Fig. 1
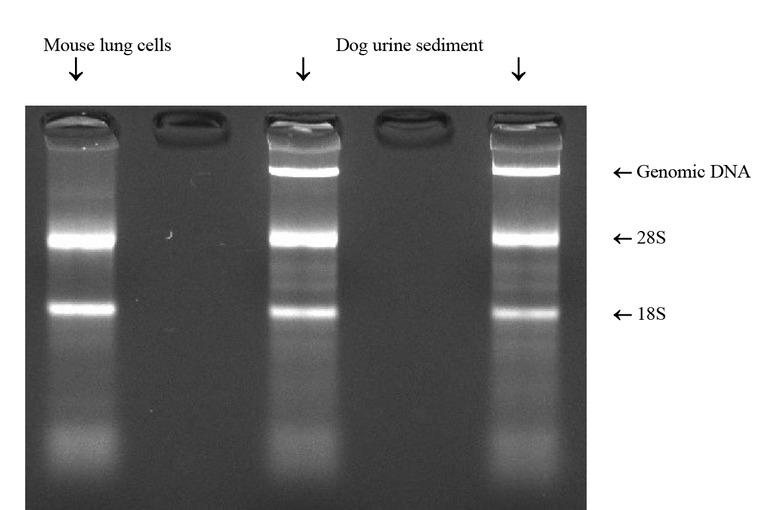
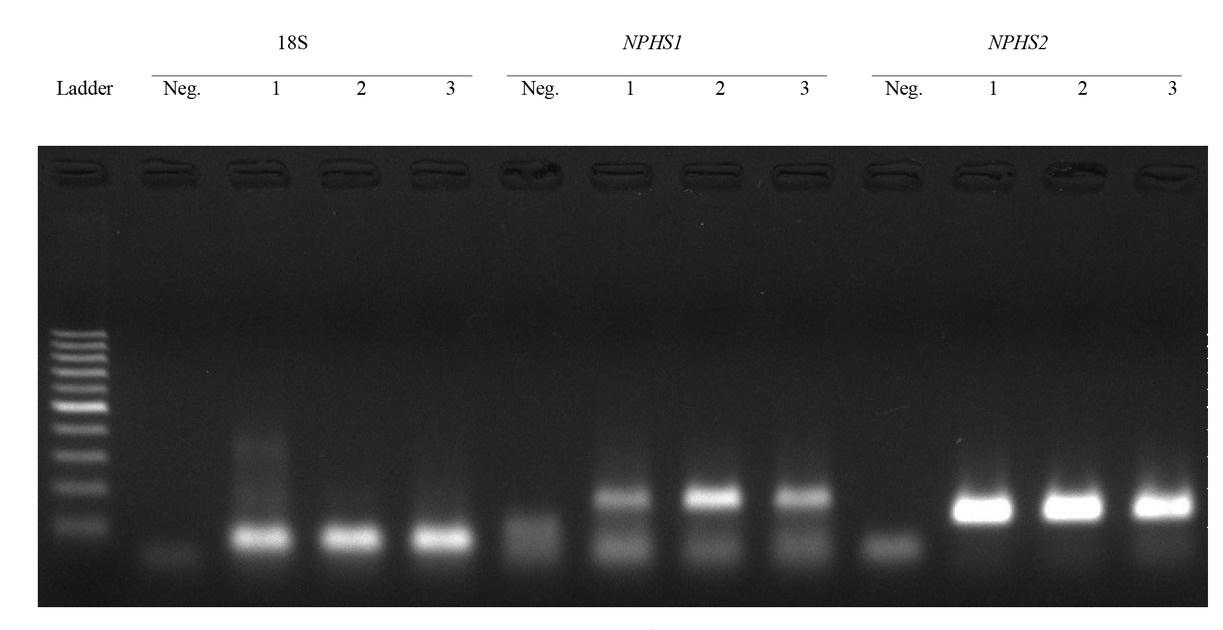
Fig. 2
Results for blood haematological parameters in healthy dogs and dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at different stages
| CKD dogs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter (reference range) | Healthy dogs (n = 10) | Stage 1 or 2 (n = 5) | Stage 3 or 4 (n = 9) |
| RBC (106/μL) (5.5–8.5) | 6.7 ± 0.35 | 6.7 ± 0.49 | 4.7 ± 0.36** |
| HGB (g/dL) (12–18) | 17.3 ± 0.83 | 16.7 ± 1.17 | 11.6 ± 0.88** |
| HCT (%) (37–55) | 50.1 ± 2.49 | 49.7 ± 3.52 | 34.9 ± 2.63** |
| MCV (fL) (60–77) | 75.2 ± 1.49 | 75.0 ± 2.11 | 75.2 ± 1.57 |
| MCH (pg) (21–26) | 26.0 ± 0.58 | 25.2 ± 0.82 | 25.0 ± 0.61 |
| MCHC (%) (32–36) | 34.6 ± 0.44 | 33.7 ± 0.62 | 33.2 ± 0.47 |
| PLT (103/μL) (200–500) | 307 ± 57.60 | 386 ± 39.7 | 378 ± 64.0 |
| RBC morphology | normal | normal | normal |
| WBC (103/μL) (6–17) | 7.1 ± 0.63 | 8.8 ± 1.35 | 7.5 ± 1.02 |
| WBC morphology | normal | normal | normal |
Results for blood biochemical parameters in healthy dogs and dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at different stages
| CKD dogs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter (reference range) | Healthy dogs (n = 10) | Stage 1 or 2 (n = 5) | Stage 3 or 4 (n = 9) |
| Albumin (g/dL) (2.3–3.8) | 3.2 ± 0.16 | 2.8 ± 0.23 | 2.7 ± 0.20 |
| Urea (mg/dL) (10–60) | 39.4 ± 5.36 | 47.3 ± 13.48 | 259.4 ± 46.70* |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) (0.5–1.4) | 1.1 ± 0.14 | 1.0 ± 0.17 | 7.4 ± 2.34* |
Semi-quantitative analysis of detection of NPHS1 (nephrin mRNA) and NPHS2 (podocin mRNA) in urine sediment samples from healthy dogs and dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at different stages
| CKD dogs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Healthy dogs | Stage 1 or 2 | Stage 3 or 4 | P value |
| NPHS1 detection | 4/10 (40%) a | 3/5 (60%) b | 1/9 (11%) c | 0.0009 |
| NPHS2 detection | 2/10 (20%) a | 4/5 (80%) b | 1/9 (11%) a | 0.0188 |
Results for routine urinary parameters in healthy dogs and dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at different stages
| CKD dogs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter (reference range) | Healthy dogs (n = 10) | Stage 1 or 2 (n = 5) | Stage 3 or 4 (n = 9) |
| USG (1.015–1.045) | 1.037 ± 0.0040 | 1.022 ± 0.0074* | 1.014 ± 0.0009** |
| Protein (mg/dL) | 29.4 ± 2.44 | 210.6 ± 11.67*** | 124.0 ± 35.76* |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 206.1 ± 24.00 | 94.4 ± 21.47** | 70.0 ± 21.47** |
| UPC (< 0.5) | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 2.25 ± 0.68* | 1.76 ± 0.50* |
| Chemical analysis | |||
| (semiquantitative testing): | |||
| pH (6.0–7.5) | 6.5 ± 0.37 | 6.4 ± 0.52 | 5.9 ± 0.39 |
| Protein | between 0 and 1+ | between 1 and 3+ | between 1 and 2+ |
| Glucose | negative | negative | negative |
| Ketones | negative | negative | negative |
| Bilirubin | negative | negative | negative |
| Urobilinogen | normal | normal | normal |
| Occult blood | negative | 1+ in the urinary sediment of 1 dog | 1+ in the urinary sediment of 2 dogs |
| Microscopic sediment | |||
| examination: | |||
| Epithelial cells/HPF (<3) | 1.70 ± 0.26 | 1.00 ± 0.22 | 1.44 ± 0.43 |
| Granular cast/HPF (<1) | rare in the urinary sediment of 1 dog | none | rare in the urinary sediment of 1 dog |
| Triple phosphate crystal | 1+ in the urinary sediment of 2 dogs | 2+ in the urinary sediment of 1 dog | none |
| Amorphous phosphate crystal | none | none | 2+ in the urinary sediment of 1 dog |
| RBC/HPF (<5) | 0.30 ± 0.13 | 0.30 ± 0.20 | 0.56 ± 0.49 |
| WBC/HPF (<5) | 0.50 ± 0.18 | 0.60 ± 0.25 | 0.83 ± 0.25 |
| Bacteria | none | none | none |
Semi-quantitative analysis of renal ultrasonographic abnormalities in dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at different stages
| CKD dogs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Stage 1 or 2 | Stage 3 or 4 | P value |
| Irregular contour | 5/5 (100%) | 6/9 (67%) | <0.0001 |
| Loss of corticomedullary differentiation | 4/5 (80%) | 8/9 (89%) | 0.1170 |
| Increased cortical echogenicity | 4/5 (80%) | 8/9 (89%) | 0.1170 |
| Increased medullary echogenicity | 0/5 | 5/9 (56%) | 0.0197 |