Figure 1
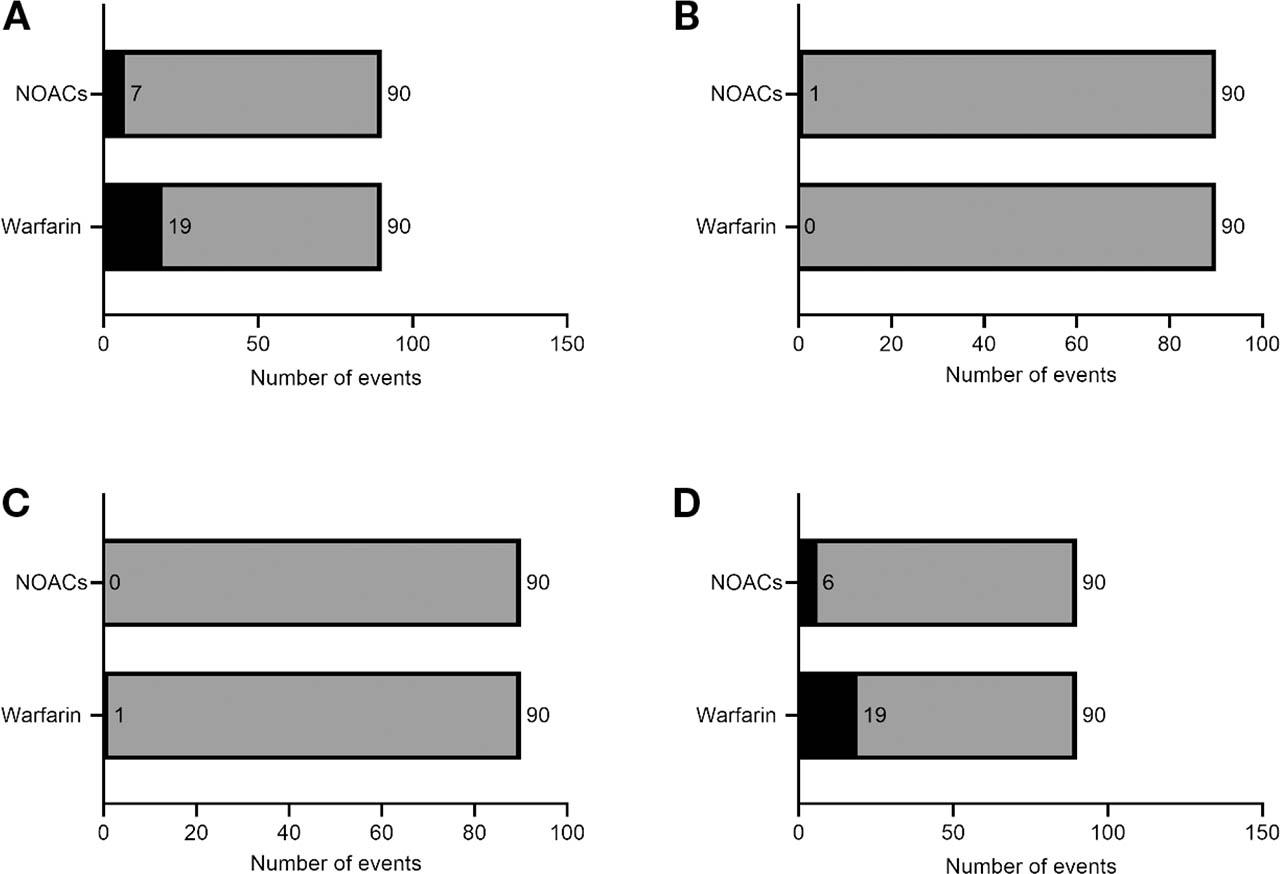
Primary and secondary outcomes of NOAC and well-controlled warfarin treatment in patients with AF
| Outcomes | Warfarin (n = 90) n (%) | NOACs (n = 90) n (%) | OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome: total bleeding or thromboembolic events or both | 19 (21) | 7 (8) | 3.17 (2.27–4.07) | 0.01* |
| Secondary outcome | ||||
| Thromboembolic events or major bleeding or both | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1.00 (−1.78 to 3.78) | >0.99 |
| Thromboembolic events | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | – | – |
| Major bleeding | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | – | – |
| Minor bleeding | 19 (21) | 6 (7) | 3.75 (2.79–4.71) | 0.01* |
| Bleeding per gum | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 2.02 (−0.40 to 4.44) | >0.99 |
| Bruising | 12 (13) | 5 (6) | 2.61 (1.53–3.69) | 0.047 |
| Hematuria | 3 (3) | 2 (2) | 1.51 (−0.29 to 3.31) | >0.99 |
| Epistaxis | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | – | – |
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | – | – |
| All-cause mortality | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | – | – |
Baseline characteristics of Thai patients with AF
| Demographic data | Total (n = 180) n (%) | Warfarin (n = 90) n (%) | NOACs (n = 90) n (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 72.8 ± 10.1 | 71.3 ± 10.2 | 74.3 ± 9.8 | 0.04* |
| Male sex | 107 (59) | 48 (53) | 59 (66) | 0.10 |
| Medical welfare | ||||
| Affiliation reimbursement | 122 (68) | 40 (44) | 82 (91) | <0.01* |
| Universal healthcare coverage | 43 (24) | 40 (44) | 3 (3) | |
| Social security scheme | 3 (2) | 3 (3) | 0 (0) | |
| Self-payment | 12 (7) | 7 (8) | 5 (6) | |
| Medical history | ||||
| Diabetes | 50 (28) | 23 (26) | 27 (30) | 0.51 |
| Hypertension | 162 (90) | 79 (88) | 83 (92) | 0.32 |
| Dyslipidemia | 139 (77) | 69 (77) | 70 (78) | 0.86 |
| Coronary artery disease | 36 (20) | 14 (16) | 22 (24) | 0.14 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | – |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 24 (13) | 13 (14) | 11 (12) | 0.66 |
| Previous ischemic stroke or TIA | 34 (19) | 14 (16) | 20 (22) | 0.25 |
| History of intracranial bleeding | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 0.50 |
| History of heart failure | 74 (41) | 43 (48) | 31 (34) | 0.07 |
| Cirrhosis | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | – |
| Chronic kidney disease | 54 (30) | 28 (31) | 26 (29) | 0.78 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 48 (28) | 23 (26) | 25 (29) | 0.66 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), median (IQR) | 70.75 (58.0, 85.8) | 70.72 (57.3, 85.1) | 70.75 (58.2, 87.0) | 0.87 |
| CHA2 DS2-VASc score, median (IQR) | 4 (3, 5) | 4 (3, 5) | 4 (3, 5.3) | 0.30 |
| HAS-BLED score, median (IQR) | 2 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 2 (1, 2) | <0.01* |
| SAMeTT2 R2 score, median (IQR) | 4 (3, 4) | 4 (3, 4) | 4 (3, 4) | 0.70 |
| 0–2 | 15 (9) | 7 (8) | 8 (9) | 0.75 |
| ≥3 | 157 (91) | 80 (92) | 77 (91) | |
| Time in the therapeutic range (%), mean ± SD | 84.9 ± 9.8 | – | – | |
| Antiplatelets | 10 (6) | 7 (8) | 3 (3) | |
| Aspirin | 3 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | – |
| P2Y12 inhibitors | 7 (4) | 5 (6) | 2 (2) | 0.44 |
| OAC | ||||
| Warfarin | 90 (100) | – | – | |
| Rivaroxaban | – | 30 (33) | – | |
| Apixaban | – | 26 (29) | – | |
| Dabigatran | – | 17 (19) | – | |
| Edoxaban | – | 17 (19) | – | |
| NSAIDs | 6 (3) | 0 (0) | 6 (7) | 0.03* |
| Proton pump inhibitors | 51 (28) | 23 (26) | 28 (31) | 0.41 |