Fig 1.
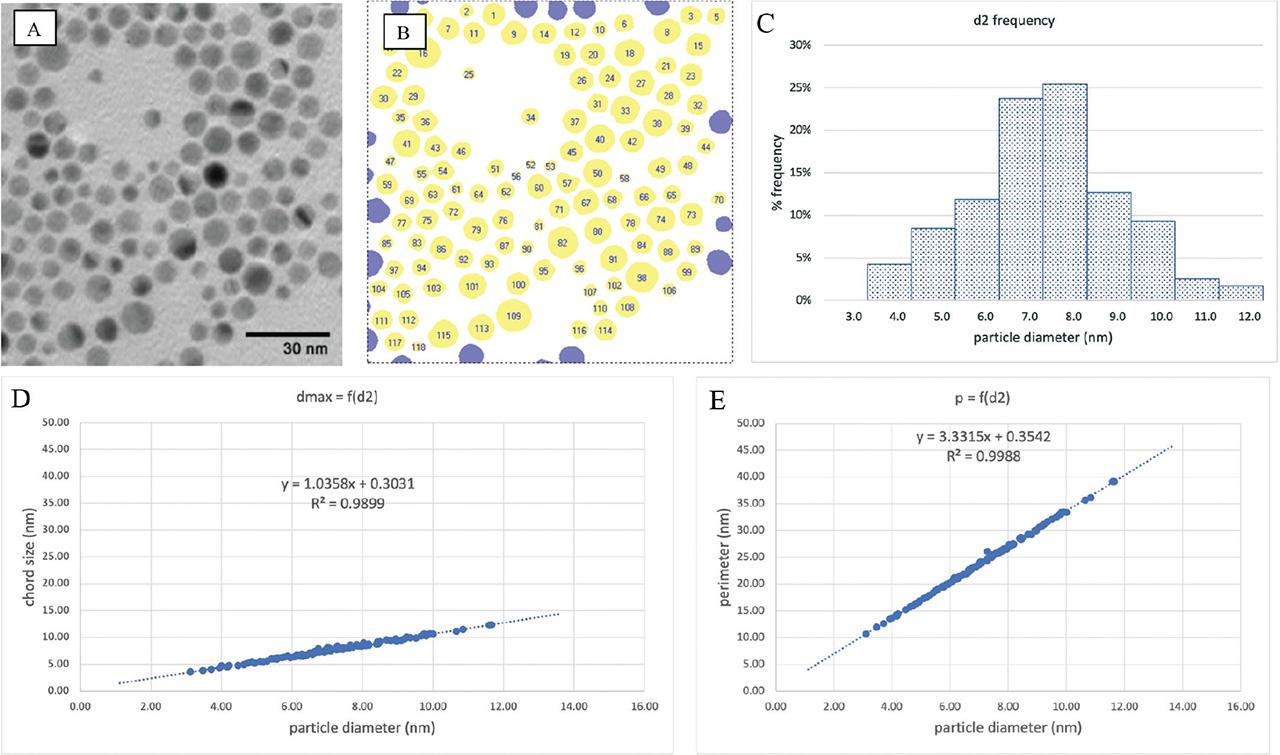
Fig 2.
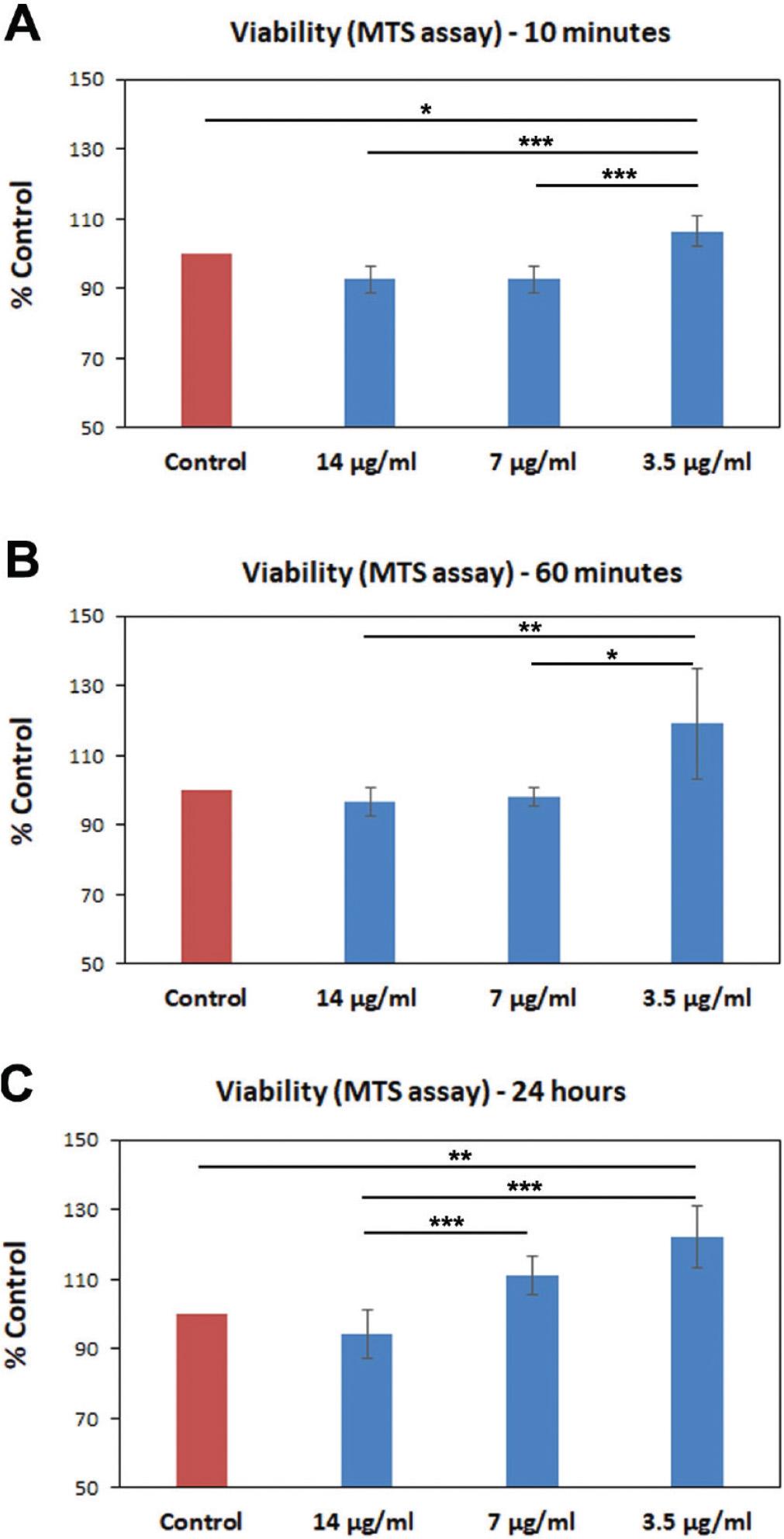
Fig 3.
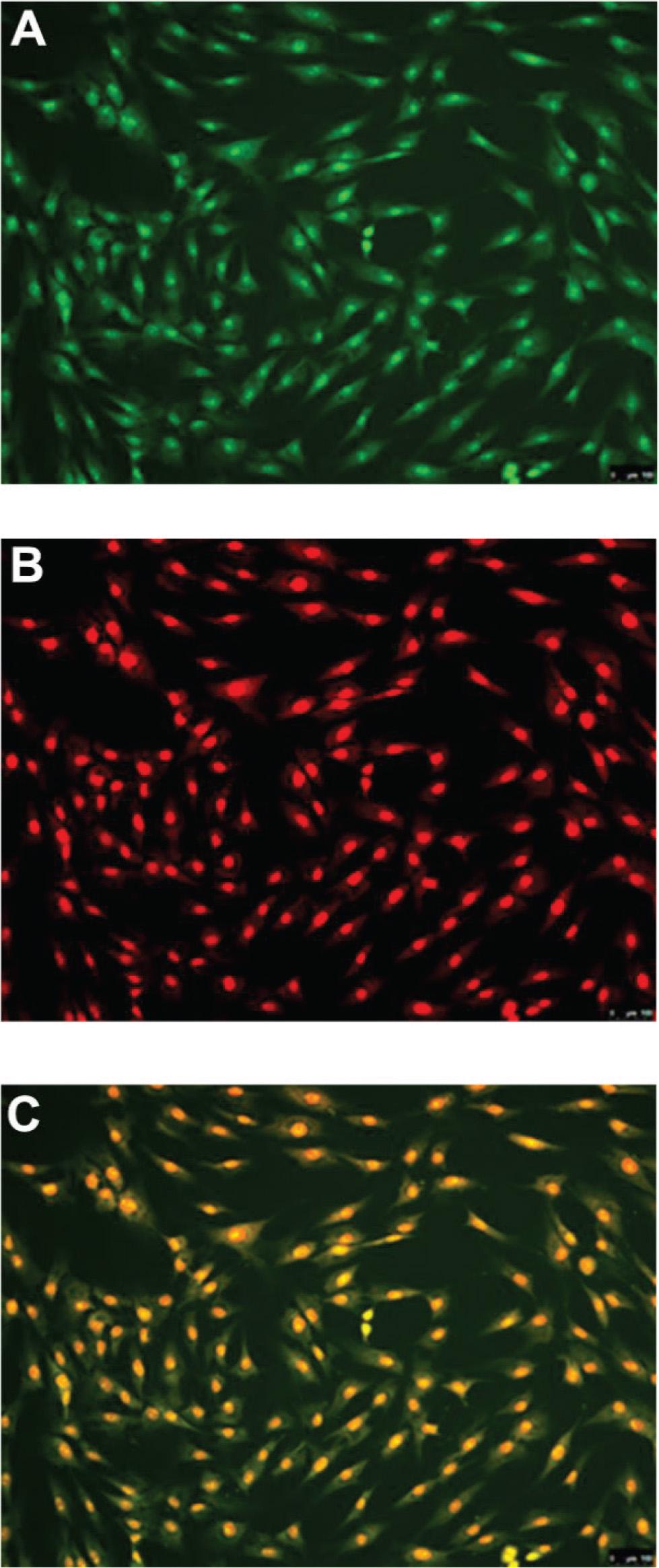
Fig 4.
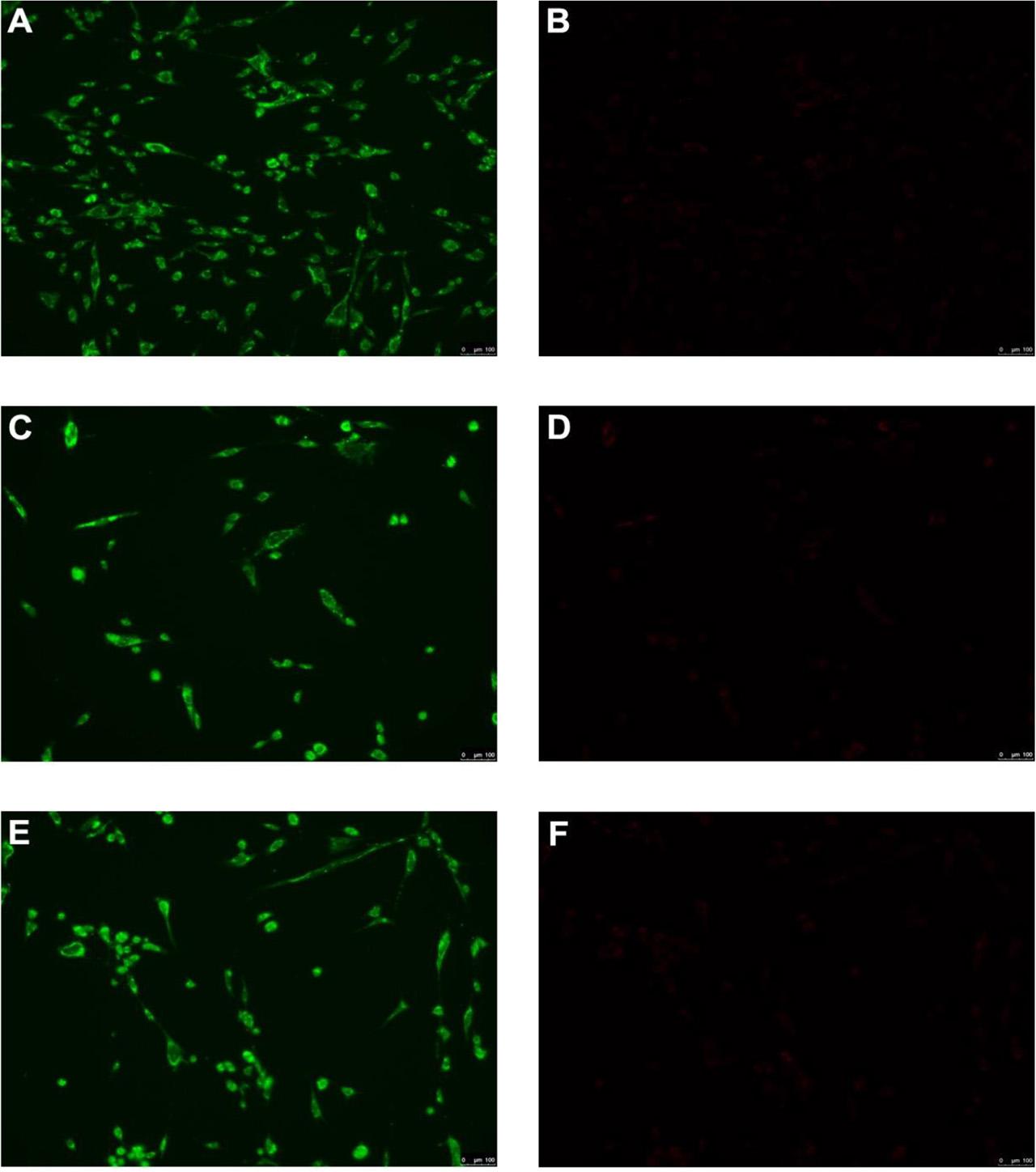
Fig 5.
Fig 6.
Fig 7.
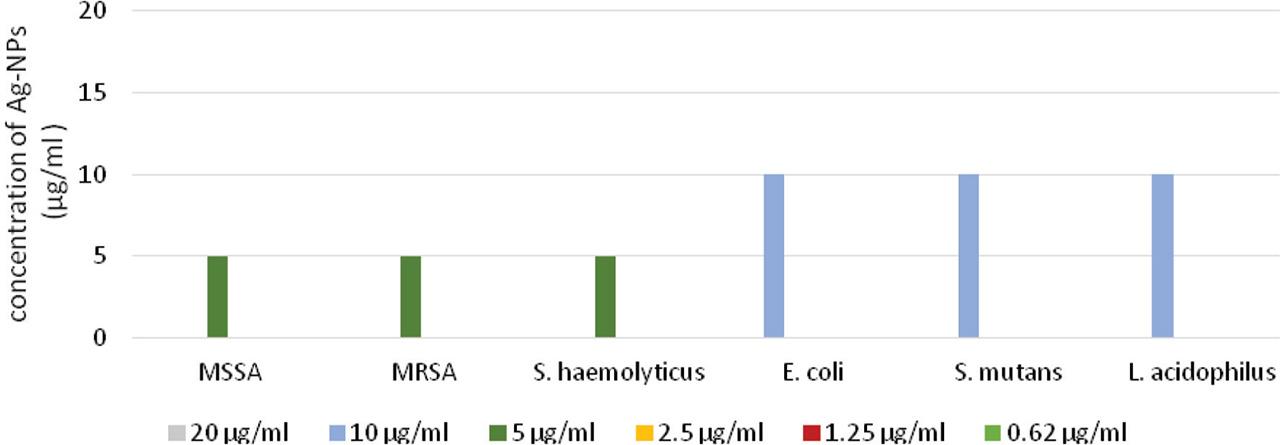
MIC and MBC values (μg/mL) of Ag-NPs for different bacterial strains
| Drug-sensitive strains | Multidrug-resistant strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus MSSA | S. mutans | E. coli | L. acidophilus | S. aureus MRSA | S. haemolyticus | |
| MIC μg/mL | 5 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| MBC μg/mL | 20 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 20 | 5 |
| MBC/MIC ratio | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |