Figure 1.

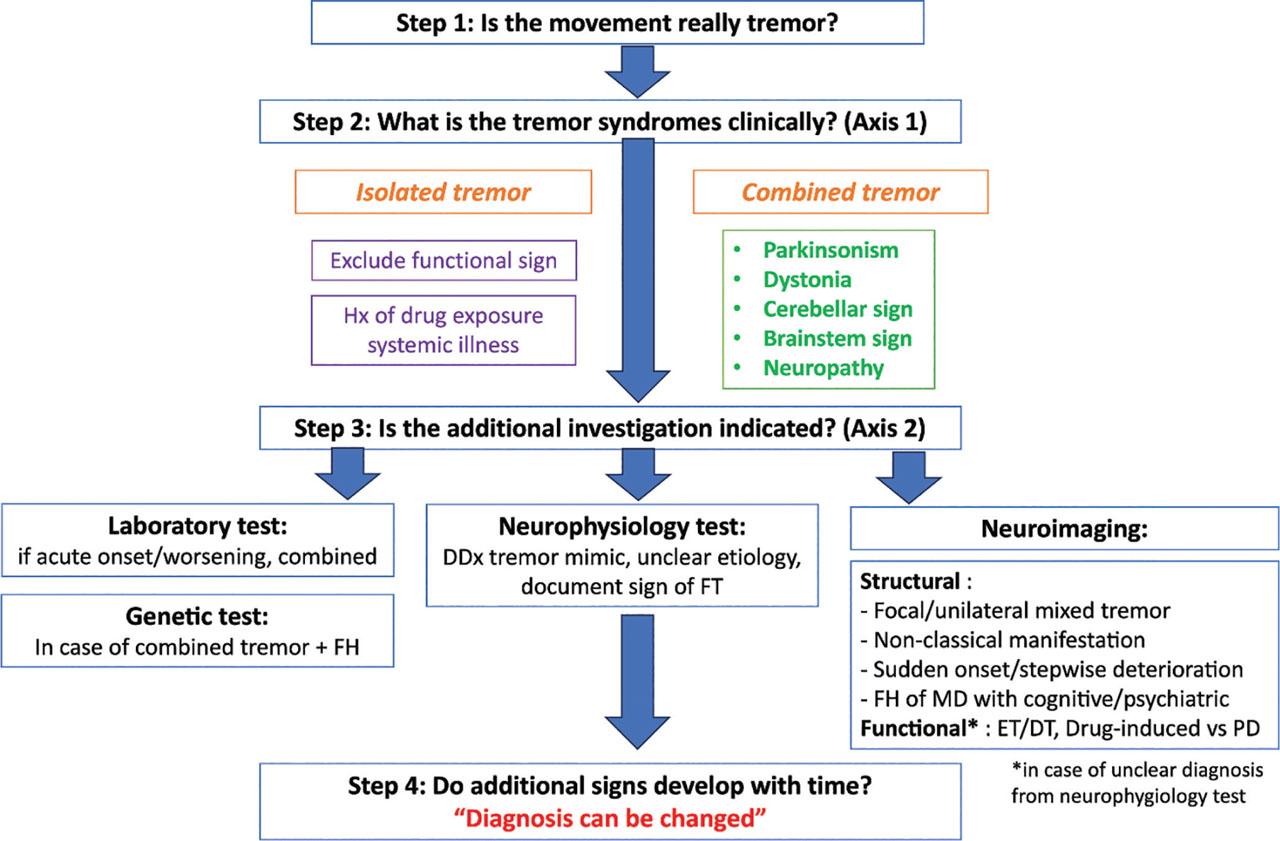
Figure 2.
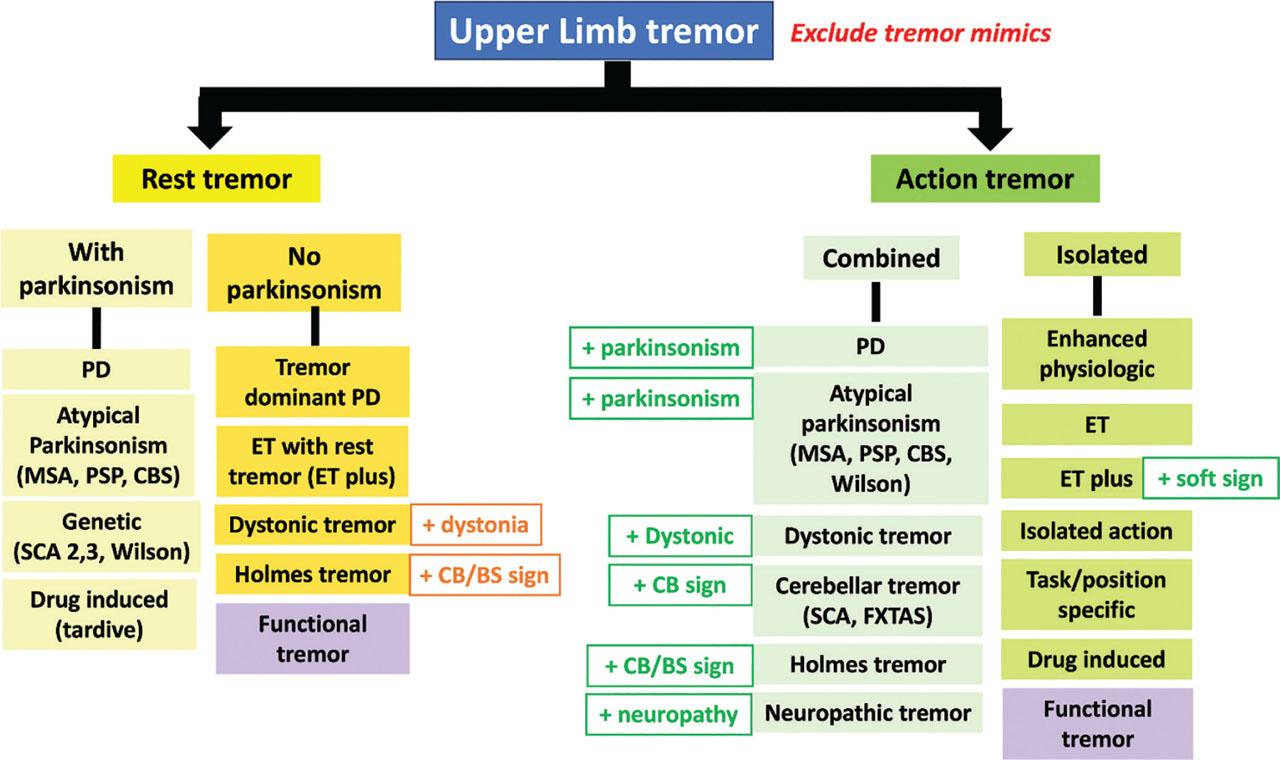
Figure 3.
Clinical features of essential tremor and enhanced physiological tremor
| Essential tremor | Enhanced physiologic tremor | |
|---|---|---|
| Activation | Kinetic (intentional component) > postural | Postural or kinetic |
| (amplitude of kinetic > postural) | (amplitude of postural > kinetic) | |
| Rest (in severe cases with action tremor) | Intentional component uncommon | |
| Distribution | Hands (flexion/extension of wrist, bilateral) | Fingers > hands (+/− voice) |
| Head, voice, jaw (with hands) | NOT head, jaw | |
| Frequency | 4–10 Hz (decrease with age) | 8–12 Hz |
| Changes with different tasks and different body parts | ||
| Amplitude | Fine to large | Fine |
| Aggravating /relieving factors | Alcohol responsiveness | Increase with stress, exercise, fatigue, caffeine |
| Pathophysiology | Central oscillator in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathway | Sympathetic overactivity and increase sensitivity of peripheral components |
| Weighting | Similar frequency | Decrease frequency |
| Treatment | Beta-blocker, primidone, topiramate | Beta-blocker |
| Surgery (DBS, MRI FUS thalamotomy) | Decrease aggravating factors | |
| Assistive devices |
Clinical characteristics of Parkinson’s disease, dystonic tremor, and essential tremor
| Parkinson’s disease | Dystonic tremor | Essential tremor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Asymmetry | Asymmetry | Symmetry (mostly) |
| Activation | R > P > K | P ~ K > R | K > P >>> rest |
| (Not intentional) | (Not intentional) | (Intentional) | |
| **Suppression of rest tremor with movements** | Rest (can be early) | Rest (in severe cases with action tremor) | |
| **Re-emergent tremor** | **position or task specific** | ||
| Distribution | Hands (pill-rolling, rotation of wrist, forearm) > jaw, tongue > leg > head | Head > Hands > jaw Isolated head, voice, jaw | Hands >> head > voice > jaw (with hands in severe cases) |
| Frequency | 4–7 Hz | 5–7 Hz | 4–10 Hz |
| Amplitude | Large, waxing & waning | Large, irregular, jerky | Fine to large |
| Association | Parkinsonism | Dystonic posture | Mild ataxia |
| Non-motor symptoms: RBD, anosmia, constipation, depression | Null point (head), overflow/mirror dystonia, sensory trick | Non-motor symptoms: anxiety, depression, cognitive impairment | |
| Family history | Usually absent in late onset | Sometimes present | Present in early onset |
| Treatment | Dopaminergic agent (response 50%) | Anticholinergics | Beta-blocker, primidone, topiramate |
| Anticholinergics | Botulinum toxin injection | Surgery (DBS, MRI FUS thalamotomy) | |
| Surgery (DBS, FUS) | Assistive devices |
Differentiation of tremor from tremor mimics
| Tremor | Cortical myoclonus | EPC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Oscillatory | Shock-like or jerky | Tonic/clonic |
| Single or repetitive | Repetitive | ||
| Rhythmicity | Regular but sometimes looks irregular in dystonic tremor syndromes or with some variability in amplitude of tremor | Irregular but can be rhythmic with repetitive myoclonus (8–18 Hz) | Regular and rhythmic (2–3 Hz) but can be irregular |
| Condition | Rest, postural, kinetic | Rest, postural, kinetic | Rest |
| Stimulus sensitivity | No reflex sensitivity | Can be triggered with sensory stimulation | No reflex sensitivity |
| Distribution | Bilateral or unilateral | Bilateral, symmetrical | Unilateral |
| Distal or proximal | Distal > proximal | Distal > proximal | |
| Upper limb > lower limb | Upper limb ~ lower limb | Upper limb > lower limb |
Step-by-step description of tremor examination
| Activation of tremor | Position/task | Provocation test/Specific observation | Associated examination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rest tremor |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| Postural tremor |
| Putting a slip of paper on top of hands (visualize fine tremor) |
|
| Putting the weight on the dorsum of hands | |||
|
| ||
| *Listening to high frequency tremor with stethoscope* | |||
| Kinetic tremor |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| Specific signs for functional tremor | Keep the position that elicits tremor | ||
|
| ||
| *Observe co-activation sign* | |||