Figure 1
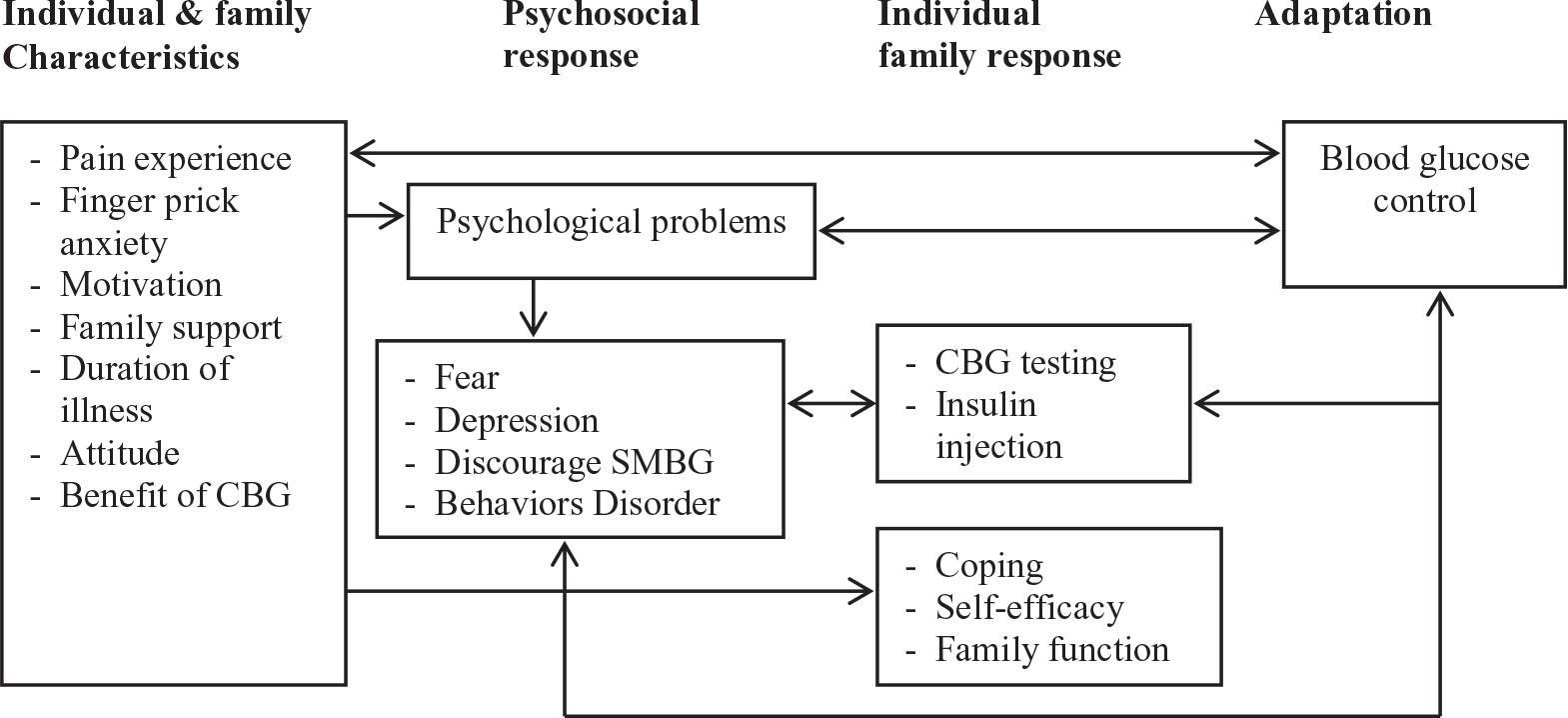
Factors related to fear and psychological issues of CBG testing_
| Authors | Factors related to psychological problems | Impacts of psychological problems on CBG testing and insulin injection |
|---|---|---|
| Ong et al. 201419 |
|
|
| Taylor et al. 201726 |
|
|
| Nazmi et al. 201330 |
|
|
| Shlomowitz and Feher 20148 |
|
|
Strategies to manage the psychological problems related to CBG monitoring and insulin injection_
| Authors | Strategies | Description of the strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Snoek et al. 200821 | A 5-step psychosocial model of SMBG |
|
| Welschen et al. 201334 | Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) |
|
| Funnell et al. 200436 | Confrontation, persistence, and reality (CPR) strategy |
|
| Cox et al. 200635 | Blood glucose awareness training (BGAT) |
|
Database search and keywords_
| Sources of data | Keywords |
|---|---|
| PubMed | * Fear AND Capillary blood glucose OR Insulin injection AND Diabetes |
| Scopus | * Fear AND Capillary blood glucose OR Insulin injection AND Diabetes |
| CINAHL | * Fear AND Capillary blood glucose OR Insulin injection AND Diabetes |
| Google Scholar | * Fear AND Capillary blood glucose OR Insulin injection AND Diabetes |
Psychological issues related to CBG testing and insulin injection_
| Authors | Study designs | Psychological issues related to CBG testing and insulin injection |
|---|---|---|
| Ong et al. 201419 | Qualitative design |
|
| Taylor et al. 201726 | Mixed qualitative and quantitative design |
|
| Van Dooren et al. 201627 | Cohort study |
|
| Gucciardi et al. 201320 | Qualitative design |
|
| Shlomowitz et al. 20148 | Cross-sectional study |
|
| Yoshioka 201824 | Editorial |
|
| Bai et al. 201825 | Meta-analysis |
|