Figure 1.

Figure 2.

Figure 3.

Figure 4.

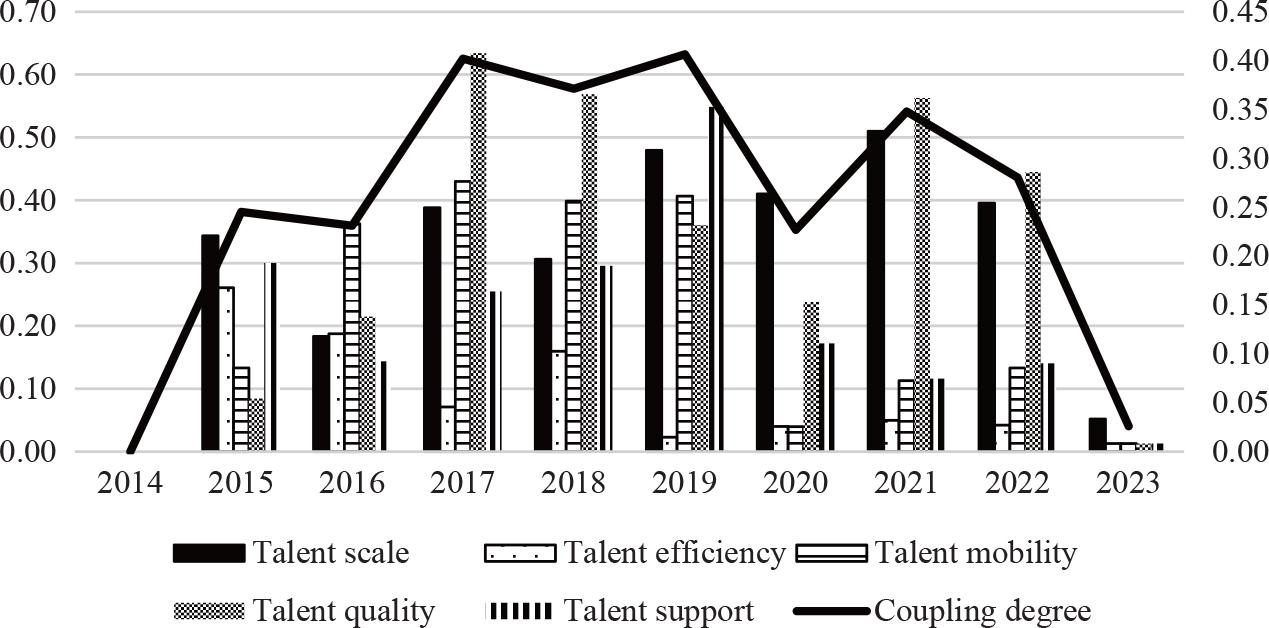
Figure 5.
Quantitative scoring criteria for policy objectives_
| Scoring | Quantitative scoring standards for policy tools |
|---|---|
| 5 | Clear objectives with specific and detailed content |
| 4 | Clear objectives, involving some content |
| 3 | Clear objectives, but the content is somewhat vague |
| 2 | Clear objectives, but without specific content |
| 1 | Only involves objectives, with no specific content |
Policy tool coding and scoring classification system_
| Primary classification | Secondary classification | Evaluation content |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluation and incentive | Funding Support | Government provides various types of funding and financial support to incentivize talent development. |
| Talent Rewards | Rewards are given based on outstanding performance to motivate talent. | |
| Talent Titles | High evaluations of talent lead to titles being conferred, including designations | |
| Management and service | Public Service Provision | Addressing issues related to education, healthcare, children’s schooling, and social security for talent. |
| Talent Management System | The system and model established by the government for managing talent. | |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Building, standardizing, and improving the intellectual property protection system to safeguard the rights of talent and employers. | |
| Financial and Fund Management | Policies related to finance, taxation, interest subsidies, and fund management. | |
| Strategic Measures | Government formulates strategic measures based on the needs of talent development, including strategic layouts and core tasks. | |
| Flow and configuration | Employment Encouragement | The government encourages employment for college graduates and other talents to promote mobility. |
| Industry-Academia-Research Collaboration | Strengthening regional talent mobility through collaboration among industry, academia, and research. | |
| Inter-Regional Mobility | Policies like the “Three Supports and One Assistance” and Science and Technology Commissioner programs specifically designate talent for mobility. | |
| Import and cluster | Introduction of Foreign Talent | Implementing measures to attract foreign talent. |
| Domestic and International Talent Entrepreneurship | Supporting talent entrepreneurship to achieve talent aggregation. | |
| Training and development | Infrastructure Development | Establishing talent platforms such as training bases, including their application and management. |
| Training Methods | Proposing various methods for talent training, such as attending training courses. | |
| Talent Training System | Establishing a system or model for talent training. | |
| Development planning | Goal Clarity | Planning policies with clearly defined goals. |
| Implement ability of Measures | Measures in the planning are detailed and actionable, not overly vague or broad. | |
| Comprehensive | Department Authority | The more authoritative the department, the better it can coordinate various policy tools from a higher level. |
| Diversity of Measures | The more diverse the policy tools, the stronger the policy effectiveness. |
Quantitative scoring standards for policy tools_
| Scoring | Quantitative scoring standards for policy tools |
|---|---|
| 5 | There are specific policy tools with detailed implementation content. |
| 4 | There are specific policy tools that involve some implementation content. |
| 3 | There are specific policy tools that involve implementation content, but it is somewhat vague. |
| 2 | Policy tools are mentioned, but there is no implementation content. |
Policy objective coding and rating classification_
| Primary classification | Evaluation content |
|---|---|
| Increase in Talent Scale | Emphasizes the expansion of the talent pool, increasing the number of talents, and enhancing talent aggregation. |
| Improvement in Talent Quality | Emphasizes the enhancement of the quality and capabilities of the talent workforce. |
| Enhancement of Talent Effectiveness | Emphasizes generating economic and social benefits through talent development, thereby driving regional industrial growth or enhancing innovation capabilities. |
| Increase in Talent Mobility | Emphasizes the orderly and reasonable flow of talents both domestically and internationally, as well as between regions. |
| Optimization of Talent Support | Emphasizes providing funding, infrastructure, projects, and other support for talents. |
Evolution of compensatory fit value in China’s science and technology talent policy_
| Year | Value of compensatory fit | Year | Value of compensatory fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | (0.707, 1) | 2019 | (0.902, 1) |
| 2015 | (0.767, 1) | 2020 | (0.911, 1) |
| 2016 | (0.774, 1) | 2021 | (0.944, 1) |
| 2017 | (0.821, 1) | 2022 | (0.992, 1) |
| 2018 | (0.842, 1) | 2023 | (0.999, 1) |
Talent demand - goal analysis system_
| Primary classification | Secondary classification |
|---|---|
| Talent scale | Scale of Junior Talent - Number of Graduates from Higher Education Institutions (10,000 persons) |
| Scale of Intermediate Talent - R&D Personnel Full-Time Equivalent (10,000 person-years) | |
| Scale of Senior Talent - Number of Academicians of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (persons) | |
| Talent efficiency | Economic Efficiency - Per Capita GDP (hundred yuan/person) |
| Social Efficiency - Overall Labor Productivity (100 million yuan/10,000 persons) | |
| Technology Conversion Efficiency - Transaction Volume of Technology Market (hundred billion yuan) | |
| Talent mobility | Regional Talent Circulation - Urbanization Rate (%) |
| Regional Talent Disparity - Disposable Income Ratio of Rural and Urban Residents (ratio) | |
| Regional Talent Employment - Ratio of Employment between Urban and Rural Areas (ratio) | |
| Talent quality | Basic Talent - Number of Published Scientific Papers (10,000 papers) |
| Technical Talent - Number of Authorized Invention Patent Applications (items) | |
| Talent support | Medical Support for Talent - Number of Medical and Health Institutions (10,000) |
| Cultural Support for Talent - Number of Public Library Institutions (units) |