Figure 1
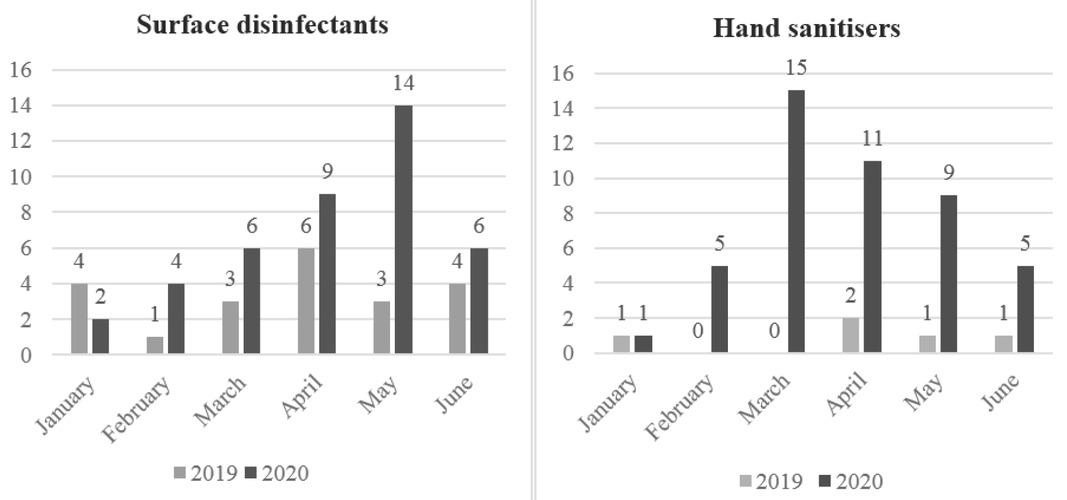
Differences in the pattern of exposure to surface disinfectants and hand sanitisers (data reported to CPCC from 1 January to 30 June 2020)
| Surface disinfectants (N=41) | Hand sanitisers (N=46) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age groups*: | ||
| Young children (0–5 years) | 16 (39 %) | 32 (70 %) |
| School children (6–11 years) | 2 (5 %) | 3 (6 %) |
| Adults (≥18 years) | 23 (56 %) | 11 (24 %) |
| Route of exposure: | ||
| Ingestion | 27 (66 %) | 43 (93 %) |
| Inhalation | 8 (20 %) | - |
| Skin | - | 1 (2 %) |
| Eye | 2 (5 %) | 2 (4 %) |
| Nasal mucosa | 1 (2 %) | - |
| Combination** | 3 (7 %) | - |
| Circumstances of exposure: | ||
| Accidental exposure | 32 (78 %) | 45 (98 %) |
| Attempted suicide | 1 (2 %) | - |
| Substance abuse | 2 (5 %) | - |
| Psychiatric disorder | 1 (2 %) | - |
| At work | 5 (12 %) | - |
| Other | - | 1 (2 %) |
| Symptoms at the time of CPCC call: | ||
| None | 21 (51 %) | 32 (70 %) |
| Mild*** | 19 (46 %) | 14 (30 %) |
| Severe**** | 1 (2 %) | - |