 8 | S62–63 | Ottawa sand | 900/II | 225 | 90 | 9 | |
| 9 | S70 | Crystal sand (0–5 mm) | 900/V | 180 | 18 | 18 | MRPC |
| 10 | S68 | Sand (0–5 mm) | 900/V | 180 | 18 | 18 | |
| 11 | C | Gravel + sand | 900/II | – | – | – | C |
| 12 | SCC | Gravel + sand | 900/II | 60–70 | 74–120 | – | SCC |
Prices reserved for consumable materials_
| Materials | Quartz (ton) | PCE (kg) | Cement (ton) | Silica fume (ton) | Colloidal nanosilica (kg) | Ottawa sand (kg) | Gravel + sand (ton) | Crystal sand (ton) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price, $ | 4 | 1.6 | 16 | 44 | 4.8 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
Properties of colloidal nanosilica, powdered nanosilica and silica fume_
| SiO2, % | Size, nm | Specific surface area, m2/g | Salt content (%) | Type | Density, kg/m3 (lb/yd3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colloidal nanosilica | 99.9 | 35 | 400 | 24 | Combiner | 1.05 (1.77) |
| Powdered nanosilica | 99 | 20–30 | 160–200 | 100 | Powder | 0.150–0.220 (0.253–0.37) |
| Silica fume | 90 | 229 | 20.7 | 100 | Powder | 2.1 (3.54) |
Test results for the compressive strength, surface resistivity, water penetration and modulus of elasticity (Ed)_
| No. | Mixtures | Compressive strength (28 days), MPa | Surface resistivity, kΩ·cm | Water penetration, mm | Ed, GPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23°C | 80°C | |||||
| 1 | S 62 | 138.8 | – | 95 | 9.5 | 56.68 |
| 2 | S63 | 118.7 | – | 73 | 12.1 | 52.66 |
| 3 | S64 | 146.3 | – | 63.9 | 12.4 | 59.32 |
| 4 | S65 | 174.5 | – | 68 | 12.1 | 67.82 |
| 5 | S68 | 100.6 | – | 79.1 | 10.5 | 49.17 |
| 6 | S70 | 118.1 | – | 89.6 | 11 | 53.63 |
| 7 | S72 | 120.2 | – | 107.9 | 7.5 | 55.98 |
| 8 | S73 | 113.4 | – | 76.6 | 10 | 48.24 |
| 9 | S76 | 137 | 193.5 | 125 | 6.1 | 78.53 |
| 10 | S77 | 125.3 | 187 | 123 | 6.6 | 74.27 |
| 11 | RP,S 1 | 98.1 | 125.3 | 154 | 5.2 | 48.82 |
| 12 | RP,S2 | 96.5 | 127.2 | 104 | 5.4 | 49.29 |
| 13 | RPS,3 | 97.6 | 118.3 | 112 | 6.1 | 50.87 |
| 14 | RP,S4 | 95.2 | 115.4 | 195 | 4.2 | 48.68 |
| 15 | RP,O1 | 89.8 | 112.4 | 174 | 4.4 | 42.05 |
| 16 | RP,O2 | 93.5 | 127.2 | 121 | 5.5 | 43.87 |
| 17 | RP,O3 | 95.4 | 118.6 | 158 | 4.1 | 49.85 |
| 18 | RP,O4 | 91.4 | 115.9 | 83 | 7.4 | 42.61 |
| 19 | RP,M1 | 121.2 | 174.3 | 124 | 6.4 | 65.63 |
| 20 | RP,M2 | 119.4 | 161.2 | 92 | 9.5 | 61.97 |
| 21 | RP,M3 | 105.4 | 145.4 | 113 | 7.5 | 63.97 |
| 22 | RP,M4 | 104.3 | 138.3 | 180 | 4.5 | 59.37 |
| 23 | SCC1 | 52.3 | – | 42.35 | 15 | 34.43 |
| 24 | SCC2 | 48.9 | – | 37.5 | 18 | 33.76 |
| 25 | SCC3 | 57.6 | – | 77.85 | 12 | 38.22 |
| 26 | SCC4 | 55.1 | – | 33 | 14.3 | 34.98 |
| 27 | SCC5 | 44.2 | – | 37 | 16 | 31.51 |
| 28 | C1 | 38.2 | – | 5.2 | 21.5 | 41.57 |
| 29 | C2 | 36.5 | – | 4.8 | 33.3 | 37.53 |
| 30 | C3 | 35.4 | – | 7.3 | 35.5 | 34.64 |
Selection options in the software_
| Mixtures, kg/m3 | S62–63 | S64–65 | S72–73 | S76 | RPO | RPM | RPS | S68 | S70 | S77 | SCC | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregate | Ottawa sand | Sand (0–75 μm) | Crystal sand (0–75 μm) | Quartz (0–75 μm) | Quartz (0–75 μm), Ottawa | Sand + quartz | Quartz (0–1 mm) | Sand (75 μm–6 mm) | Crystal sand (0–5 mm) | Quartz (0–1 mm) | Gravel + sand | Gravel +sand |
| Cement type | II | V | II | II | II | II | II | V | V | II | II | II |
| Silica fume | 225 | 180 | 180 | 165 | 165 | 165 | 167 | 180 | 180 | 165 | 6–70 | – |
| Powder nanosilica | 90 | 18 | – | – | 85–165 | – | – | 18 | 18 | – | 74–120 | – |
| Colloidal nanosilica | 9 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | – | – |
| Concrete | RPC | MRPC | SCC | C | ||||||||