Figure 1:
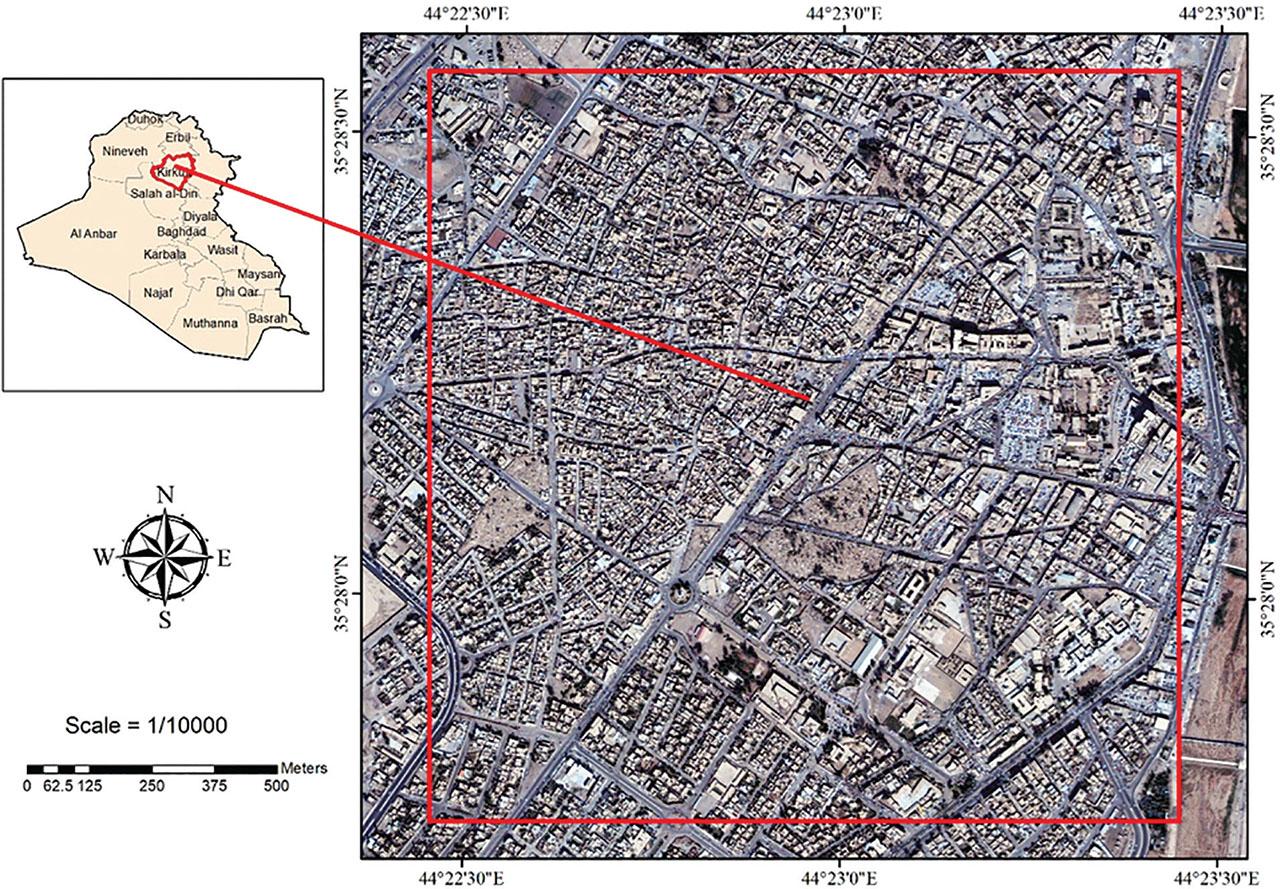
Figure 2:
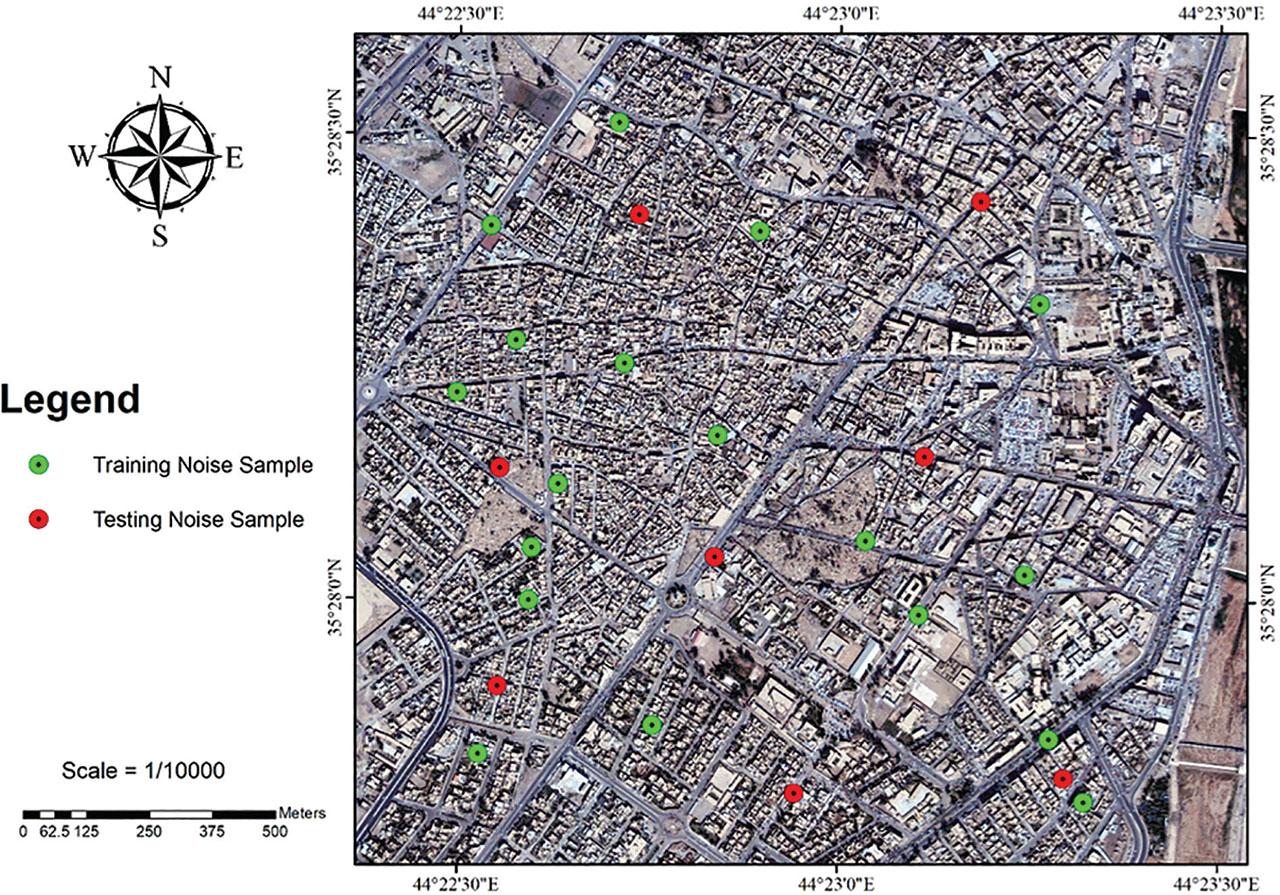
Figure 3:
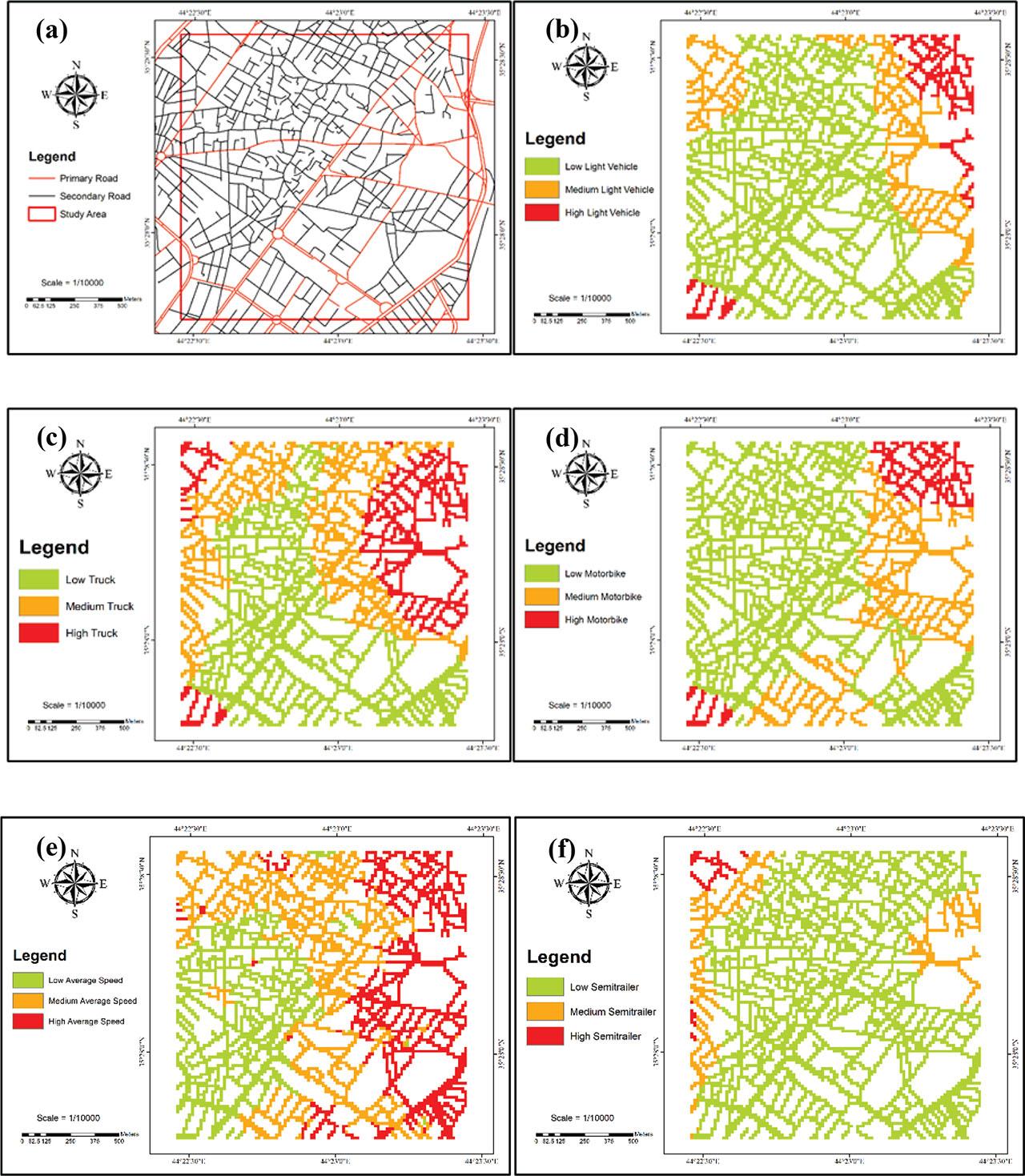
Figure 4:
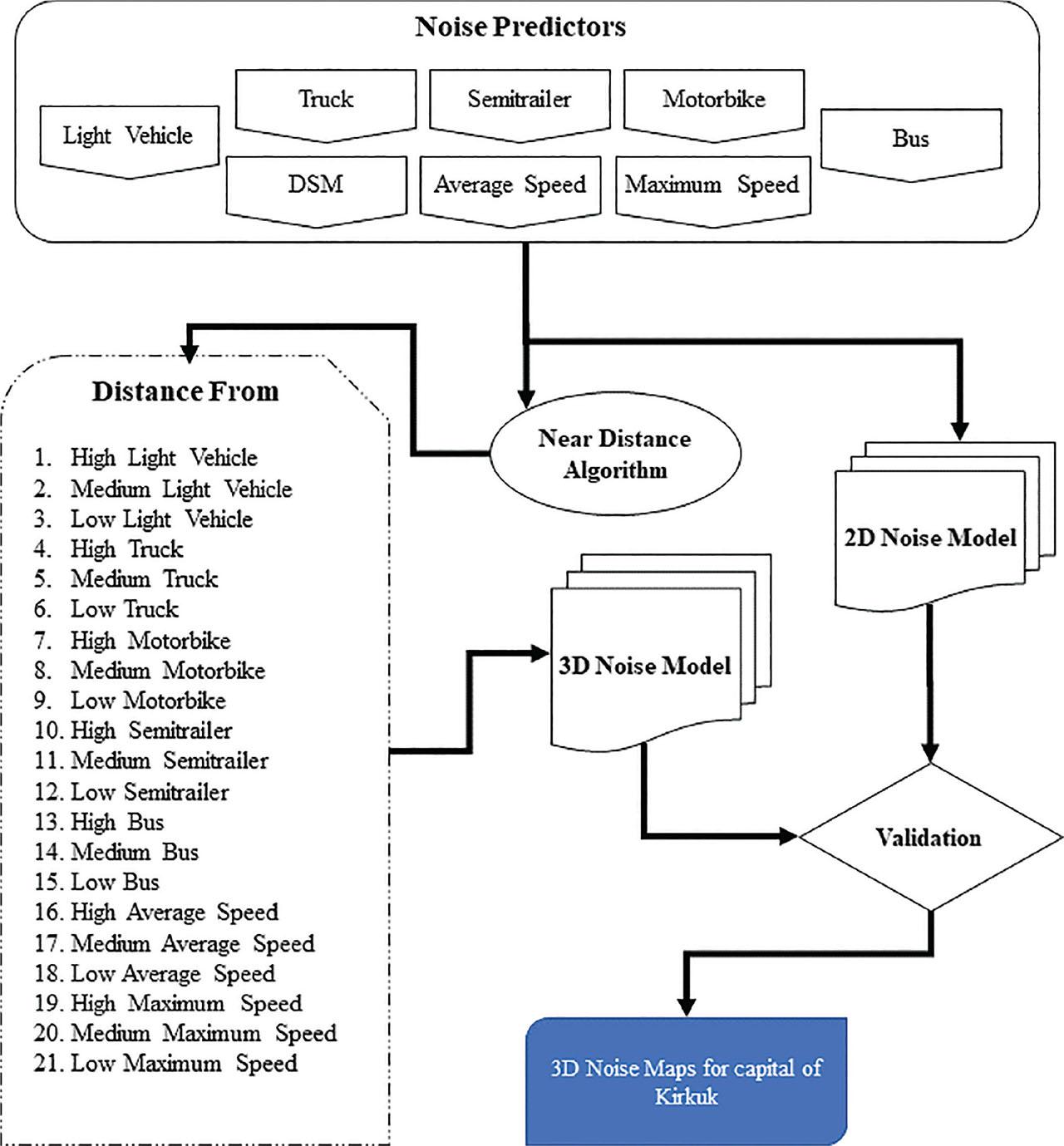
Figure 5:
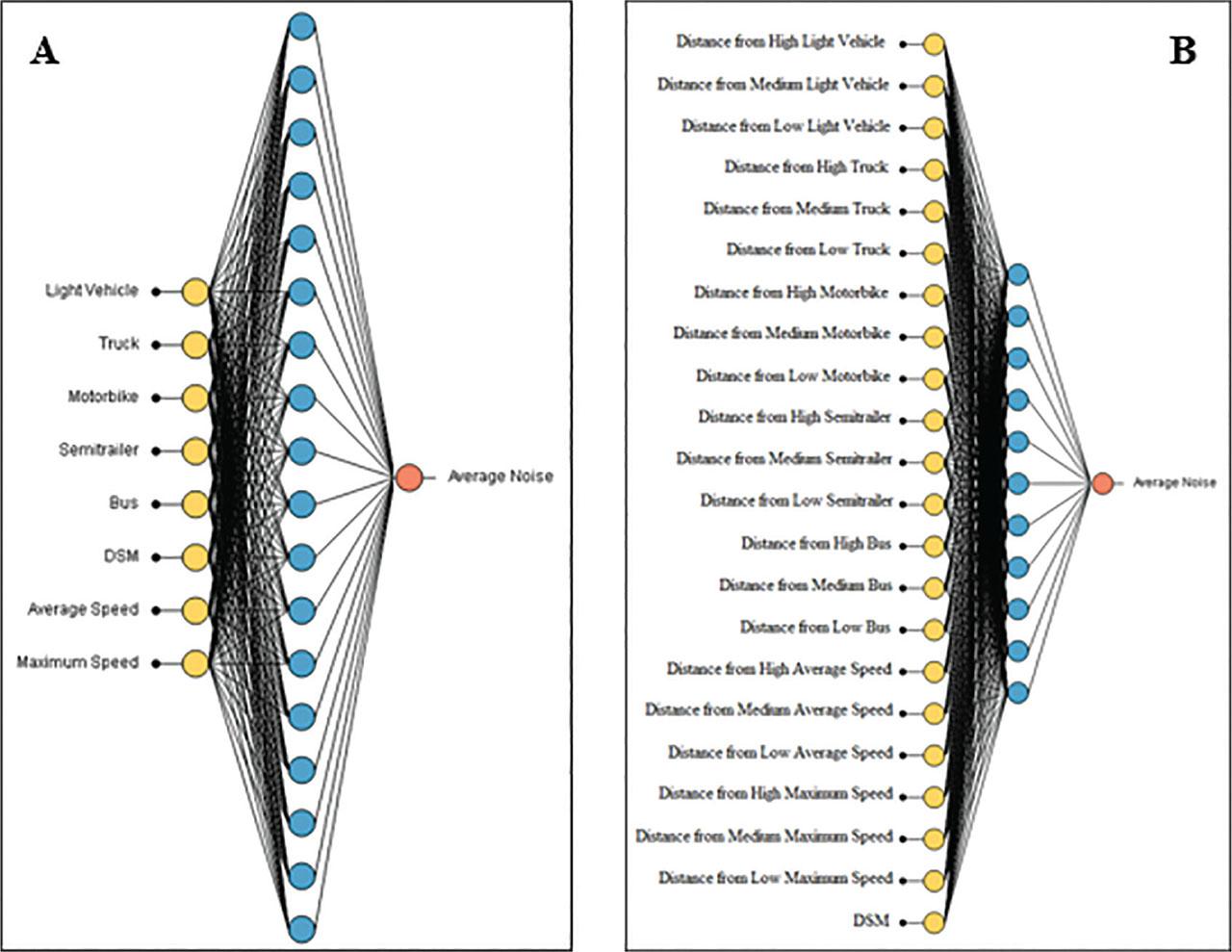
Figure 6:
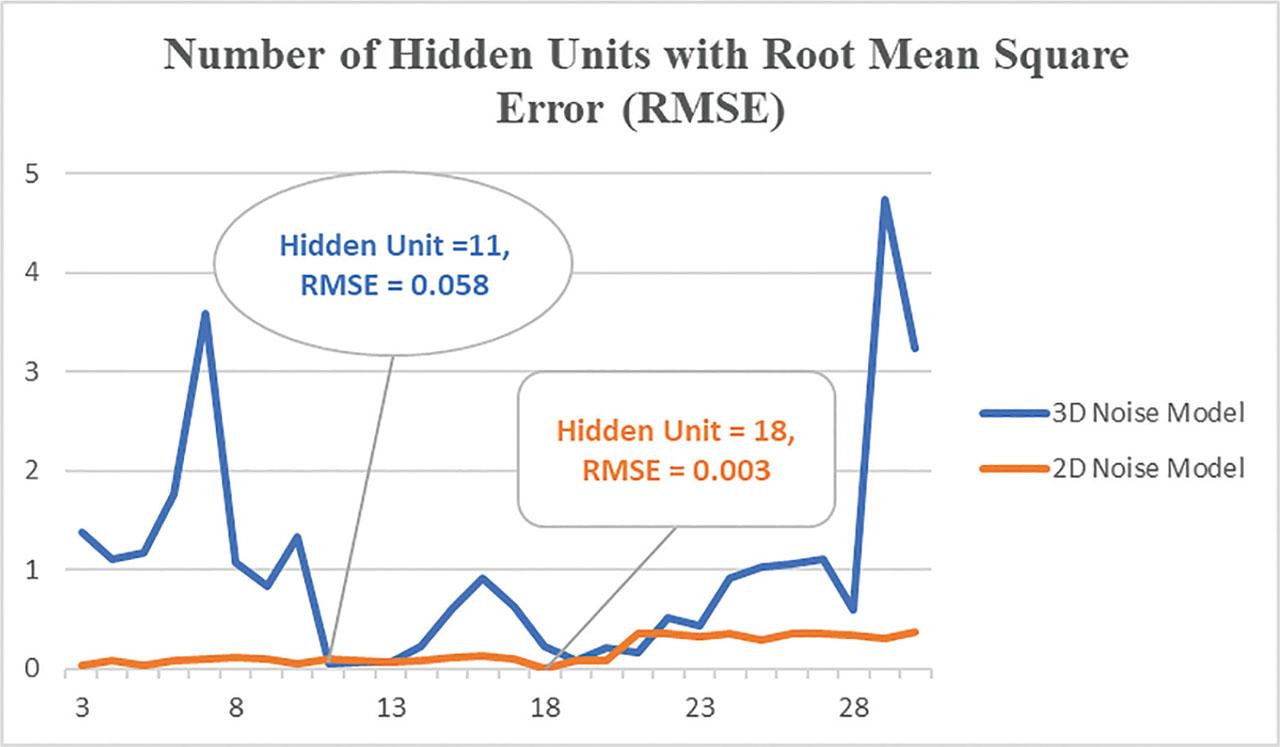
Figure 7:
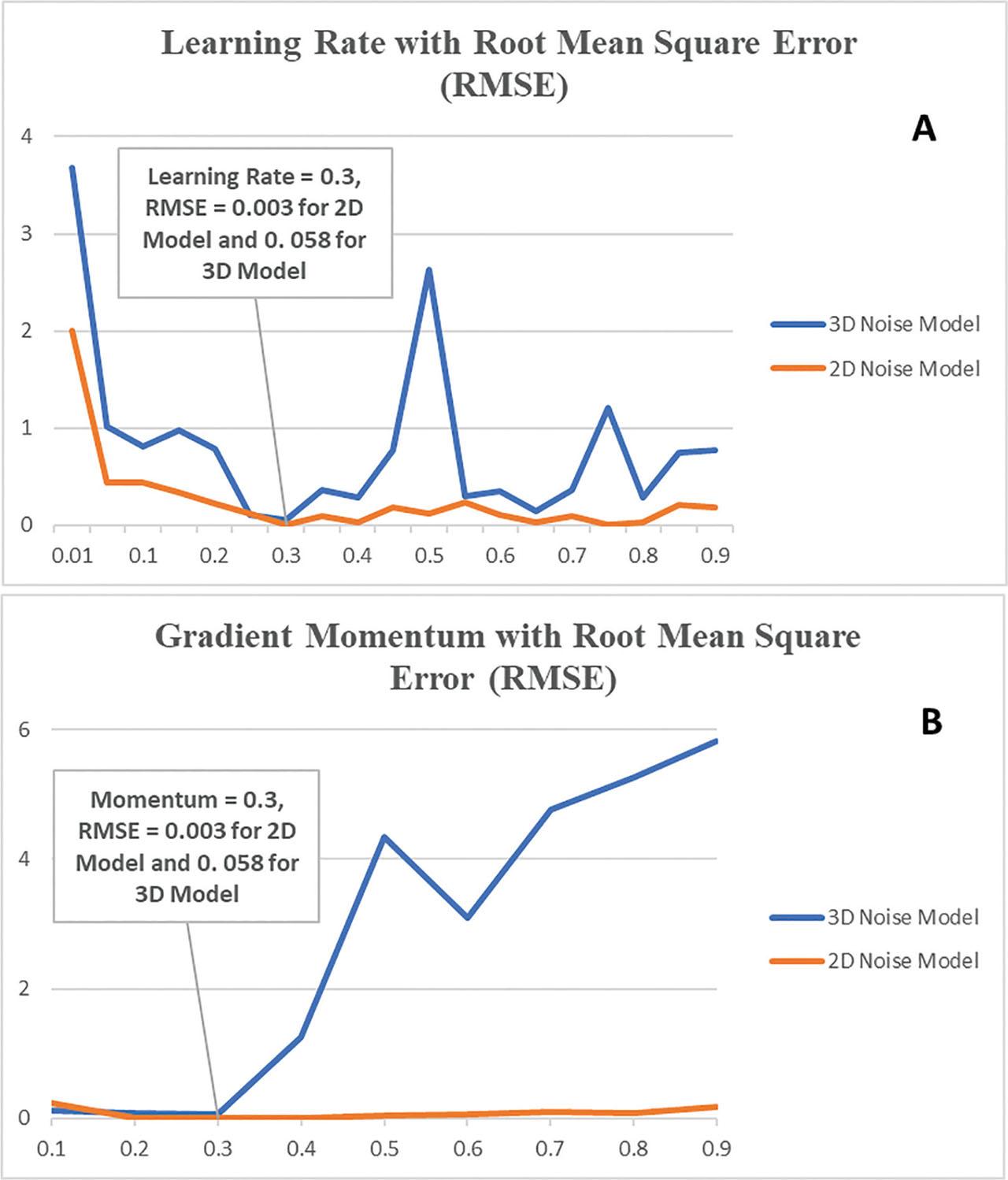
Figure 8:
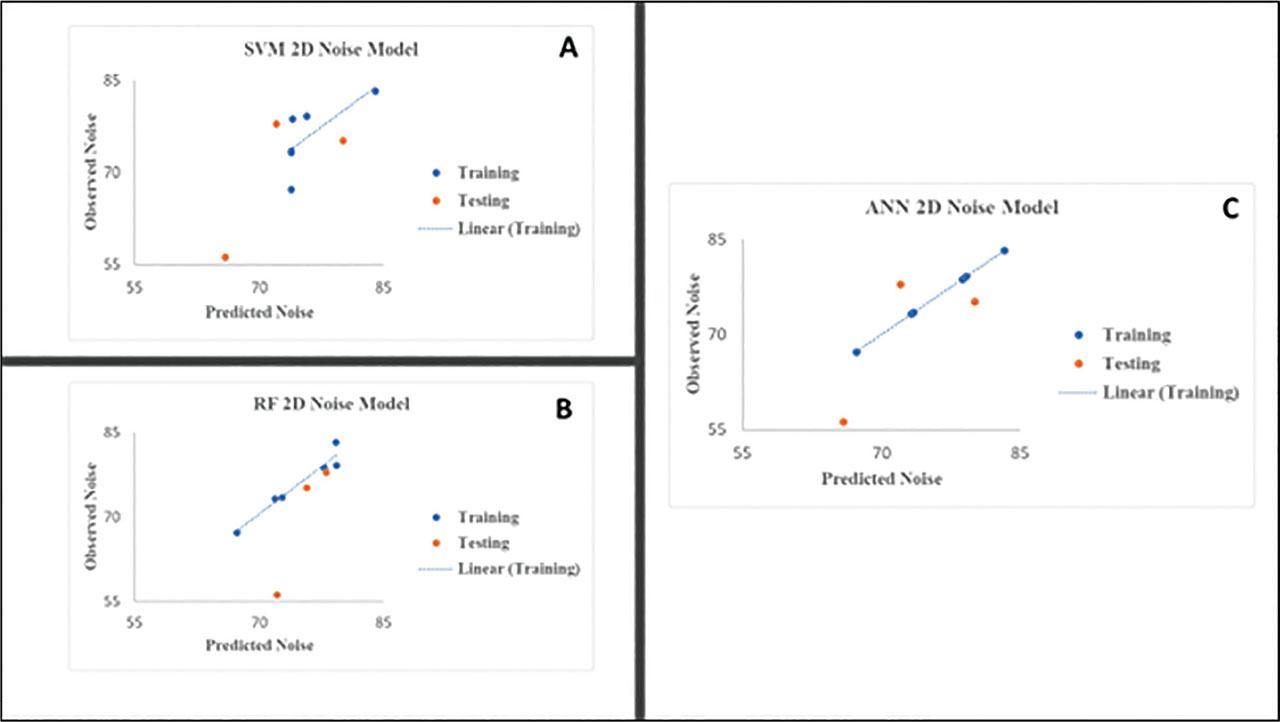
Figure 9:
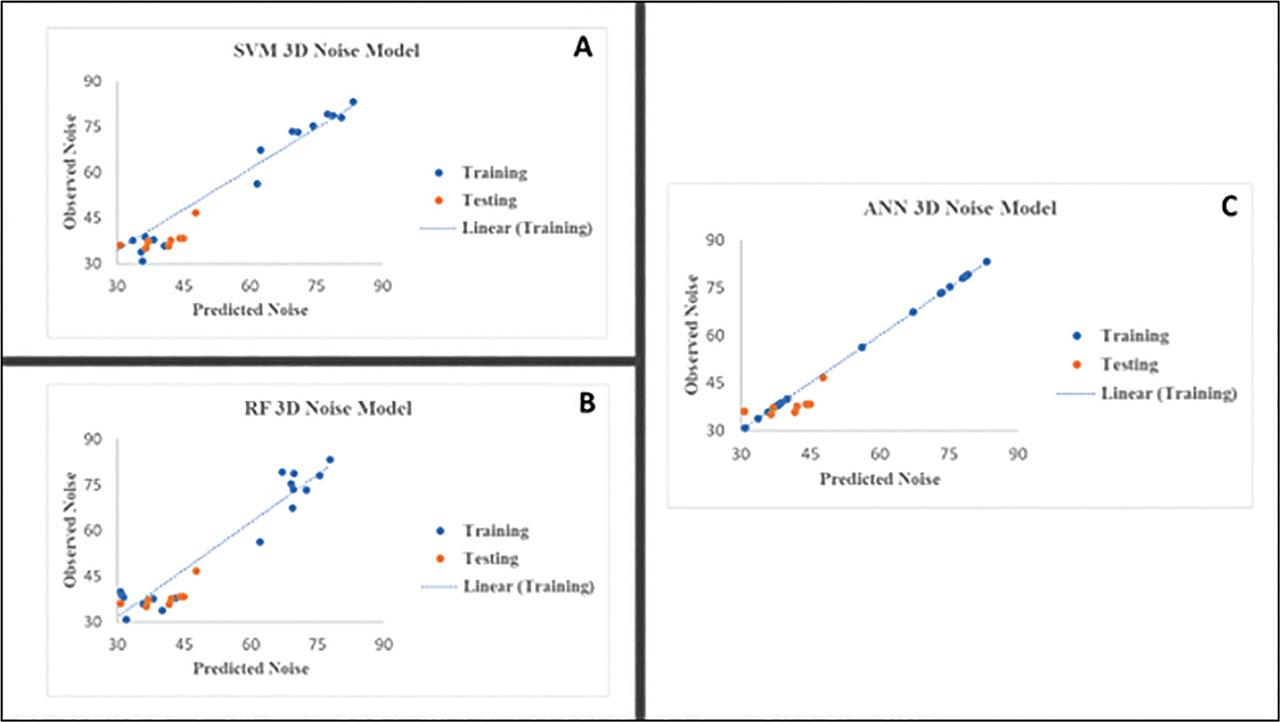
Figure 10:
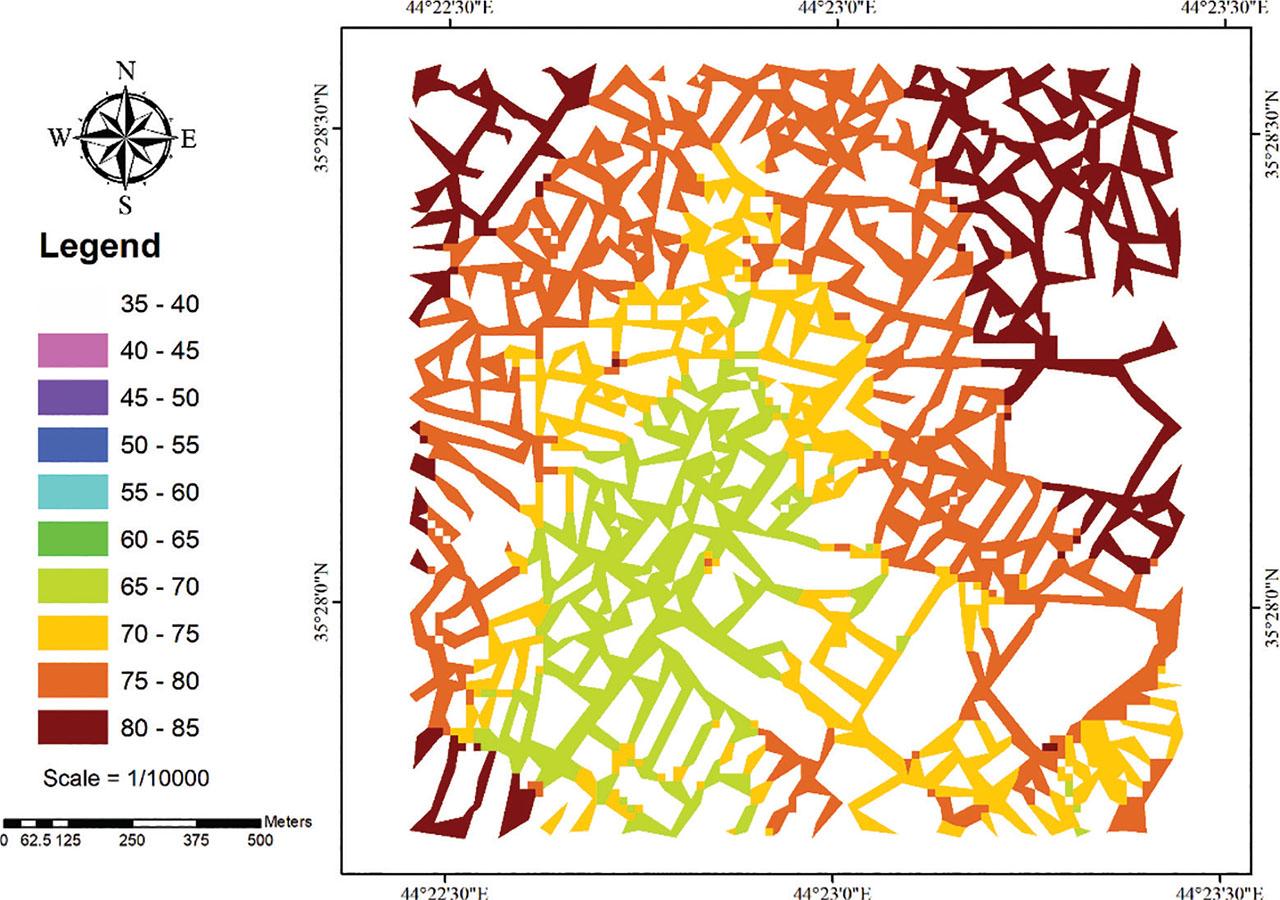
Figure 11:
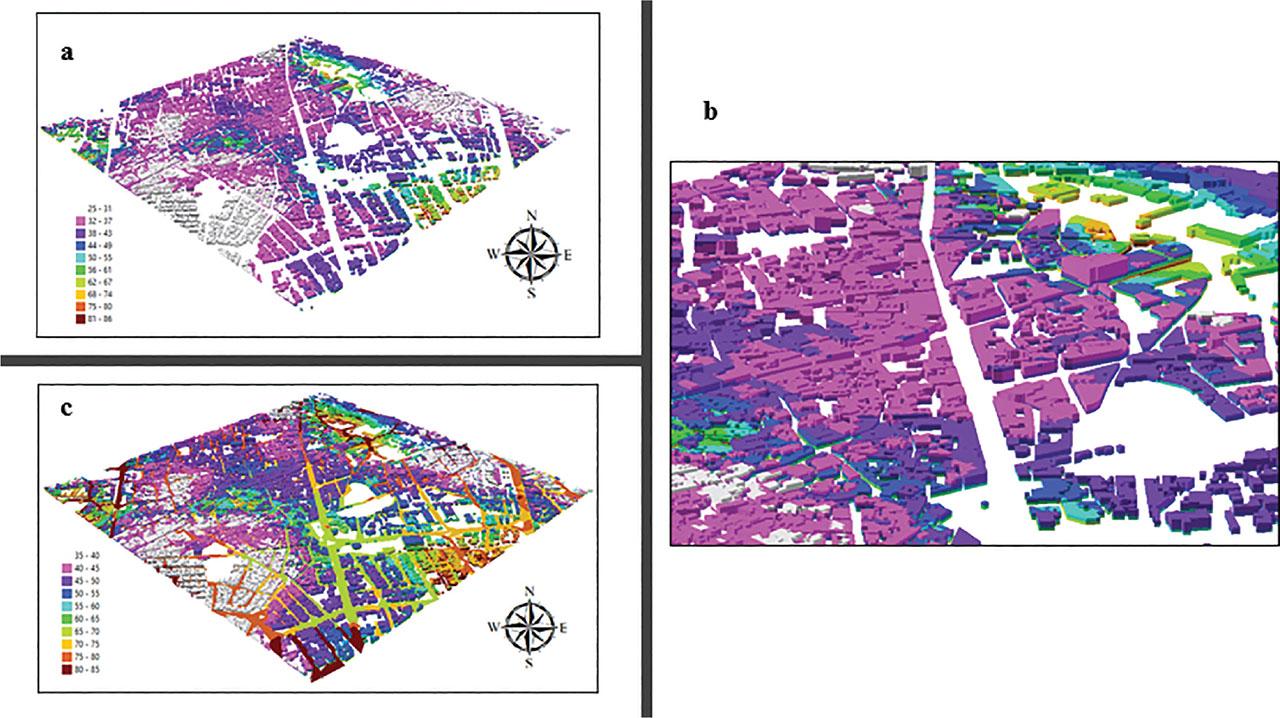
Statistical summary of noise predictors of 2D and 3D noise models
| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average noise | 28.21 | 83.28 | 47.71 | 20.14 |
| Light vehicle | 0.00 | 354.00 | 20.15 | 70.01 |
| Truck | 0.00 | 92.00 | 8.69 | 22.76 |
| Motorbike | 0.00 | 29.00 | 2.00 | 5.87 |
| Semitrailer | 0.00 | 108.00 | 5.53 | 21.39 |
| Bus | 0.00 | 129.00 | 9.69 | 26.92 |
| DSM | 2.47 | 29.2 | 13.73 | 15.66 |
| Average speed | 0.00 | 49.64 | 11.65 | 17.02 |
| Maximum speed | 0.00 | 66.00 | 13.69 | 21.57 |
| Distance from high volume of light vehicle | 0.00 | 1079.08 | 432.70 | 261.98 |
| Distance from medium volume of light vehicle | 0.00 | 1002.72 | 252.37 | 239.22 |
| Distance from low volume of light vehicle | 0.00 | 539.36 | 58.45 | 103.52 |
| Distance from high volume of truck | 0.00 | 628.94 | 220.19 | 164.74 |
| Distance from medium volume of truck | 0.00 | 594.40 | 119.59 | 129.21 |
| Distance from low volume of truck | 0.00 | 738.88 | 120.67 | 161.98 |
| Distance from high volume of motorbike | 0.00 | 1157.50 | 468.80 | 268.63 |
| Distance from medium volume of motorbike | 0.00 | 926.08 | 243.85 | 233.62 |
| Distance from low volume of motorbike | 0.00 | 569.75 | 65.09 | 114.28 |
| Distance from high volume of semitrailer | 0.00 | 1549.70 | 636.87 | 378.83 |
| Distance from medium volume of semitrailer | 0.00 | 849.06 | 250.78 | 191.34 |
| Distance from low volume of semitrailer | 0.00 | 379.29 | 25.43 | 47.44 |
| Distance from high volume of bus | 0.00 | 910.39 | 158.78 | 208.53 |
| Distance from medium volume of bus | 0.00 | 445.29 | 84.82 | 88.49 |
| Distance from low volume of bus | 0.00 | 1059.13 | 295.93 | 272.59 |
| Distance from high volume of average speed | 0.00 | 666.25 | 141.29 | 137.27 |
| Distance from medium volume of average speed | 0.00 | 406.50 | 78.55 | 81.38 |
| Distance from low volume of average speed | 0.00 | 652.80 | 117.52 | 129.15 |
| Distance from high volume of maximum speed | 0.00 | 722.50 | 170.70 | 178.77 |
| Distance from medium volume of maximum speed | 0.00 | 442.07 | 75.57 | 84.09 |
| Distance from low volume of maximum speed | 0.00 | 829.62 | 179.87 | 195.56 |
Hyperparameters of the proposed model for traffic noise prediction and their search space used for fine-tuning
| Hyperparameters | Search domain |
|---|---|
| Type of network | {multilayer perceptron (MLP)} |
| Number of hidden units | (3–30) |
| Training algorithm | {BFGS, RBFT} |
| Hidden and output activation | {Identity, Logistic, Tanh, Exponential, Gaussian} |
| Learning rate | (0.01–0.9) by step of 0.05 |
| Momentum | (0.1–0.9) by step of 0.1 |
Performance of models such as ANN, SVM, and RF for 2D and 3D noise models
| Model | Type of model | Training (R) | Testing (R) | Training (R2) | Testing (R2) | Training (RMSE) | Testing (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Noise Model | ANN | 1.00 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.003 | 7.14 |
| SVM | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 3.60 | 10.34 | |
| RF | 0.98 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 0.68 | 1.82 | 9.83 | |
| 3D Noise Model | ANN | 1.00 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.058 | 4.46 |
| SVM | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 0.60 | 6.16 | 4.75 | |
| RF | 0.98 | 0.80 | 0.96 | 0.64 | 6.00 | 4.50 | |
Shows the hidden and output activation of the ANN model
| Model | Hyperparameter | Identity | Logistic | Tanh | Exponential | Gaussian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Noise Model | Hidden and output activation | 0.003 | 0.0248 | 0.1892 | 2.0043 | 0.2373 |
| 3D Noise Model | 0.0805 | 0.058 | 0.3584 | 1.2066 | 0.1166 |