Figure. 1
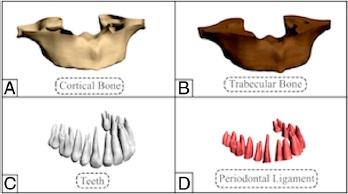
Figure. 2
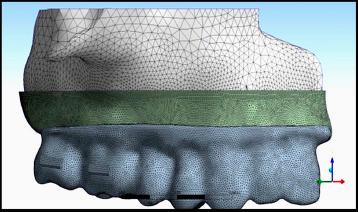
Figure. 3
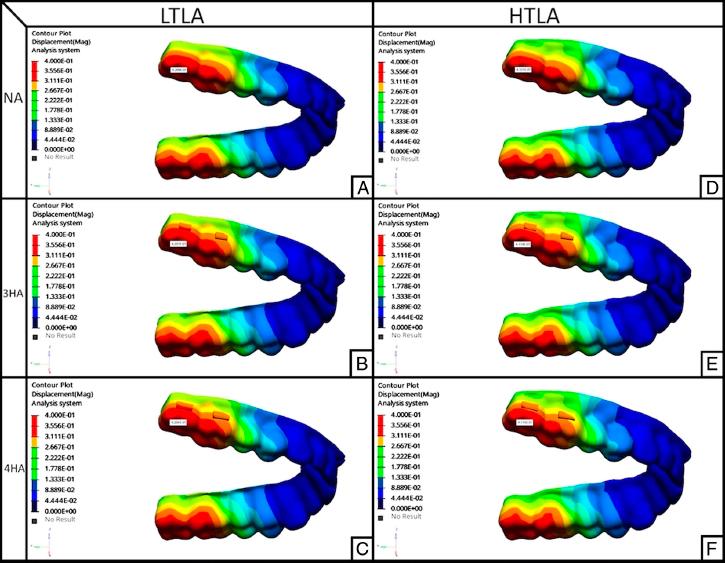
Figure. 4

Figure. 5
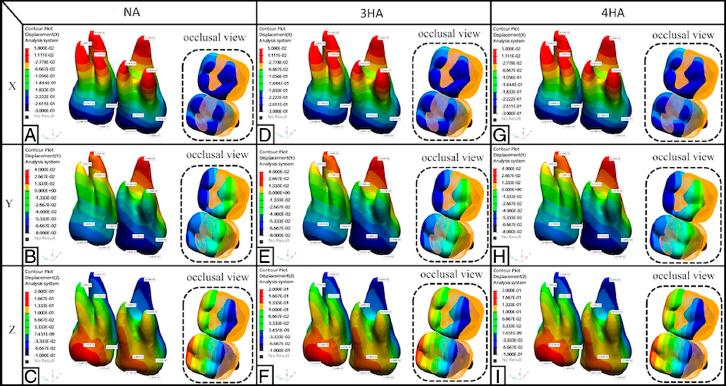
Figure. 6
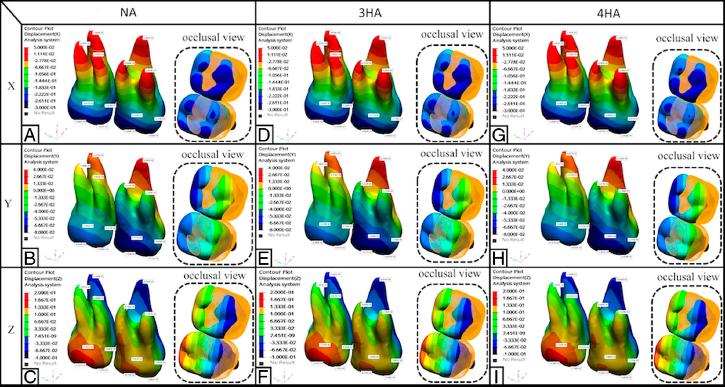
Figure. 7

Quantity of nodes and elements within each group
| Models | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 477893 | 481455 | 482530 | 476430 | 477132 | 478566 |
| Elements | 1800007 | 1811720 | 1815508 | 1796580 | 1798170 | 1803712 |
Directional movements of maxillary first and second molar teeth in the X, Y, Z axes
| Measurement points | LTLA | HTLA | ||||||
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |||
| Maxillary First Molar | ||||||||
| NA | Crown | DPC | -0.42270 | -0.02778 | -0.05881 | -0.41190 | -0.02110 | -0.05823 |
| DBC | -0.39710 | -0.07859 | 0.09173 | -0.38680 | -0.07149 | 0.08710 | ||
| MPC | -0.38330 | -0.01627 | -0.07791 | -0.37290 | -0.00965 | -0.07852 | ||
| MBC | -0.35940 | -0.06824 | 0.07563 | -0.34930 | -0.06114 | 0.06965 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.11290 | 0.04356 | -0.09336 | 0.10840 | 0.04085 | -0.09292 | |
| DBA | 0.07082 | -0.01224 | 0.07460 | 0.06668 | -0.01277 | 0.06766 | ||
| MBA | 0.10520 | -0.01138 | 0.08203 | 0.10130 | -0.01266 | 0.07557 | ||
| 3HA | Crown | DPC | -0.42020 | -0.03068 | -0.05902 | -0.41120 | -0.02404 | -0.05926 |
| DBC | -0.39470 | -0.08151 | 0.09027 | -0,386 | -0.07477 | 0.08579 | ||
| MPC | -0.38070 | -0.01918 | -0.07690 | -0.37180 | -0.01252 | -0.07841 | ||
| MBC | -0.35670 | -0.07121 | 0.07534 | -0.34810 | -0.06442 | 0.06950 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.11060 | 0.04444 | -0.09261 | 0.10740 | 0.04228 | -0.09314 | |
| DBA | 0.06857 | -0.01199 | 0.07350 | 0.06574 | -0.01223 | 0.06663 | ||
| MBA | 0.10310 | -0.01116 | 0.08191 | 0.10070 | -0.01216 | 0.07562 | ||
| 4HA | Crown | DPC | -0.41860 | -0.03122 | -0.05910 | -0.40600 | -0.02346 | -0.05866 |
| DBC | -0.39380 | -0.07995 | 0.09021 | -0.38100 | -0.07342 | 0.08483 | ||
| MPC | -0.37950 | -0.02004 | -0.07719 | -0.36710 | -0.01211 | -0.07775 | ||
| MBC | -0.35670 | -0.06970 | 0.07430 | -0.34380 | -0.06302 | 0.06853 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.11060 | 0.04270 | -0.09291 | 0.10680 | 0.04144 | -0.09225 | |
| DBA | 0.06841 | -0.01112 | 0.07192 | 0.06582 | -0.01213 | 0.06583 | ||
| MBA | 0.10230 | -0.01073 | 0.08162 | 0.10020 | -0.01206 | 0.07456 | ||
| Maxillary Second Molar | ||||||||
| NA | Crown | DPC | -0.37410 | -0.03655 | -0.01012 | -0.36120 | -0.03534 | -0.01292 |
| DBC | -0.37080 | -0.06763 | 0.15280 | -0.35810 | -0.06490 | 0.14410 | ||
| MPC | -0.36470 | -0.02798 | -0.04917 | -0.35240 | -0.02717 | -0.05065 | ||
| MBC | -0.36800 | -0.06248 | 0.12770 | -0.35570 | -0.06002 | 0.11970 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.08220 | 0.03165 | -0.10440 | 0.07848 | 0.02973 | -0.10380 | |
| DBA | 0.10000 | 0.01395 | 0.02268 | 0.09560 | 0.01288 | 0.01871 | ||
| MBA | 0.07726 | 0.00664 | 0.04126 | 0.07355 | 0.00592 | 0.03650 | ||
| 3HA | Crown | DPC | -0.37260 | -0.03812 | -0.01106 | -0.35920 | -0.03518 | -0.01297 |
| DBC | -0.36930 | -0.06901 | 0.15120 | -0.35620 | -0.06395 | 0.14320 | ||
| MPC | -0.36330 | -0.02969 | -0.04928 | -0.35080 | -0.02728 | -0.05048 | ||
| MBC | -0.36660 | -0.06401 | 0.12690 | -0.35430 | -0.05927 | 0.11910 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.08127 | 0.03206 | -0.10460 | 0.07818 | 0.02935 | -0.10340 | |
| DBA | 0.09893 | 0.01454 | 0.02175 | 0.09526 | 0.01302 | 0.01853 | ||
| MBA | 0.07629 | 0.00712 | 0.04071 | 0.07300 | 0.00615 | 0.03625 | ||
| 4HA | Crown | DPC | -0.36890 | -0.03773 | -0.01073 | -0.35850 | -0.03568 | -0.01303 |
| DBC | -0.36570 | -0.06783 | 0.15020 | -0.35530 | -0.06537 | 0.14280 | ||
| MPC | -0.36000 | -0.02954 | -0.04862 | -0.34950 | -0.02752 | -0.05014 | ||
| MBC | -0.36340 | -0.06301 | 0.12610 | -0.35260 | -0.06050 | 0.11900 | ||
| Root | PA | 0.08102 | 0.03158 | -0.10350 | 0.07767 | 0.03027 | -0.10300 | |
| DBA | 0.09858 | 0.01456 | 0.02183 | 0.09462 | 0.01331 | 0.01843 | ||
| MBA | 0.07587 | 0.00726 | 0.04061 | 0.07295 | 0.006310 | 0.03632 | ||
Material properties
| Material | Elastic modulus [MPa] | Poisson ratio [v] |
|---|---|---|
| Trabecular bone28–30 | 1.37 × 103 | 0.30 |
| Cortical bone28–30 | 1.37 × 104 | 0.26 |
| Teeth28–30 | 1.96 × 104 | 0.30 |
| PDL28–30 | 6.9 × 10-1 | 0.45 |
| Attachments28–30 | 1.25 × 104 | 0.36 |
| CA28,29 | 5.28 × 102 | 0.36 |
Maximum aligner deformation and location
| Models | Maximum deformation (mm) | Maximum deformation location |
|---|---|---|
| LTLA-NA | 0.4209 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |
| LTLA-3HA | 0.4207 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |
| LTLA-4HA | 0.4204 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |
| HTLA-NA | 0.4121 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |
| HTLA-3HA | 0.4119 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |
| HTLA-4HA | 0.4116 | Occlusal surface of the second molar |