Fig. 1.
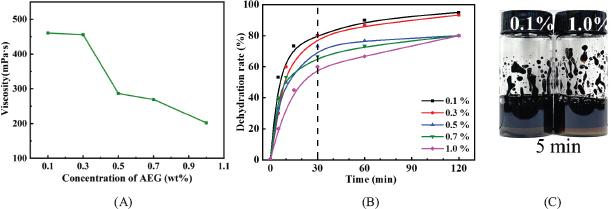
Fig. 2.
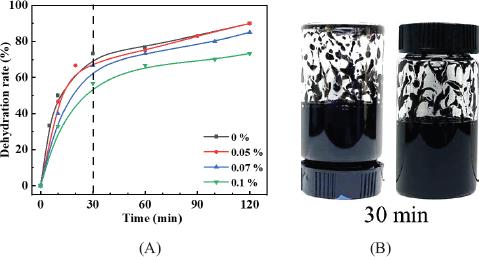
Fig. 3.
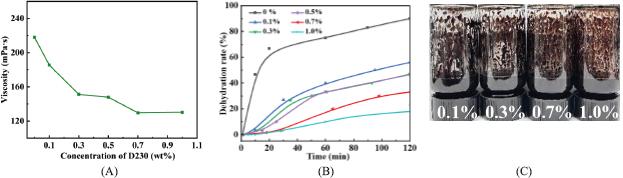
Fig. 4.
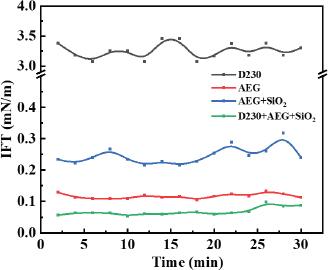
Fig. 5.
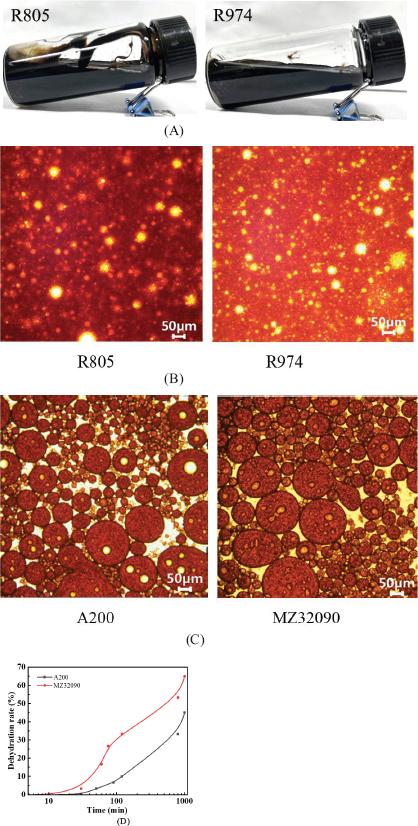
Fig. 6.
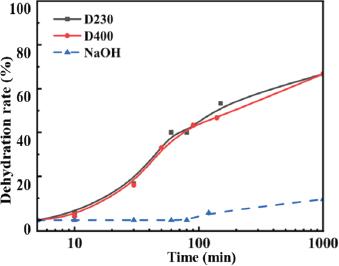
Fig. 7.
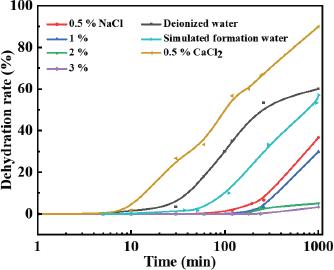
Fig. 8.
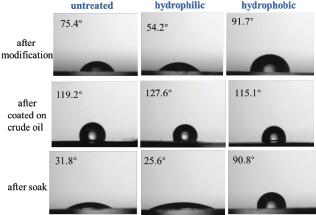
Fig. 9.

Imbibition recovery rate of artificial core
| Viscosity reducer immersion | Formation water immersion | |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation (%) | 78.5 | 74.0 |
| Recovery rate (%) | 49.4 | 29.6 |
Basic properties of crude oil used in this study
| Samples | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Acid value (mg KOH/g) | Saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene (SARA) composition (%) | Moisture content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25◦C | 50◦C | Saturate | Aromatic | Resin | Asphaltene | |||
| 1# | 52212 | 6862 | 2.27 | 34.07 | 35.20 | 27.63 | 3.10 | 10 |
| 2# | 21494 | 2458 | 0.43 | 39.08 | 32.47 | 23.31 | 5.14 | 21 |
Influence of SiO2 nanoparticles on viscosity of acidic crude oil emulsion
| Nanoparticles type | Diameter (nm) | Surface wettability (water contact angle) | Viscosity (mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A200 | 12 | 18.2◦ | 135.9 |
| MZ32090 | 30 | 30.5◦ | 134.7 |
| R974 | 12 | 117.2◦ | – |
| R805 | 12 | 131.3◦ | – |
Effect of salinity on viscosity of acidic crude oil emulsion
| Total salinity (mg/L) | Deionized water | NaCl | CaCl2 | Simulated formation water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | 5000 | 10000 | 20000 | 30000 | 50000 | 5000 | 5722 | |
| Viscosity (mPa·s) | 123 | 281 | 221 | 153 | 223 | – | 114 | 128 |
Effect of alkali type on viscosity of acidic crude oil emulsion
| Types of alkali | pH of viscosity reducer | Viscosity emulsion (mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|
| D400 | 10.82 | 109.6 |
| D230 | 10.89 | 129.6 |
| NaOH | 12.62 | 133.7 |