Figure 1.
Figure 2.
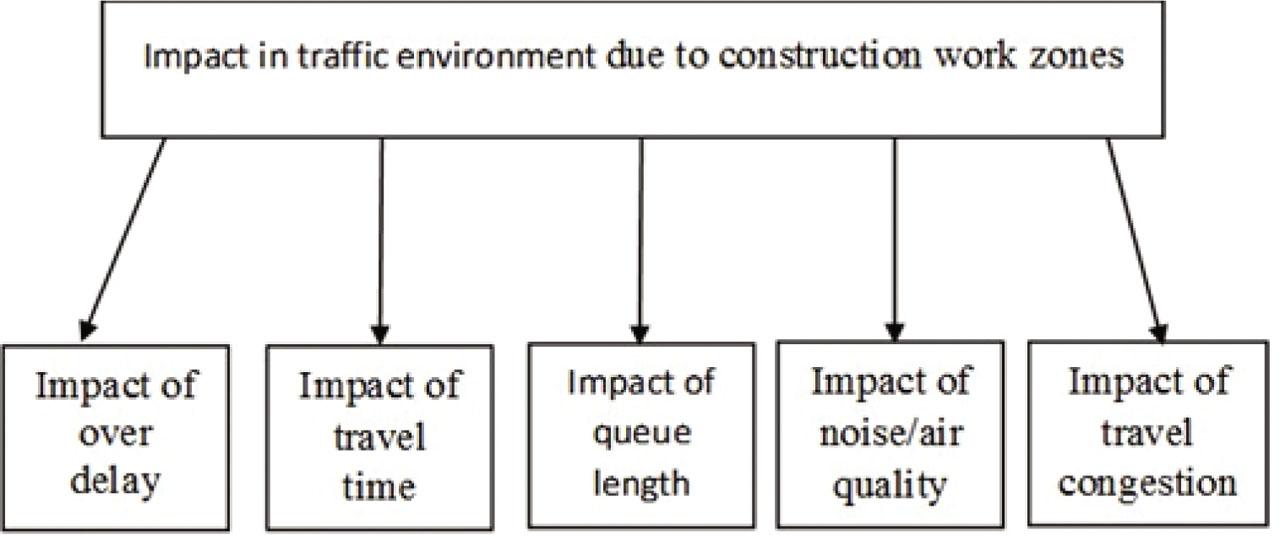
Figure 3.

Figure 4.
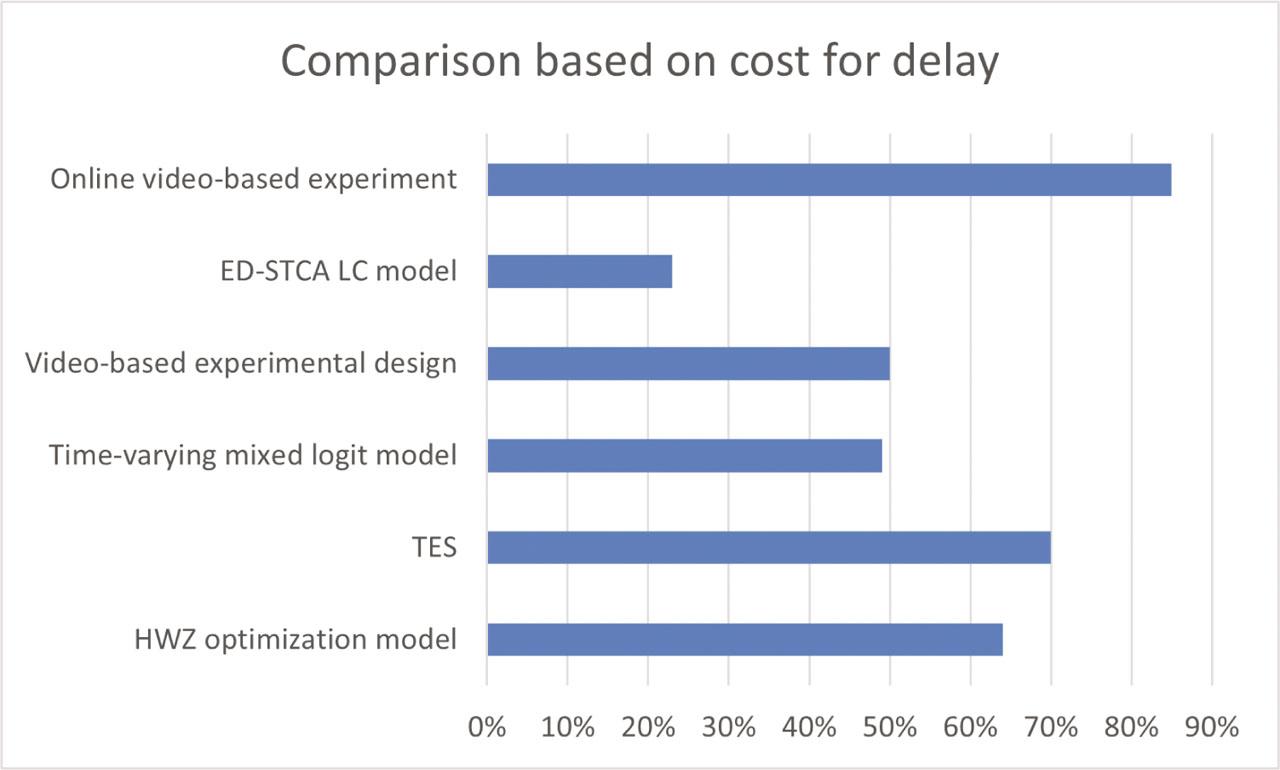
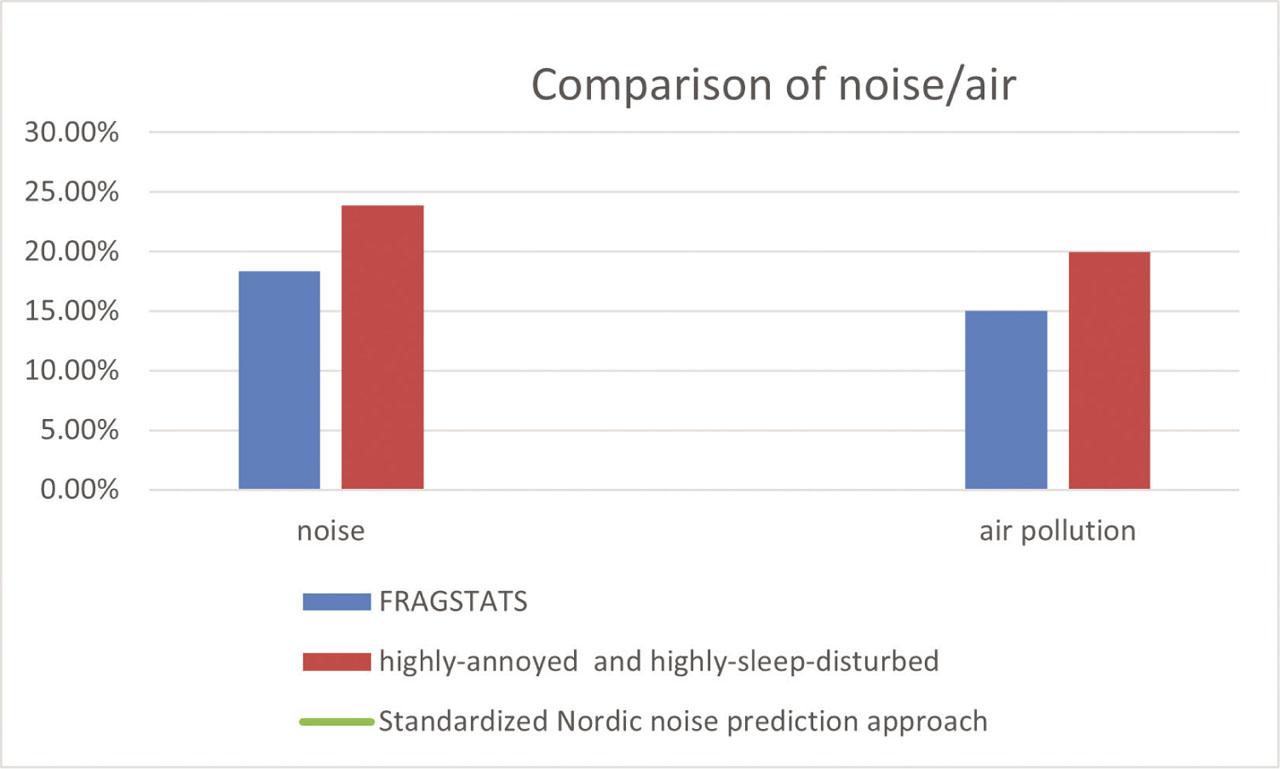
Figure 5.
Effects of noise and air quality on the traffic environment in a work zone
| Reference No. | Method/Tool | Significance | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [34] | Investigation of the urban morphology features | Ascertains how urban morphology affects the environmental noise such as TN | Does not investigate the time delay, queen length, and capacity of the traffic environment |
| [35] | FRAGSTATS | Investigates the influences of UEN in the Shenzhen Metropolitan Region of China | Needs improvement to estimate new types of noises |
| [36] | Highly annoyed (%HA) and highly sleep disturbed (%HSD) | Calculates the noise levels brought on by traffic during both day and night, as well as evaluates the negative effects on people's health | Needs to improve the prediction of noise levels |
| [37] | CALMET | Evaluates the air impact in highways | Pertains only to motorways |
| [38] | Standardized Nordic noise prediction approach | Discovers a 13%–29% decrease in the population exposed to levels over 55 dB equivalent | Does not estimate the noise level |
| [39] | TransCAD | Estimates air pollution due to increased traffic during and after the construction of the A-25 expansion project | More information is needed to fully understand how increased traffic may affect air quality |
| [40] | ANFIS, FFNN, SVR, and MLR | Estimates TN level in Nicosia City using three AI-based models | Needs to improve the prediction accuracy of TN |
| [41] | MOVES | Evaluates the fuel use and GHG emissions produced by on-road vehicles under various CWZ conditions | Needs to reduce the simulation cost |
Impact on travel time in traffic environment due to CWZ
| Reference No. | Method/Tool | Significance | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Agent-based modeling framework | Determines the impact of changing MP and traffic flow rates on the advantages of mobility | Needs high computational power to apply higher traffic volume |
| [12] | TIMS | Determines how a road construction project will affect the highway and any connecting arterial streets’ link-level traffic times | No information on the amount of construction activity or the times when it really occurred |
| [13] | Cooperative traffic control technique | Makes merging control easier when vehicles are coming up in the obstructed lane | Ignores the safety issues such as the safety of the workforce in a work zone |
| [14] | Statistical methods | Determines the severity of the speeding issue in HWZs | Not consistently statistically significant |
| [15] | PARAMICS | Predicts the trip time through a work zone to assist users in choosing more efficient routes | Does not explore the vehicle penetration rates and work-zone types |
| [16] | SUMO, DFROUTER | Outlines the street segments in Valencia in terms of trip times under various levels of traffic congestion | The traffic management system must be improved. |
| [17] | HCM6 TTD | Predicts the distribution of average travel time in the urban streets | Inaccuracy in analyzing the traffic parameters |
| [18] | VISSIM | Examines how work-zone advisory systems affect safety | Does not accurately portray how drivers will respond to DMS and CV warning signs in the real world |
Impact on traffic congestion in traffic environment due to CWZ
| Reference No. | Method/Tool | Significance | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | Analytical model | Optimizes the work zone to increase the road capacity | Needs to consider the maintenance cost |
| [43] | Fault-tolerant VSL control system | Detects and diagnoses the stationary sensor failures online utilizing real-time traffic data | Only considers the stationary sensor faults and ignores the concurrent faults and probe sensor faults |
| [44] | Multi-source data fusion and data analytical tool | Ascertains the factors having a maximum impact in terms of influencing traffic congestion | Needs a combined strategy for reducing the traffic congestion |
| [45] | Investigation of the significant variations in congestion levels | Offers helpful insights into the means of creating a traffic management system | Needs more depth analysis for congestion prediction |
| [46] | Mathematical decision model | Measures the network's work-zone disturbances’ mutually interacting impact on traffic and delay | Does not investigate the working complexity |
| [47] | Investigation of the effects of several temporary traffic management techniques | Estimates the impacts of changes in traffic volumes, work-zone length, and construction period duration | Needs additional research for arriving at a better understanding concerning the specific factors applying to work-zone safety |
Impact on overall delay in traffic environment due to CWZ
| Reference No. | Method/Tool | Significance | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | HWZ optimization model | Measures the effects of HWZs on worker safety, mobility, and costs | Does not consider the effects on traffic flow |
| [20] | VISSIM | Minimizes traffic delays in the construction zone in the case of a 3-to-1 lane closure | During the 3-to-1 lane restrictions at the project, traffic diversion are not considered |
| [21] | MGORP | Serves as a tool using which to observe the impact of variables like the speed limit and the number of lanes in various work-zone designs | Does not consider the work-zone duration and specific work-zone speed limit |
| [22] | Time-varying mixed logit model | Determines how a vehicle is behaving when entering a work zone | Does not account for the impact of work-zone configuration |
| [23] | TES | Ascertains the safety-enhanced method for various traffic volume scenarios | Needs to enhance the work-zone truck egress safety |
| [24] | Video-based experimental design | Investigates the impact of apparent roadwork activities on work-zone speed | Uses only two work zones to predict the roadwork activity |
| [25] | ED-STCA LC model | Estimates the traffic performance of the work zone | Requires more computation time |
| [26] | Online video-based experiment | Investigates if the presence of obvious roadwork activity affected the predicted link between personality characteristics and speed in work zones | More research is needed to investigate other variables |
Impact on queue length in traffic environment due to CWZ
| Reference No. | Method/Tool | Significance | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | VASL | Significantly reduces queue length, enhancing compliance with overall safety regulations in congested areas | The effects of lowered speed limits and shorter lines on travel time are not studied. |
| [28] | Hybrid machine-learning model | Has been used to anticipate traffic delays on certain highway portions upstream of a work zone in New Jersey | The work zones are not concentrated on arterials with signalized junctions. |
| [29] | Multi-objective optimization model | Finds and recognizes a collection of Pareto-optimal work-zone designs that offer a variety of optimal trade-offs between reducing traffic delays and the risk of accidents | Does not consider how this optimization would affect the cost of the work zone |
| [30] | VISSIM | Enhances the control systems for two-lane highway lane-closure work zones | The flagger control approach requires an improved mathematical delay model. |
| [31] | VISSIM | Serves as a tool using which to find a late merge system with and without CVs | Does not focus on the safety aspect of cooperative merging in work zones |
| [32] | LiDAR | Serves as a tool using which to identify problems encountered in queue length detection, as well as carry out improvement of detection accuracy | Needs to improve detection accuracy by reducing the number of assumptions |
| [33] | IM approach | Demonstrates excellent stability in response to parameter changes | Heavy vehicle percentage affects the performance of the IM |