Figure 1:
![(a) Normal cells; and (b) leukemia cells [9].](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/65ccbc5b3bc2d770e76b839c/j_ijssis-2024-0013_fig_001.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251206%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251206T011824Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=3d8cd4436c6be2551a89aba63f214728275f08a54828a9db5808e15d24abfece&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
Figure 2:
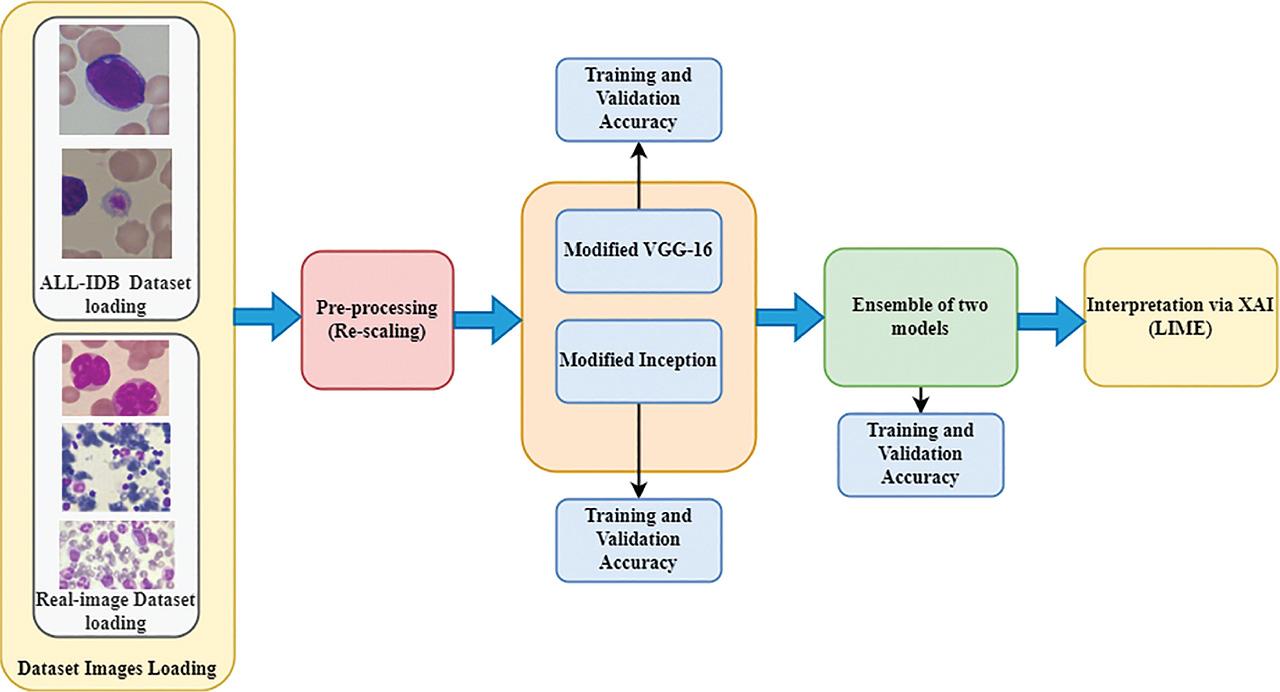
Figure 3:
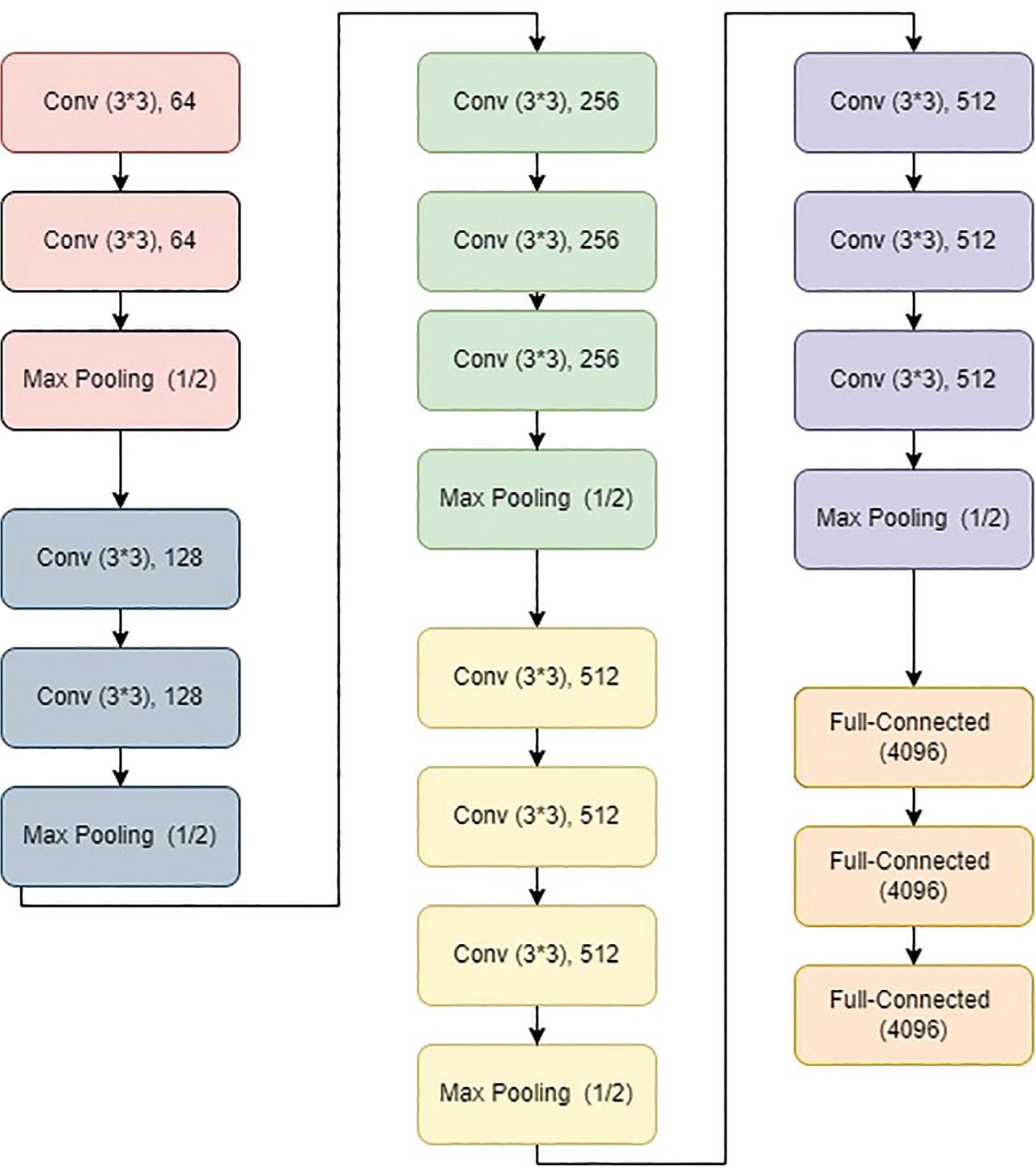
Figure 4:
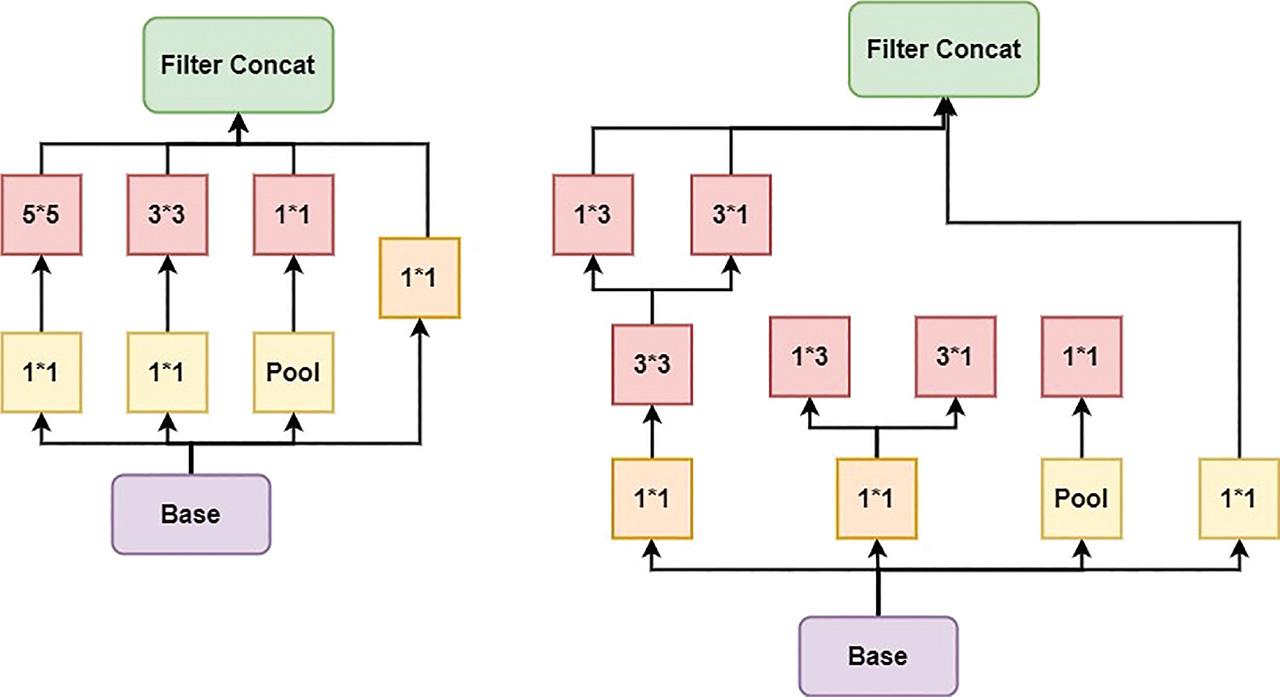
Figure 5:
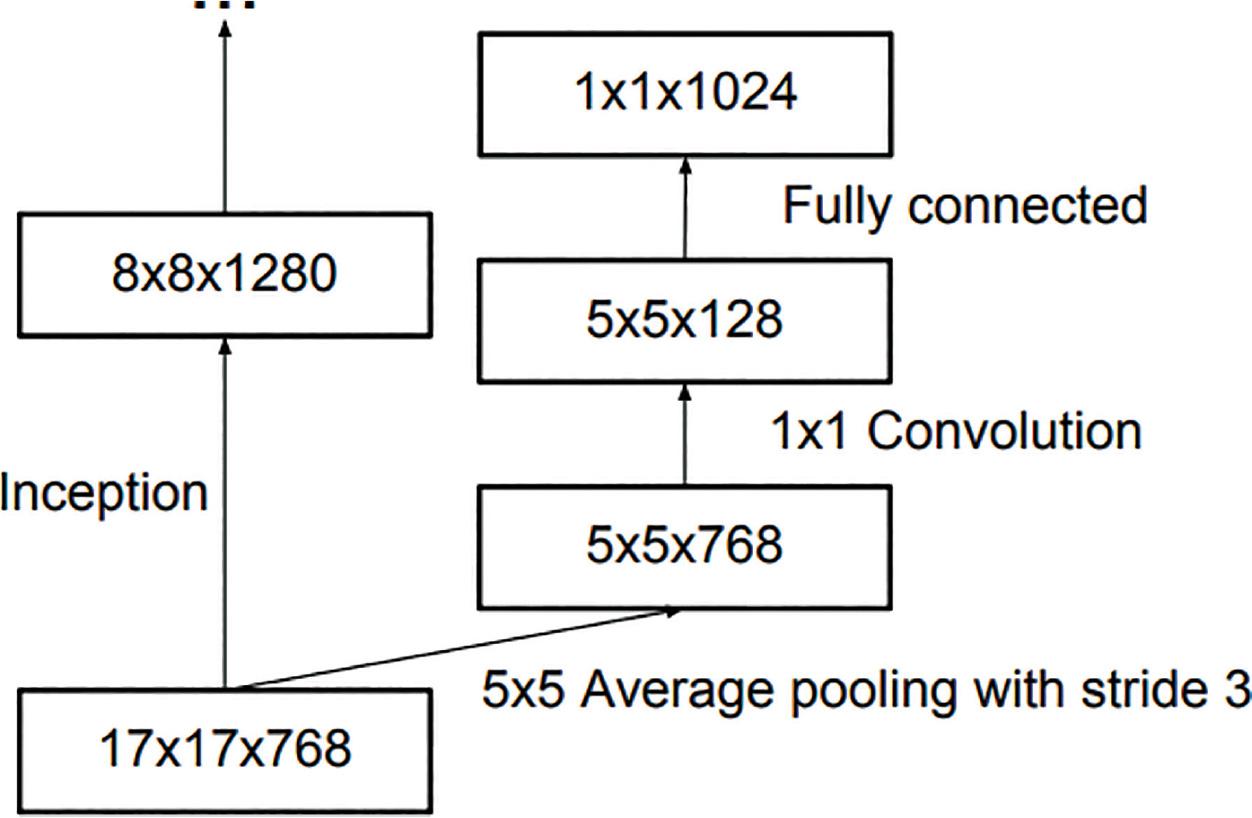
Figure 6:
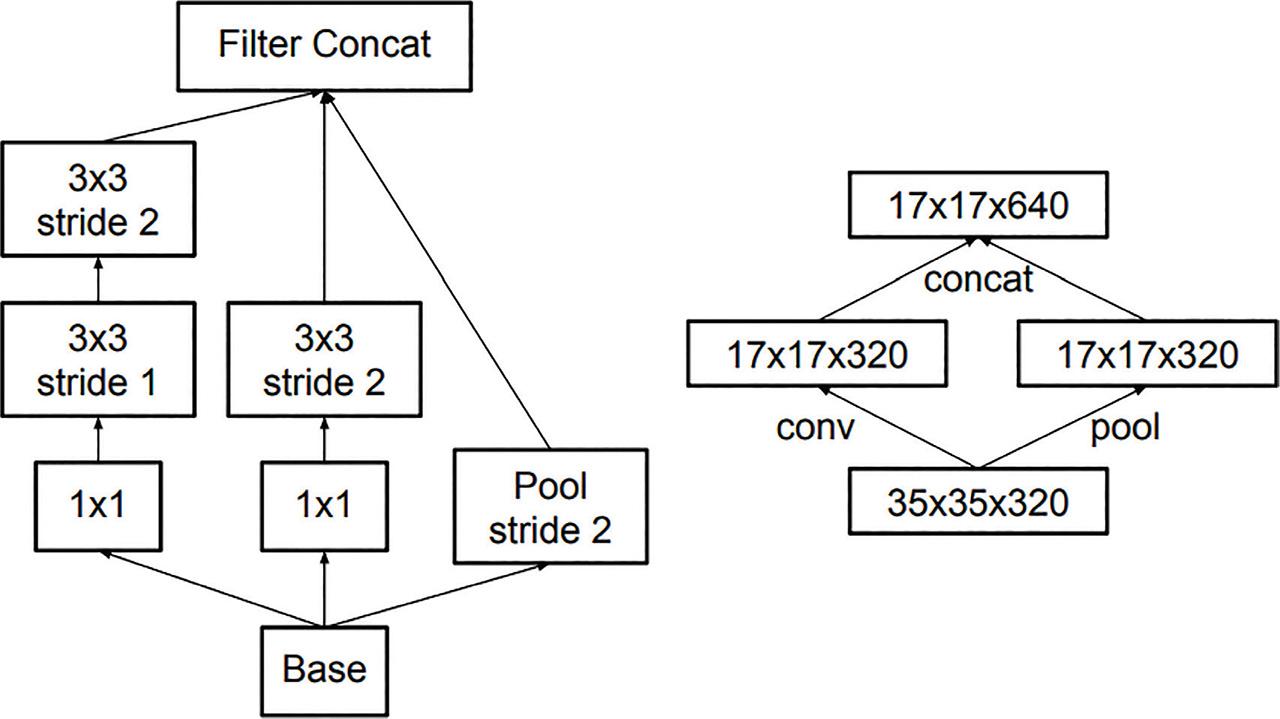
Figure 7:
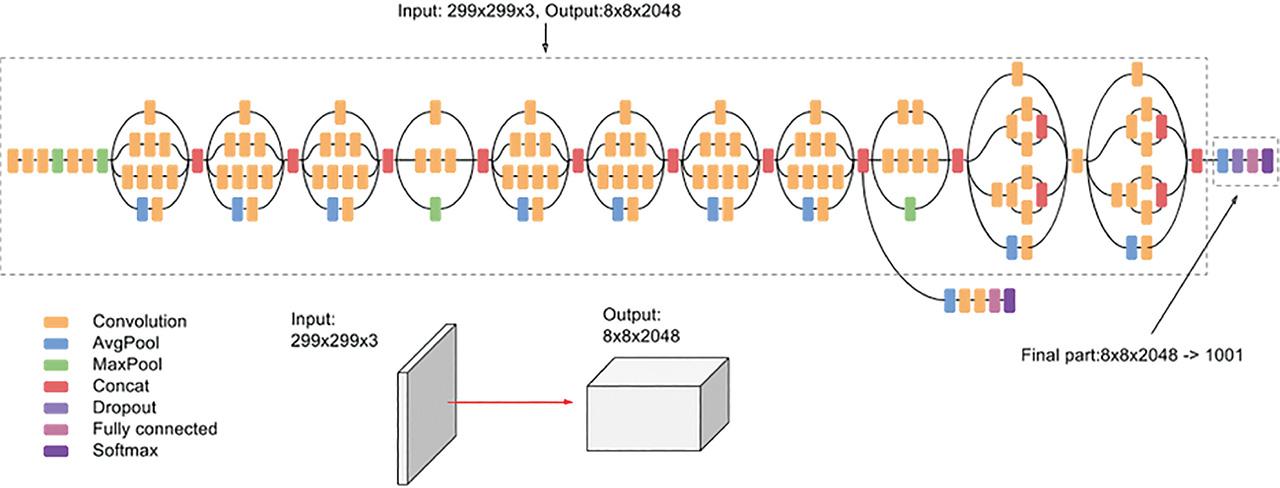
Figure 8:
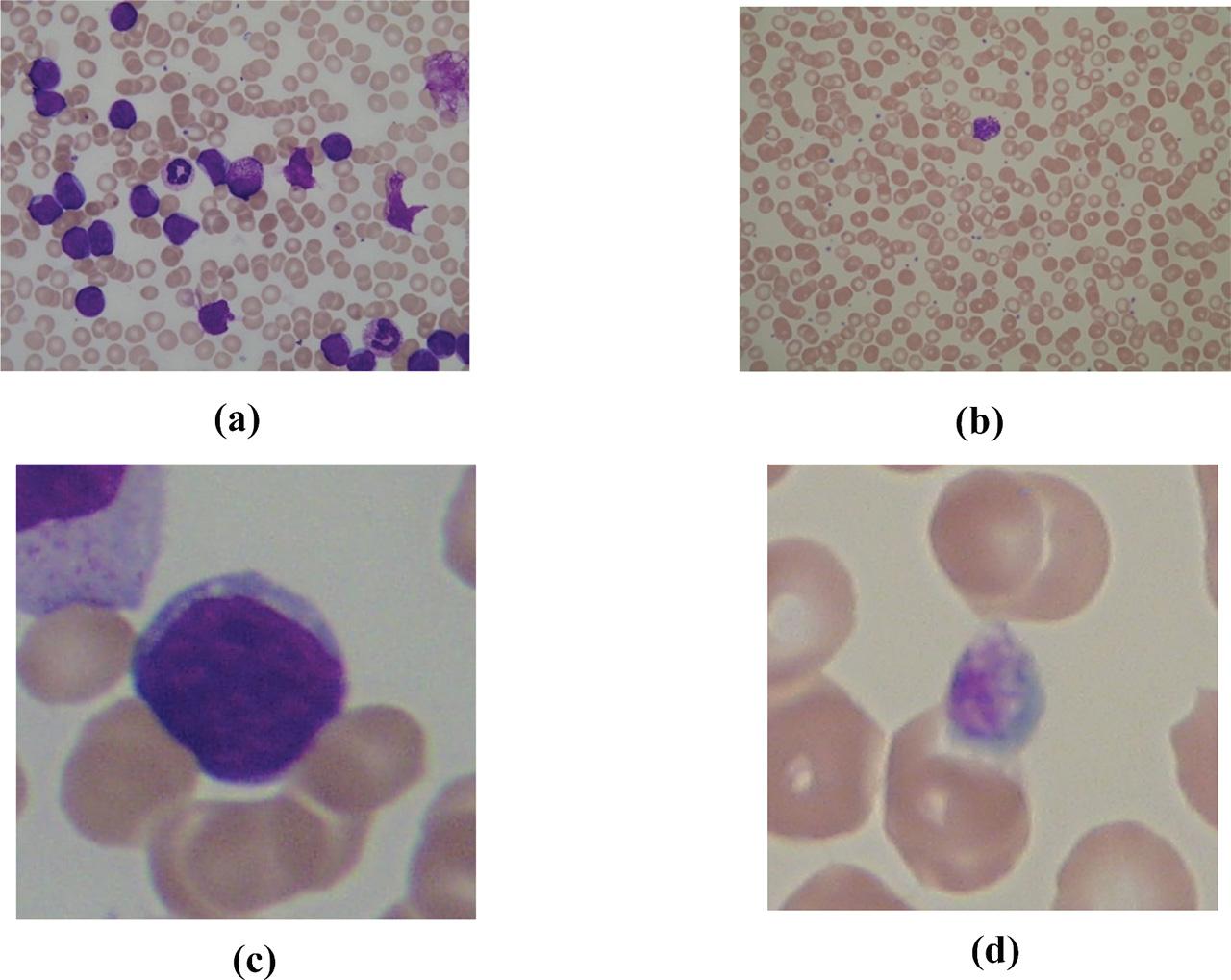
Figure 9:
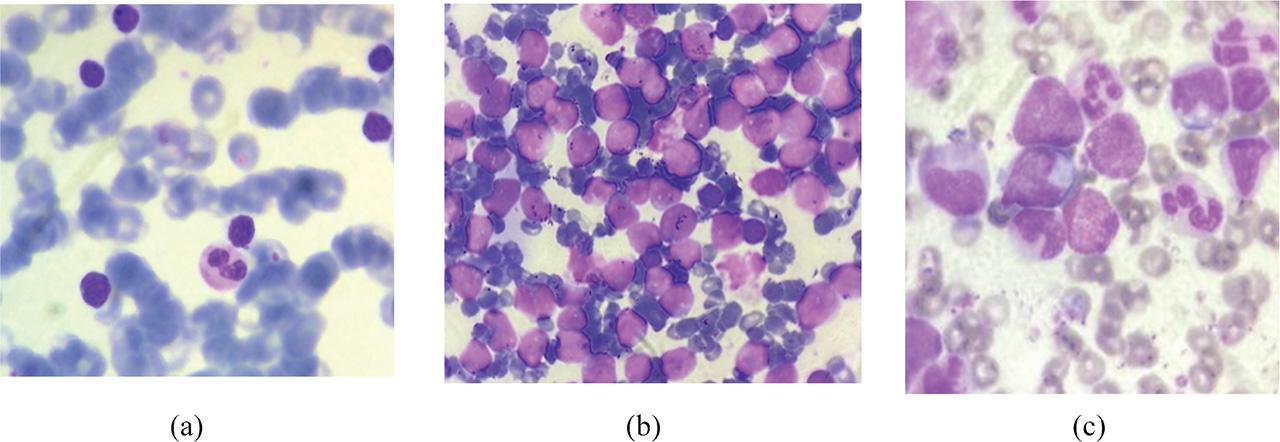
Figure 10:
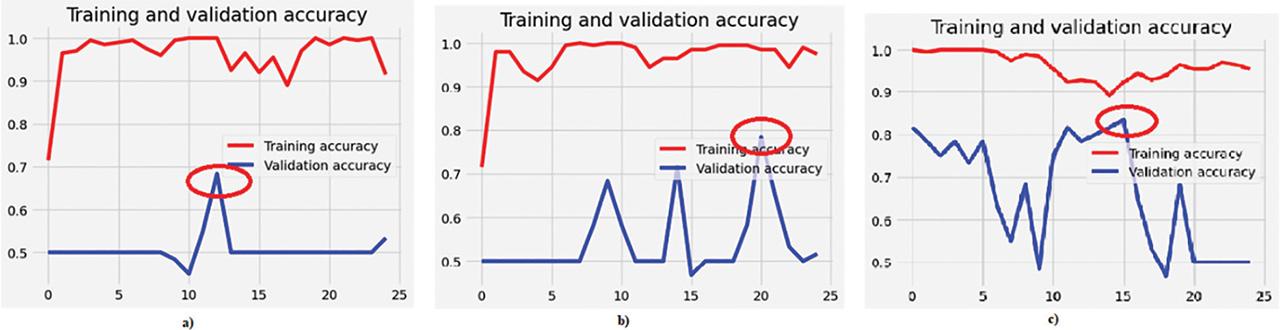
Figure 11:
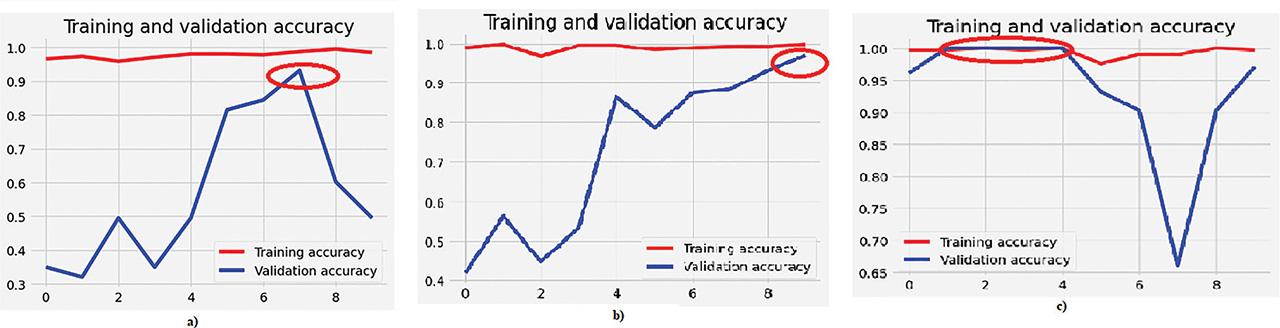
Figure 12:
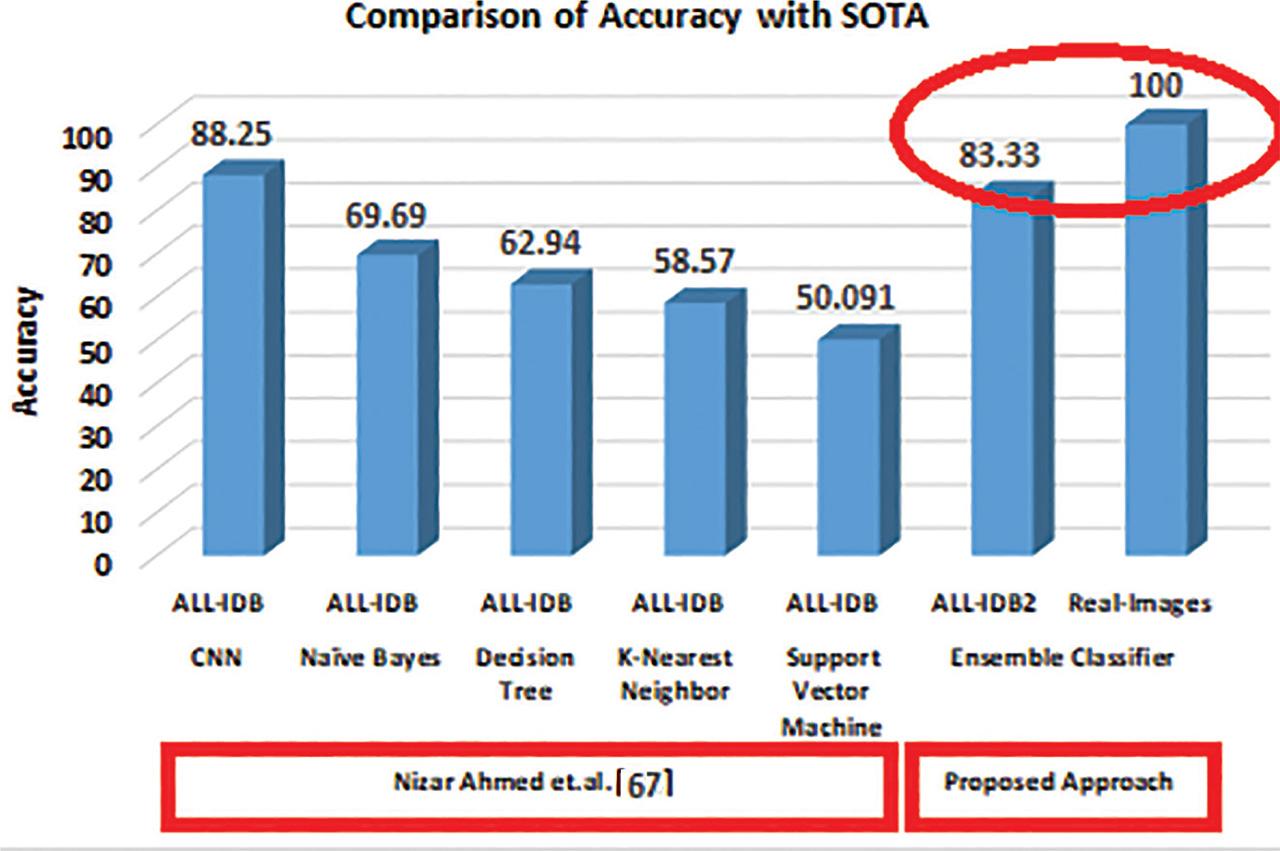
Figure 13:
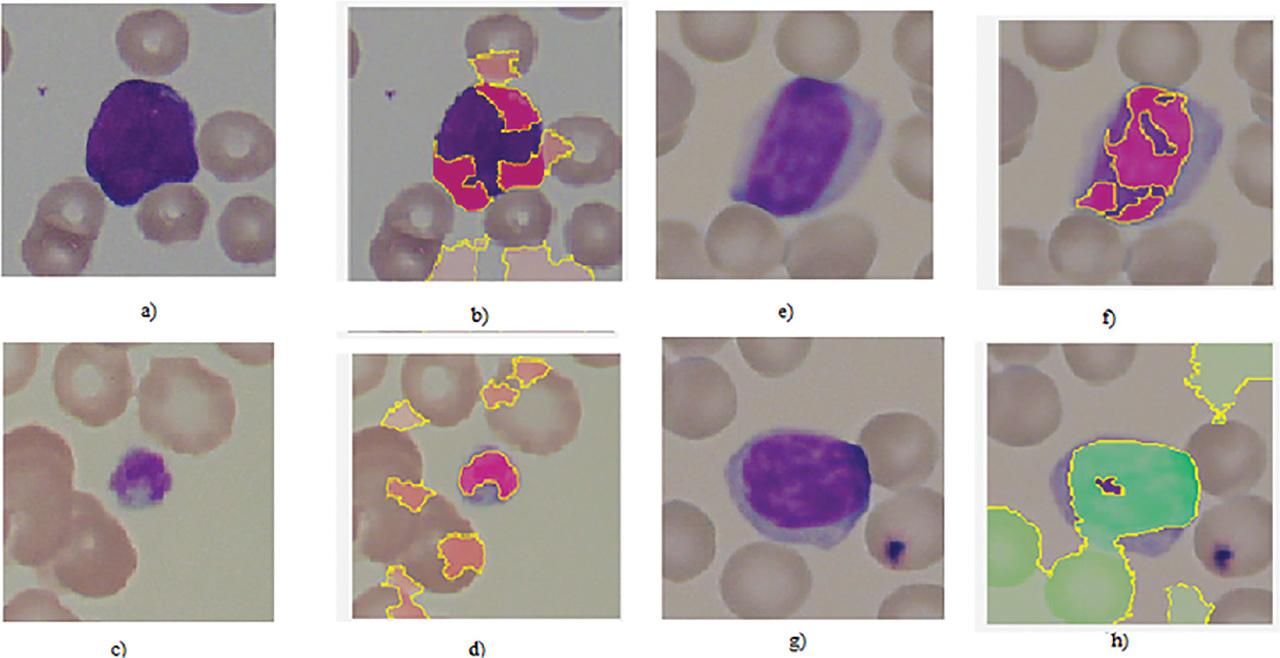
Metrics showing performance metric of binary and multi-class classification_
| DL classifier algorithm | Class/dataset | Maximum training accuracy (%) | Maximum validation accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modified VGG-16 classifier | Binary (ALL-IDB) | 98.50 | 68.33 |
| Modified InceptionNet classifier | 98.50 | 78.33 | |
| Ensemble classifier | 94.50 | 83.33 | |
| Modified VGG-16 classifier | Multi-class (real-images) | 98.56 | 93.20 |
| Modified InceptionNet classifier | 99.76 | 97.87 | |
| Ensemble classifier | 100 | 100 |
Comparison of the proposed approach with popular SOTA_
| Advantage criteria | Ensemble (VGG-16 + inception) | Pre-trained VGG-16 | Pre-trained inception | Random forest | SVM | ResNet50 (deep learning) | EfficientNet (deep learning) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversity in features | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Generalization performance | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Robustness to overfitting | High | High | High | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Ensemble averaging benefit | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Feature learning capabilities | Rich | Deep hierarchical | Diverse | Moderate | Linear | Deep hierarchical | Diverse |
| State-of-the-art performance | Yes | No (dated architecture) | Yes (at the time) | No | No | Yes | Yes (as of the time of training) |