Figure 1
Japanese and South Korean FDI in offshore centres in percentage of the total outward FDI, 2017
| Share of offshore centres in total outward FDI stock | |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 6.4% |
| Japan | 3.5% |
Details of the interviews conducted in the framework of the research
| Company No. | Year of establishment/acquisition | Entry mode | Number of employees at present | Date of interviews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1989 | greenfield | 2500 permanent + 500 seasonal | 12 April 2017 |
| 2 | 2005 | greenfield | 330 (white-collar, directly) + 2500 (blue-collar, indirectly) | 4 times between the winter of 2016 and April 2017 |
| 3 | 1991 | greenfield | 3000 permanent + 200 seasonal | April 2017 |
| 4 | One in 2009; Second in 2011; Third in 2016 | brownfield | 2400 altogether | January 2017 |
| 5 | 2006 | brownfield | 850 altogether | December 2016 |
| 6 | 2017 | acquisition (the acquired plant was established through a greenfield investment) | 2000 | April–May, 2019 |
| 7 | 1998 | greenfield | 650–700 | May, 2019 |
| 8 | 2017 | brownfield | 260 | May, 2019 |
| 9 | 1997 | greenfield | 4000 | September, 2019 |
| 10 | 2006 | greenfield | 180 | December, 2019 |
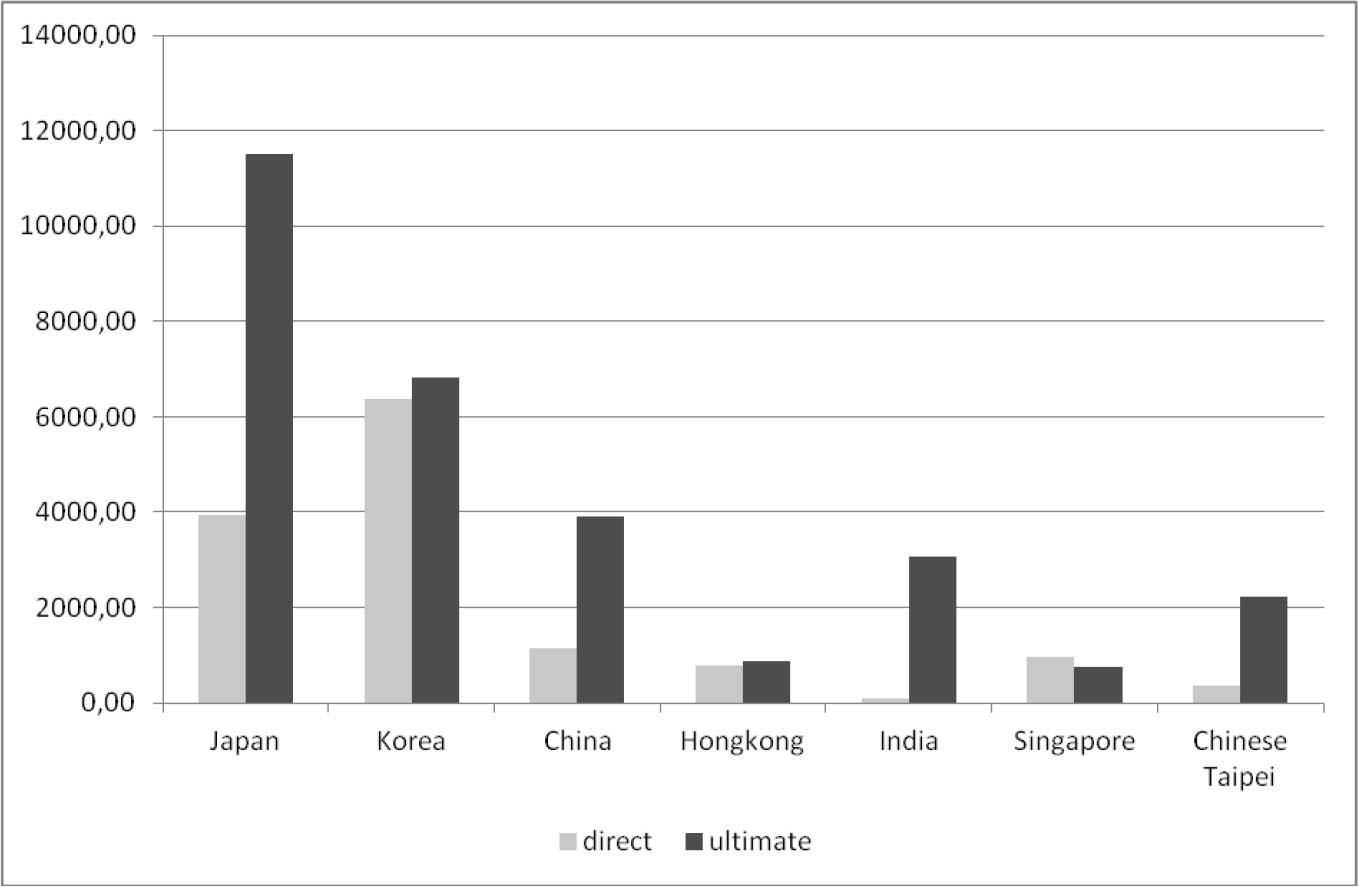
FDI stock by leading Asian investor countries in the Visegrad countries, 2017 (million USD)
| Czech Republic | Hungary | Poland | Slovakia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| direct | ultimate | direct | ultimate | direct | ultimate | direct | ultimate | |
| Japan | 1907.66 | 3314.14 | 1152.56 | 3185.93 | 887.43 | 4996.26 | 125.16 | n.d. |
| Korea | 3254.71 | 3046.01 | 1979.25 | 1986.48 | 1134.81 | 1783.54 | 3535.08 | n.d. |
| China | 707.27 | 1096.04 | 210.96 | 1973.42 | 223.11 | 826.51 | 55.12 | n.d. |
| Hong Kong, China | 115.69 | 204.41 | 319.81 | 207.51 | 347.08 | 465.06 | 25.03 | n.d. |
| India | −1.12 | 99.51 | −16.04 | 2657.56 | 103.38 | 299.41 | −2.72 | n.d. |
| Singapore | 344.64 | 699.07 | 532.29 | −55.72 | 84.74 | 109.56 | 118.49 | n.d. |
| Chinese Taipei | 283.53 | 1007.46 | 47.28 | 971.91 | 30.76 | 254.14 | 18.27 | n.d. |
| Sum of 7 countries | 6612.36 | 9466.65 | 4226.11 | 10927.09 | 2811.31 | 8734.48 | 3874.42 | n.d. |
| Sum of 7 countries in % of total FDI stock | 4.42 | 6.33 | 4.64 | 12.01 | 1.18 | 3.66 | 6.94 | n.d. |
Characteristics of the companies in our sample by the use of an intermediary country and type of the entry mode
| Company | Has it come directly or through an intermediary country? | If it came through an intermediary country, which is that? | Entry mode: greenfield or acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | direct | greenfield | |
| 2 | through intermediary | Netherlands | greenfield |
| 3 | direct | greenfield | |
| 4 | through intermediary | Cyprus | acquisition |
| 5 | through intermediary | Netherlands | acquisition |
| 6 | through intermediary | Luxembourg | acquisition |
| 7 | through intermediary | Hong Kong, China | greenfield |
| 8 | through intermediary | Switzerland | acquisition |
| 9 | through intermediary | Netherlands | greenfield |
| 10 | direct | greenfield |