Figure 1
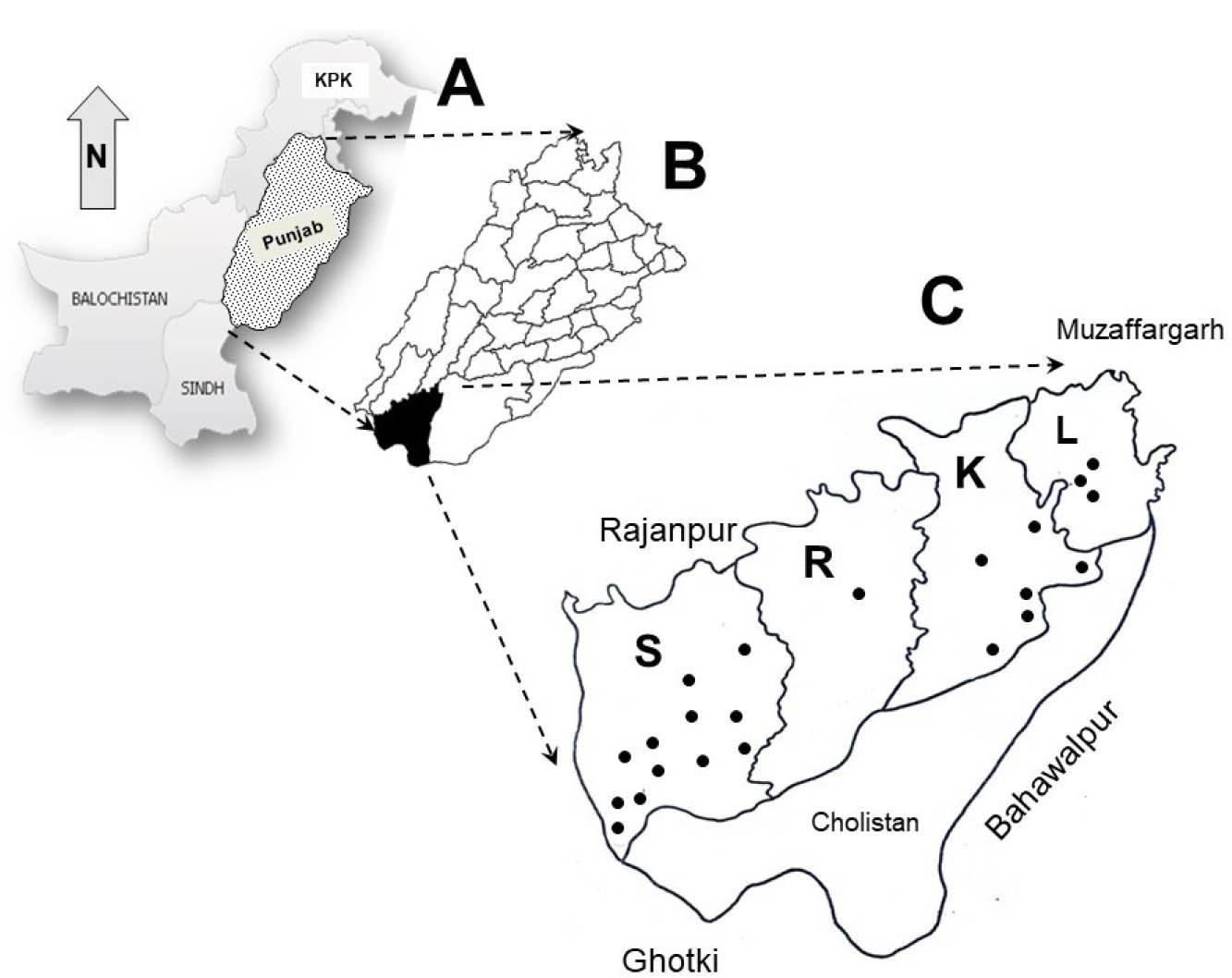
Figure 2
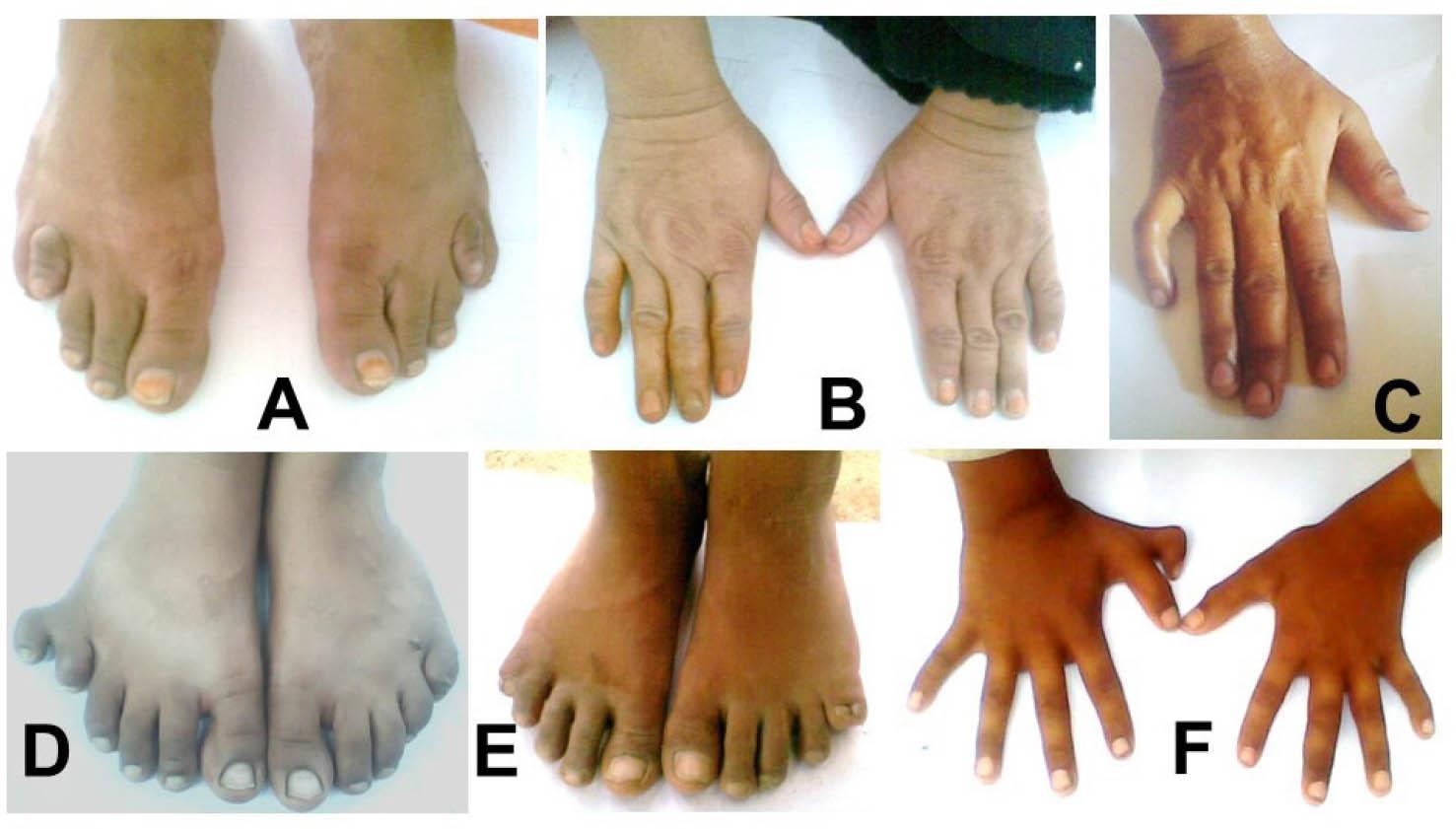
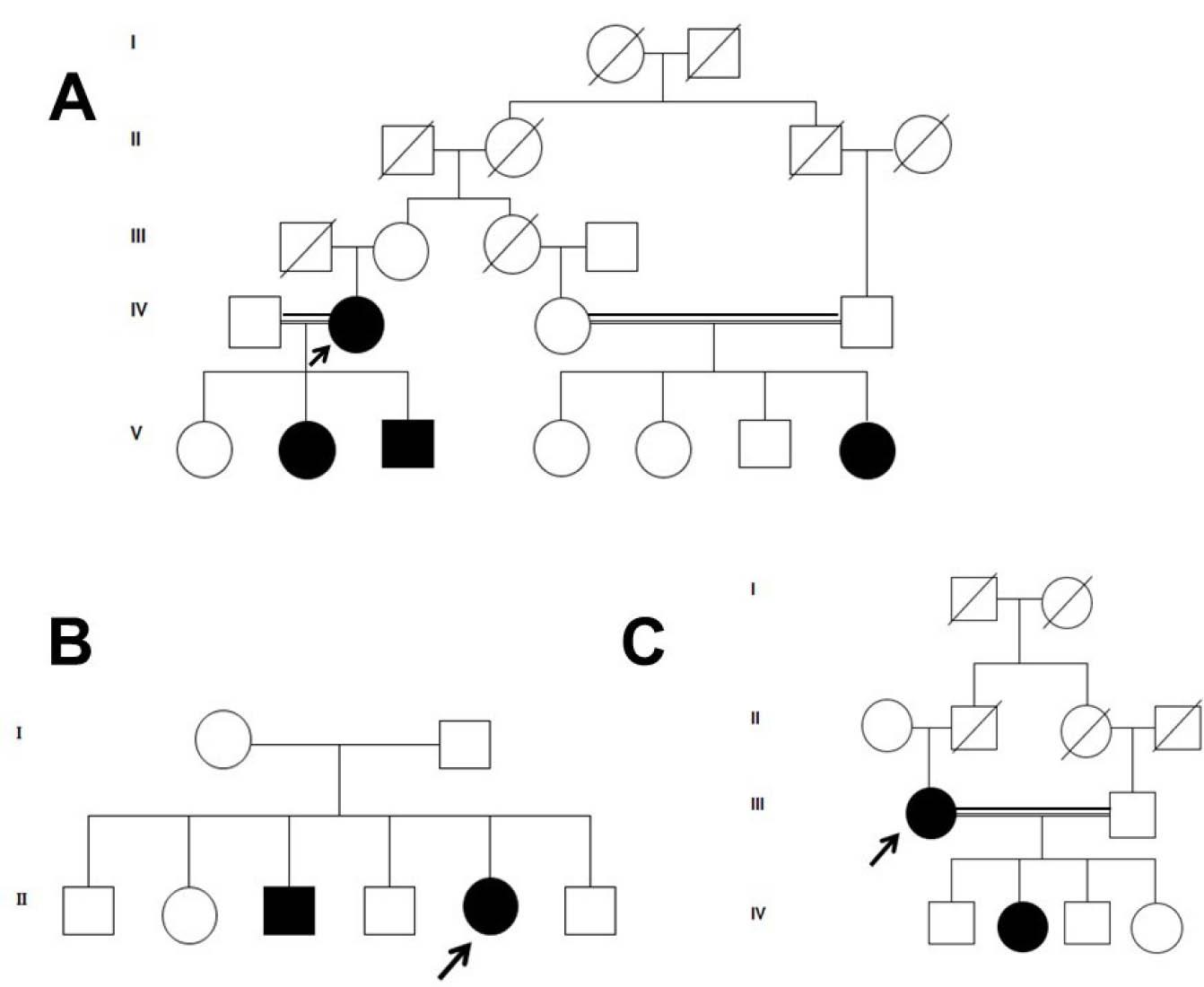
Figure 3
Association of limb anomalies in sociodemographic attributes of participants
| Variable | Affected | Unaffected | Prevalence/1,000 | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tehsil | |||||
| Rahim Yar Khan | 2 | 599 | 3.32 | Reference | |
| Khanpur | 4 | 583 | 6.81 | 2.05 | 0.37–11.27 |
| Sadiqabad | 5 | 959 | 5.20 | 1.56 | 0.30–8.08 |
| Liaquatpur | 0 | 52 | 0.0 | ||
| Total | 11 | 2193 | 4.99 | ||
| Native dialect | |||||
| Punjabi | 7 | 1105 | 6.29 | 2.01 | 0.52–7.81 |
| Saraiki | 3 | 953 | 3.14 | Reference | |
| Other | 1 | 135 | 7.35 | 2.35 | 0.24–22.80 |
| Place of residence | |||||
| Rural | 7 | 1409 | 4.94 | Reference | |
| Urban | 4 | 784 | 5.08 | 1.03 | 0.30–3.52 |
| Family structure | |||||
| Nuclear family | 9 | 1210 | 7.38 | 3.35 | 0.79–16.97 |
| Extended Family | 2 | 983 | 2.03 | Reference | |
| Parental marriage | |||||
| Consanguineous | 8 | 1290 | 6.16 | 1.87 | 0.49–7.06 |
| Nonconsanguineous | 3 | 903 | 3.31 | Reference | |
| Education | |||||
| Illiterate | 7 | 1464 | 4.76 | Reference | |
| Literate | 4 | 729 | 5.46 | 1.15 | 0.33–3.93 |
| Age group (years) | |||||
| 29 | 5 | 1075 | 4.63 | Reference | |
| >29 | 12 | 1118 | 10.62 | 2.31 | 0.81–6.57 |
Prevalence of limb anomalies in a married female population sample from Rahim Yar Khan District
| Limb anomaly | No. | Prevalence/1,000 | 95% CI | OMIM | ICD-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polydactyly (all) | 5 | 2.27 | 0.72–5.31 | 603,596 | Q69 |
| Polydactyly (postaxial A) | 4 | 1.81 | 0.48–4.67 | 174,200 | Q69.0 |
| Polydactyly (preaxial) | 1 | 0.45 | <0.001–2.57 | 174,400 | Q69.1 |
| Brachydactyly (all) | 4 | 1.81 | 0.48–4.67 | ||
| Brachydactyly (brachymetatarsia IV) | 3 | 1.36 | 0.26–4.00 | 113,475 | |
| Brachydactyly type A4 | 1 | 0.45 | <0.001–2.57 | 112,800 | |
| Camptodactyly | 1 | 0.45 | <0.001–2.57 | 114,200 | M72.0 |
| Oligodactyly (thumb aplasia) | 1 | 0.45 | <0.001–2.57 | Q71.3 | |
| Total | 11 | 4.99 | 2.48–8.94 | ||
Characteristics of limb anomalies in a married female population sample from Rahim Yar Khan District
| Features | Polydactyly (all) | Brachydactyly (all) | Camptodactyly | Oligodactyly | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of cases | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 11 |
| Total affected in all families | 12 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 19 |
| Familial/sporadic nature | |||||
| Familial | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Sporadic | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Laterality | |||||
| Unilateral | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Bilateral | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Symmetry | |||||
| Symmetrical | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Asymmetrical | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Involvement of limb | |||||
| Upper right | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Upper left | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Lower right | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Lower left | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Total limbs involved | 7 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 17 |