Figure 1
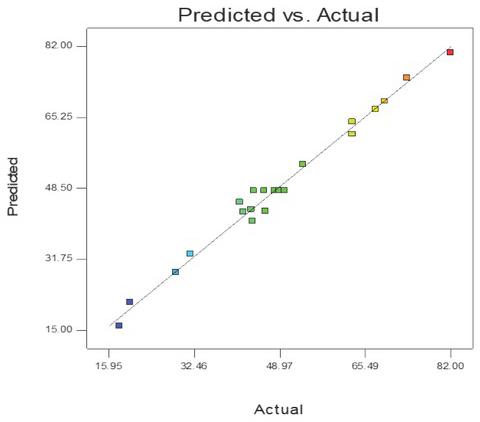
Figure 2
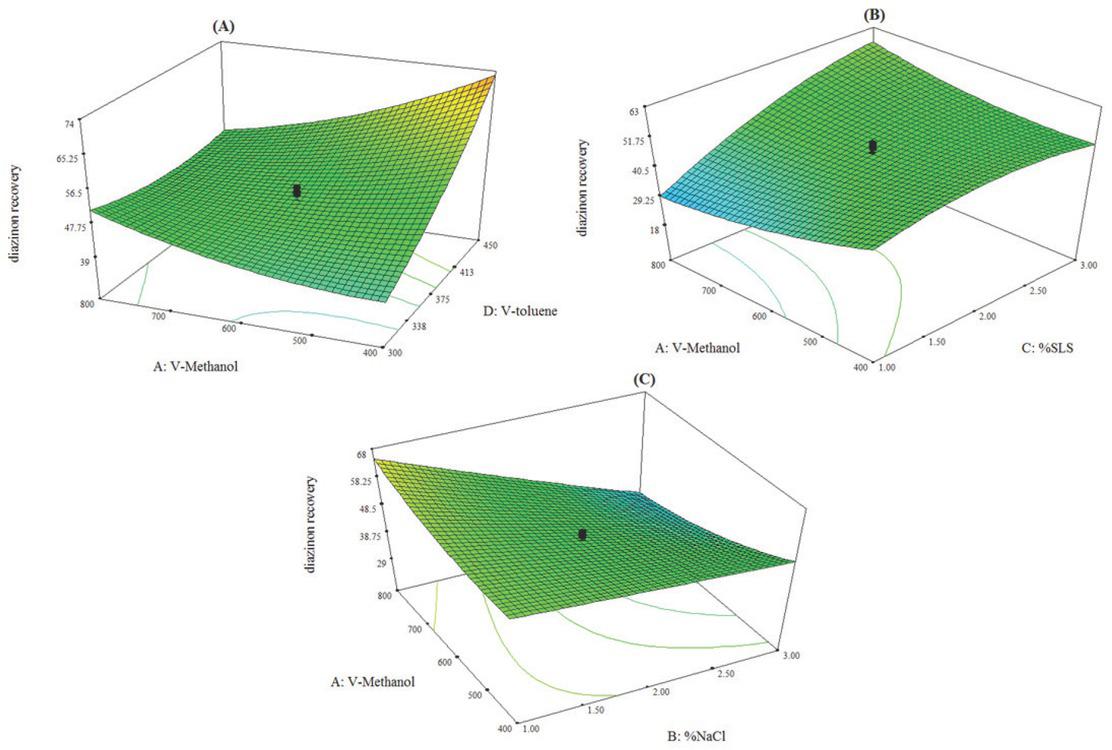
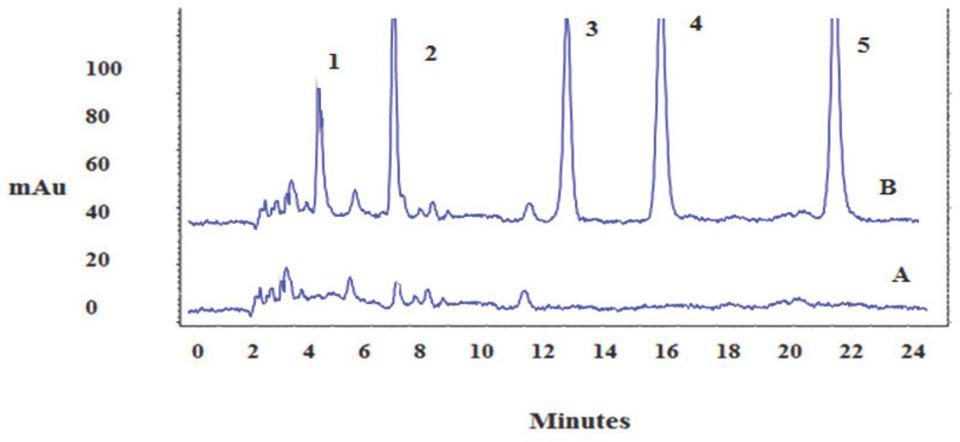
Figure 3
Variables and their levels for experimental design
| Symbol | Level 3 | Level 2 | Level 1 | Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | methanol | acetonitril | type of disperser solvent | |
| B | 10 | 0 | sonication duration (minute) | |
| C | dichloromethane | chloroform | toluene | type of extraction solvent |
| D | 600 | 300 | 100 | volume of extraction solvent (μL) |
| E | 1000 | 500 | 0 | volume of disperser solvent (μL) |
| F | 5 | 3 | 1 | surfactant concentration (% w/v) |
| G | 5 | 3 | 1 | salt concentration (% w/v) |
| H | 10 | 7 | 4 | pH |
Experimental ranges and levels of independent variables for the central composite design
| α- | 1- | 0 | 1+ | α+ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | μL | A | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| NaCl | % | B | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| SLS | % | C | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Toluene | μL | D | 225 | 300 | 375 | 450 | 525 |
Experimental conditions according to the central composite design and observed response values
| Experiment No. | Methanol volume (μL) | NaCl conc. (%w/v) | SLS conc. (%w/v) | Toluene volume (μL) | Actual recovery | Predicted recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 800 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 300.00 | 43.70 | 40.72 |
| 2 | 800 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 300.00 | 20.10 | 21.55 |
| 3 | 800 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 450.00 | 82.00 | 80.49 |
| 4 | 400 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 450.00 | 69.27 | 68.99 |
| 5 | 800 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 450.00 | 43.52 | 43.50 |
| 6 | 400 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 300.00 | 46.3 | 43.06 |
| 7 | 400 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 450.00 | 63.00 | 61.23 |
| 8 | 400 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 300.00 | 31.80 | 32.99 |
| 9 | 200 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 63.00 | 64.14 |
| 10 | 1000 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 53.50 | 54.13 |
| 11 | 600 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 67.50 | 67.14 |
| 12 | 600 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 29.00 | 28.64 |
| 13 | 600 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 375.00 | 18.02 | 15.94 |
| 14 | 600 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 375.00 | 41.33 | 45.18 |
| 15 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 225.00 | 42.00 | 42.88 |
| 16 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 525.00 | 73.60 | 74.48 |
| 17 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 48.00 | 47.89 |
| 18 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 46.00 | 47.89 |
| 19 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 49.00 | 47.89 |
| 20 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 50.00 | 47.89 |
| 21 | 600 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 375.00 | 44.00 | 47.89 |
Analysis of variance for the proposed model
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean square | F value | p-value all p-values are statistically significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 6195.89 | 14 | 442.56 | 41.69 | 0.0053 |
| A | 2223.78 | 1 | 2223.77 | 206.49 | 0.0007 |
| B | 72.231 | 1 | 72.31 | 6.81 | 0.0797 |
| C | 726.08 | 2 | 363.04 | 34.2 | 0.0086 |
| D | 862 | 2 | 431 | 40.6 | 0.0067 |
| E | 229.05 | 2 | 114.52 | 10.79 | 0.0426 |
| F | 1029.91 | 2 | 514.95 | 48.51 | 0.0052 |
| G | 915.54 | 2 | 457.77 | 43.12 | 0.0062 |
| H | 137.22 | 2 | 68.61 | 6.46 | 0.0817 |
| Residual | 31.85 | 3 | 10.62 | ||
| Correction Total | 6227.774 | 17 | |||
Analysis of variance for central composite design
| Source | Sum of squares | df | Mean square | F value | p-value all p-values are statistically significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 840.2 | 11 | 76.37 | 63.10 | <0.0001 |
| A | 16.28 | 1 | 16.28 | 13.45 | 0.0052 |
| B | 112.89 | 1 | 112.89 | 93.28 | <0.0001 |
| C | 142.35 | 1 | 142.35 | 117.63 | <0.0001 |
| D | 70.52 | 1 | 70.52 | 58.27 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 27.88 | 1 | 27.88 | 23.04 | 0.0010 |
| AC | 53.21 | 1 | 53.21 | 43.97 | <0.0001 |
| AD | 44.91 | 1 | 44.91 | 37.11 | 0.0002 |
| BC | 19.36 | 1 | 19.36 | 16.00 | 0.0031 |
| A^2 | 31.00 | 1 | 31.00 | 25.62 | 0.0007 |
| C^2 | 84.41 | 1 | 84.41 | 69.75 | <0.0001 |
| D^2 | 26.72 | 1 | 26.72 | 22.08 | 0.0011 |
| Residual | 10.89 | 9 | 1.21 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 7.37 | 5 | 1.47 | 1.67 | 0.3196 |
| Pure Error | 3.53 | 4 | 0.88 | ||
| Cor Total | 850.91 | 20 | |||
Comparison of the proposed DLLME-HPLC-DAD with other analytical methods for determination of diazinon in biological samples
| Method | Matrix | LOD (μg/mL) | Correlation coefficient (R2) | Recovery (%) | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPE-GC-MS | whole blood | 0.15 | 0.9981 | 78–87 | 15 |
| SPE-HPLC-DAD | plasma | 0.15 | 0.998 | 77.7–86.3 | 17 |
| LLE-HPLC-DAD | whole blood, serum, urine | 0.78 | 0.9996 | 97.4–99.01 (for blood and serum) | 16 |
| mini-QuEChERS-LC-MS-MS | whole blood, gastric content | 0.1 | 0.95 | 80–100 | 18 |
| MEPS-GC-MS-MS | whole blood | 0.5 | 0.99 | 61–77 | 26 |
| DBS-GC-MS-MS | whole blood | 0.05 | 0.998 | 4.56–5.11 | 27 |
| DLLME-HPLC-DAD | urine | 0.15 | 0.993 | 75.0–95.6 | this study |
Method precision and accuracy (intra-day: n=5; inter-day: n=5 series per day, 3 days)_
| Diazinon concentration (μg/mL) | Intra-day (n=5) | Inter-day (n=5) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | CV (%) | Recovery±SD (%) | Mean±SD | CV (%) | Recovery±SD (%) | |
| 0.5 | 0.46±0.04 | 7.4 | 92.1±1.0 | 0.48±0.03 | 6.9 | 95.6±1.0 |
| 1 | 0.76±0.02 | 3.3 | 76.0±2.0 | 0.75±0.01 | 1.2 | 75.0±1.1 |
| 3 | 2.33±0.09 | 4.0 | 77.4±0.9 | 2.31±0.11 | 4.9 | 77.1±1.4 |