Figure 1
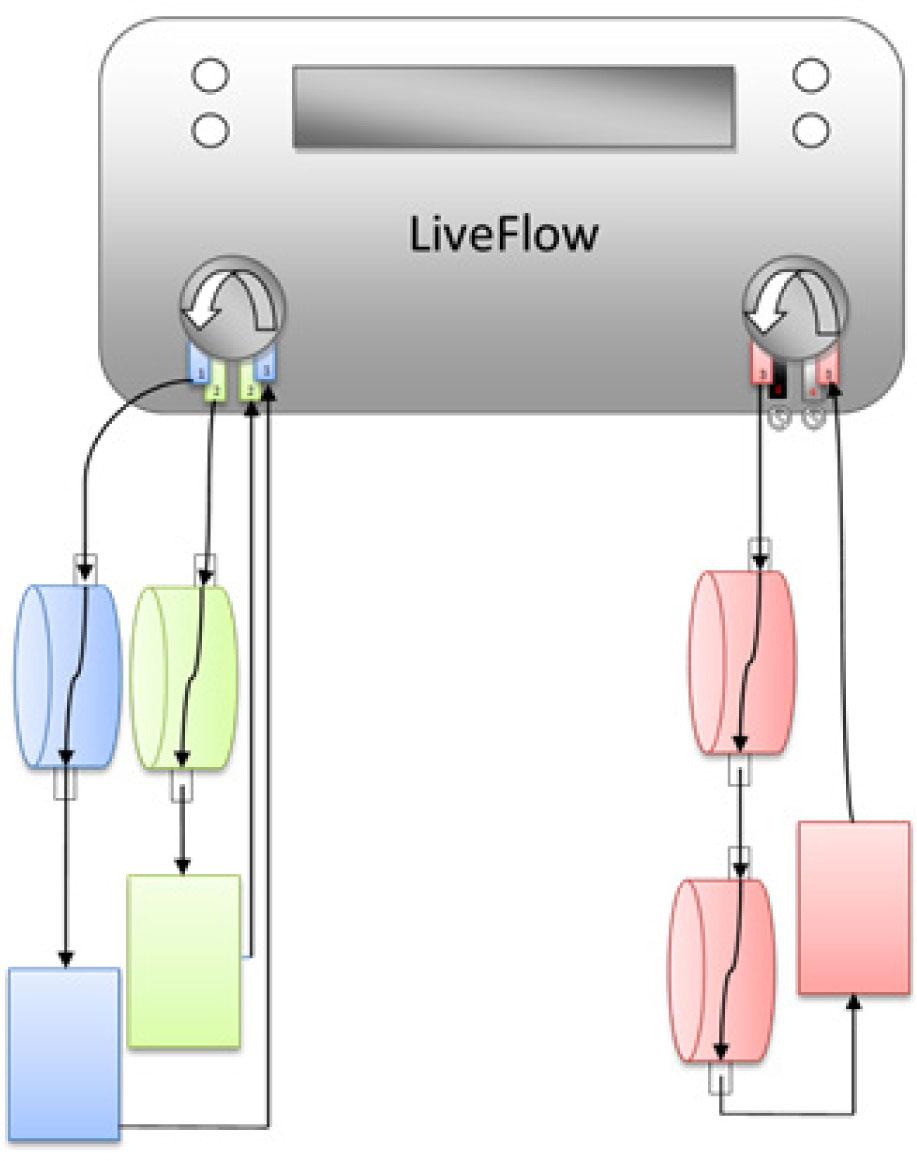
Figure 2
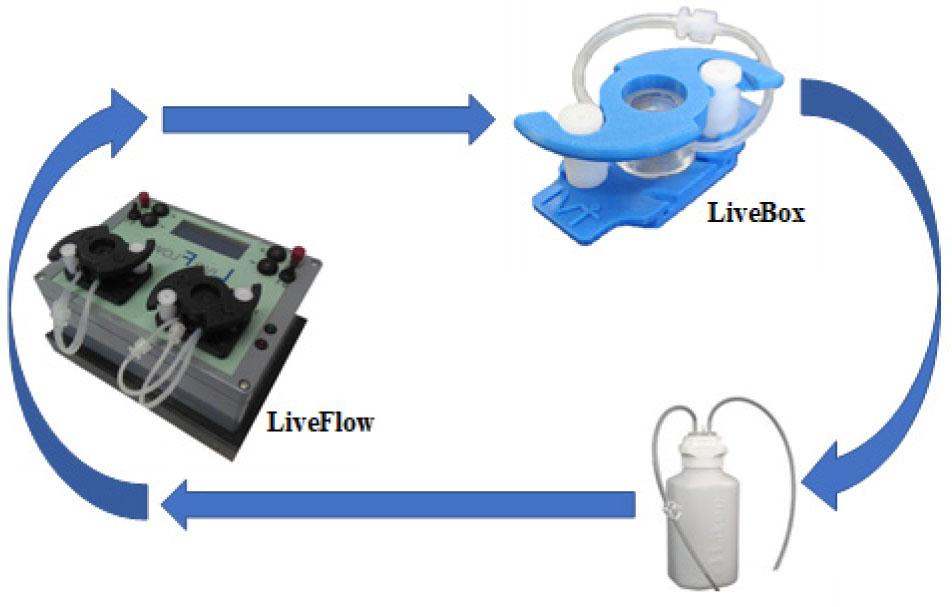
Figure 3
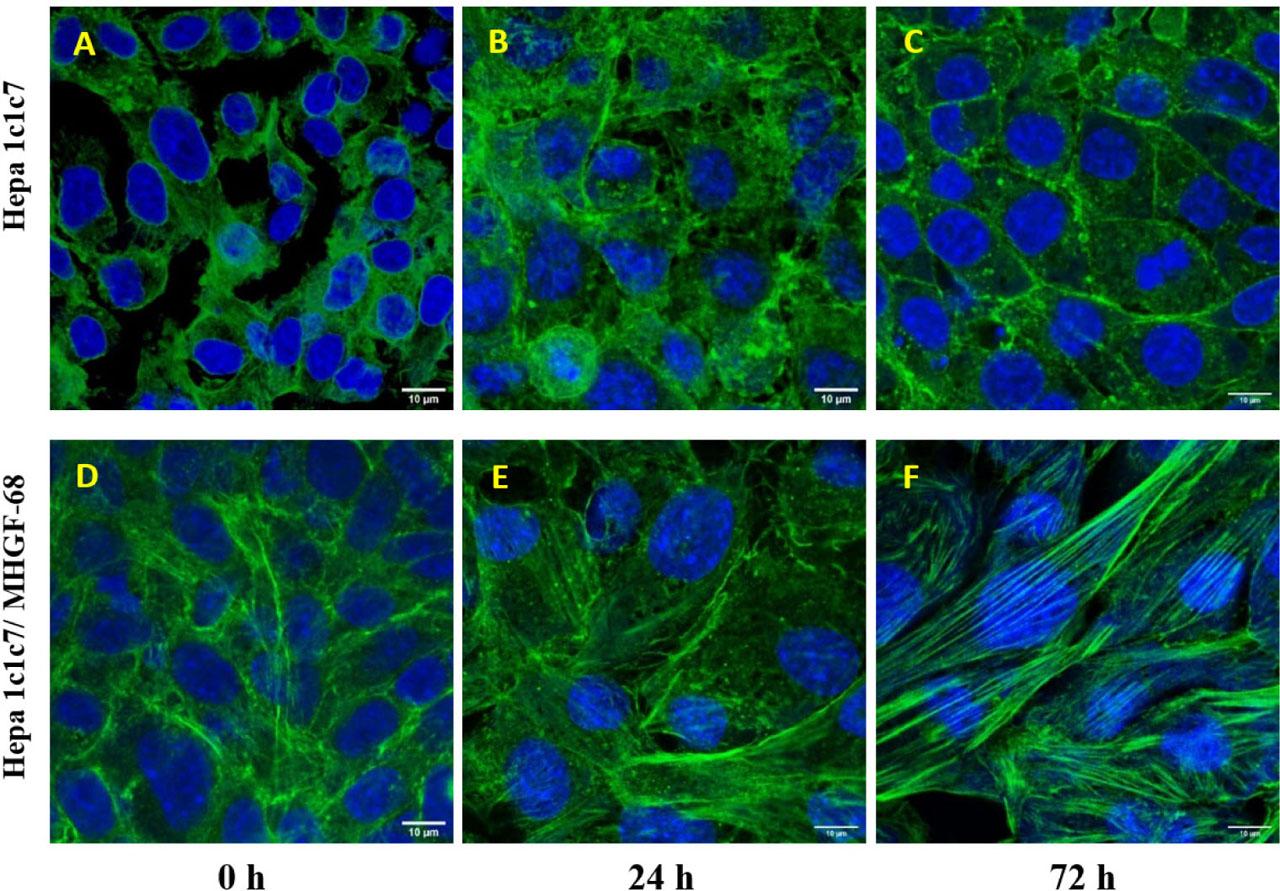
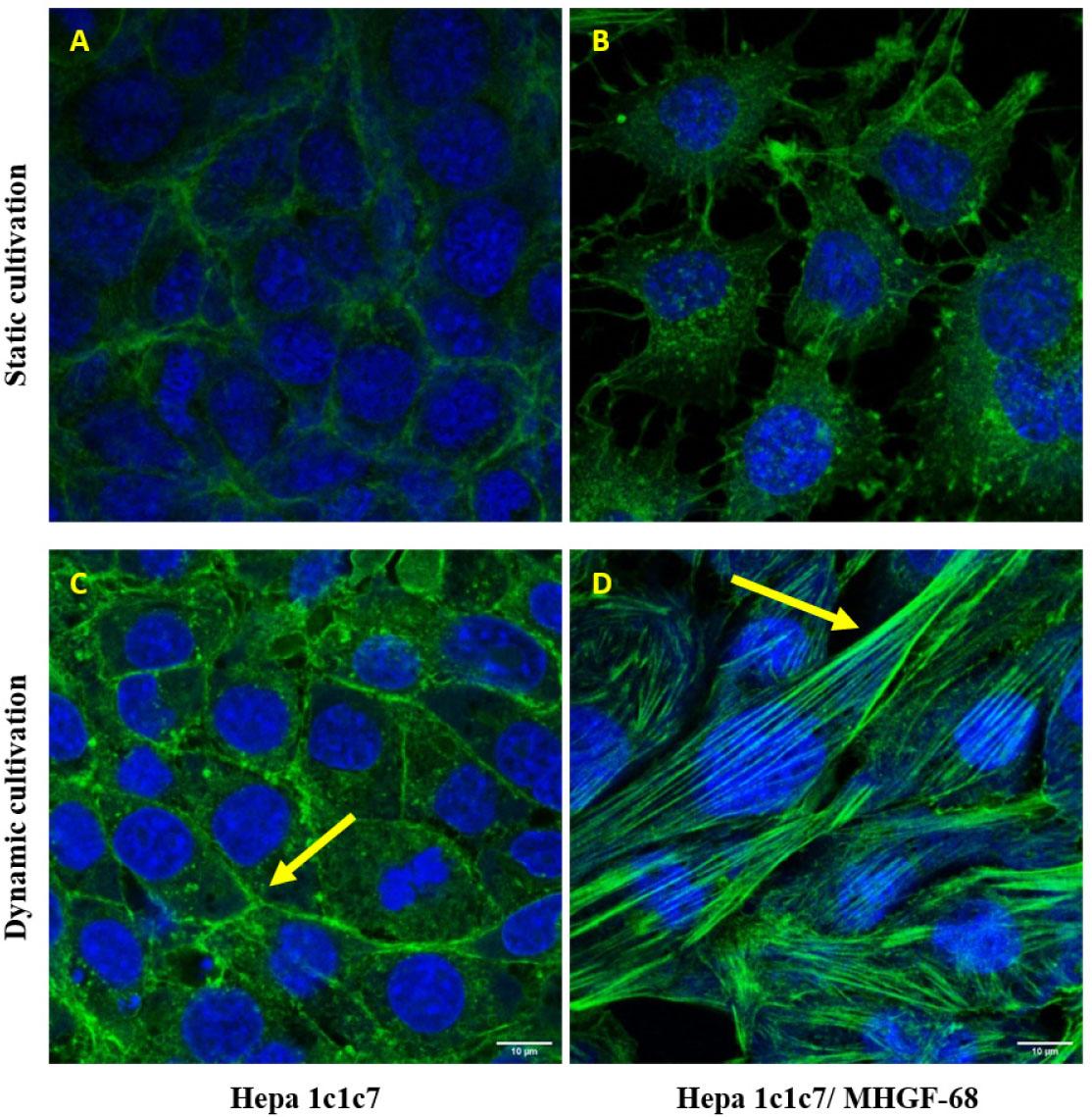
Figure 4

Figure 5
Comparison of IVTech, in vitro and in vivo testing_
| In vitro | In vivo | IVTech (advanced cell culture systems) |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of human complexity | Ethically controversial | Human organ environment simulation |
| Lack of side effects tests | Time ineffective | Multi-organ models |
| Lack of geometrical complexity | Expensive (2–30 times more than in vitro) | 3D and dynamic cell cultures |
| Cells cultivated in static conditions | No high-throughput monitoring | Real time monitoring |