Fig. 1
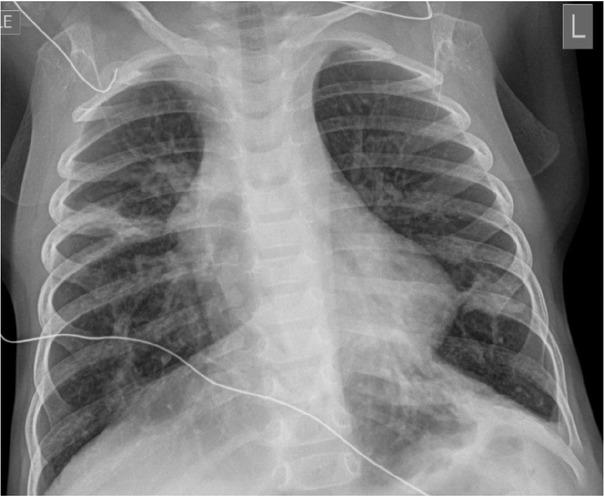
Fig. 2
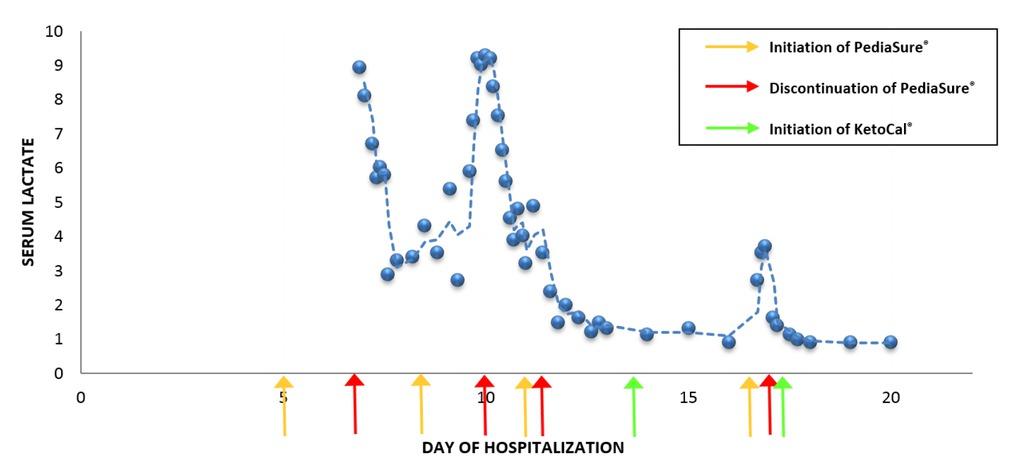
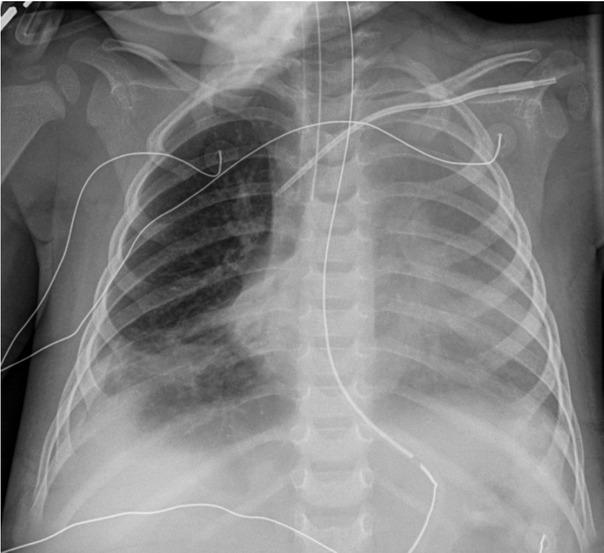
Fig. 3
Pertinent laboratory results of the patient
| Labs | Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of collection | pH | pCO2 (mmHg) | pO2 (mmHg) | HCO3 (mmol/L) | Serum lactate (mmol/L) | |
| 2 hours prior to respiratory arrest (Hospital Day 6) (Capillary gas) | 7.42 | 22 | 81 | 14.2 | 8.9 | |
| Blood | 1 hour after respiratory arrest (Hospital Day 6) (Capillary gas) | 7.12 | 41.5 | 125 | 13.5 | 8.1 |
| gases | 36 hours after initiation of Pediasure® (Hospital Day 8) (Venous gas) | 7.31 | 51.1 | 45.7 | 25.4 | 9.3 |
| After development of ARDS (Hospital Day 13) (Arterial gas) | 7.42 | 52 | 55 | 33.5 | 1.3 | |
| Serum pyruvate level (mg/dL) | 2.42 (Reference range: 0.3-1.5) | |||||
| Blood lactate to pyruvate ratio | 14.87 | |||||
| Activated PDC level (nmol/min/mg protein) | 0.35 (Reference range: 1.2-6.52) | |||||
| Skeletal muscle biopsy | PDC/E3 ratio | 0.4 (Reference range: 0.82-4.54) | ||||
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase and mitochondrial complex panel | Positive for pyruvate dehydrogenase alpha 1 (PDHA1) gene mutation | |||||