Figure 1:
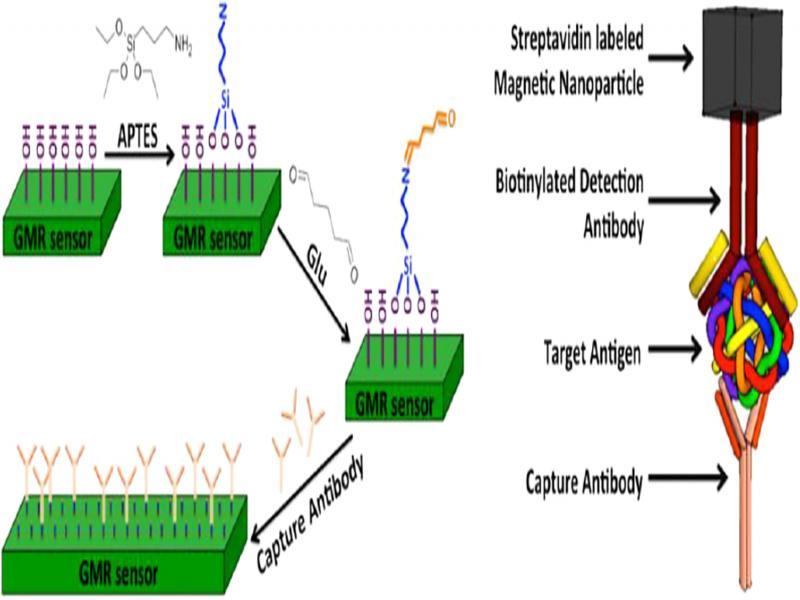
Figure 2:
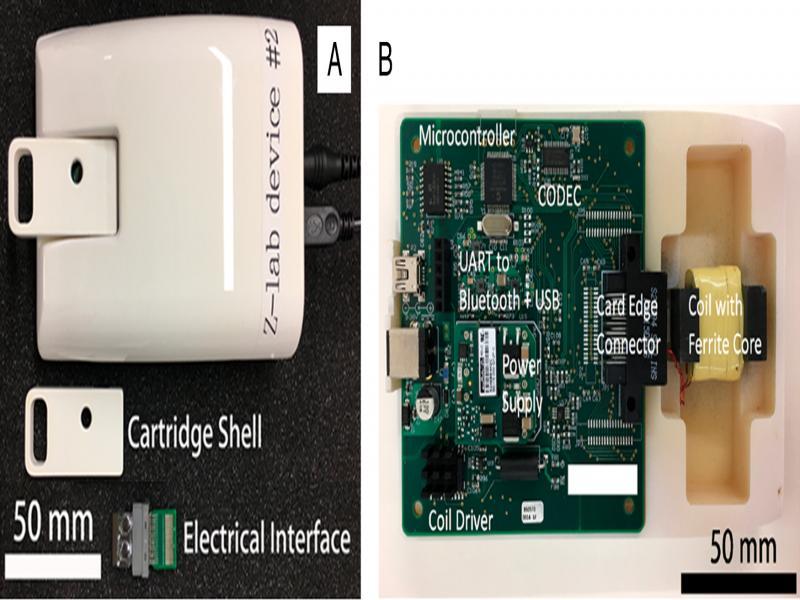
Figure 3:
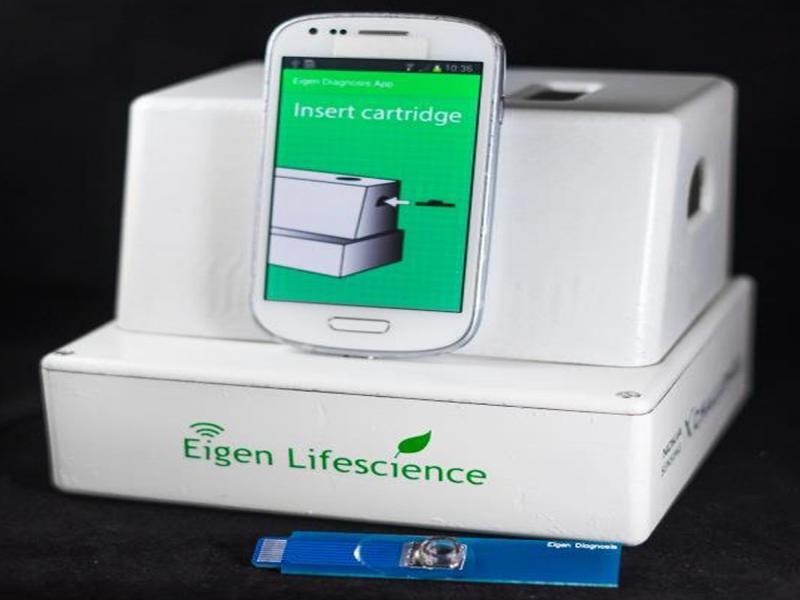
Figure 4:
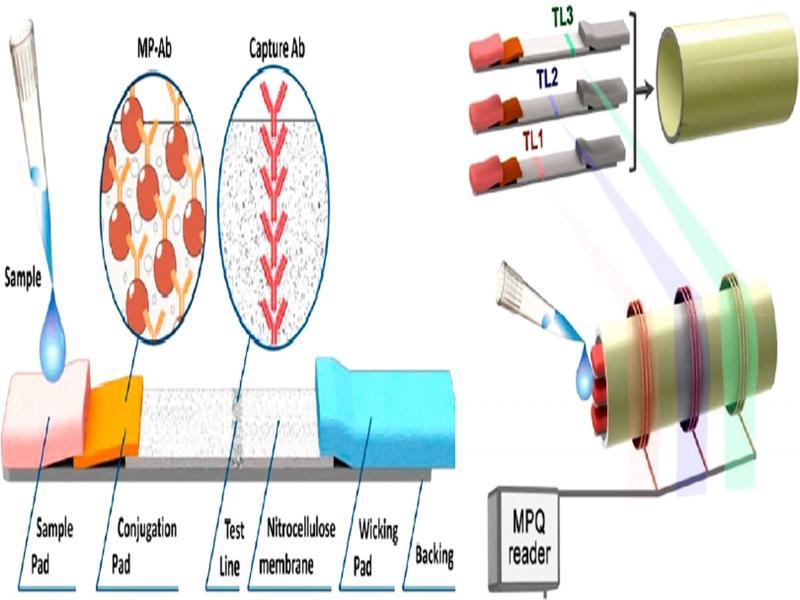
Figure 5:
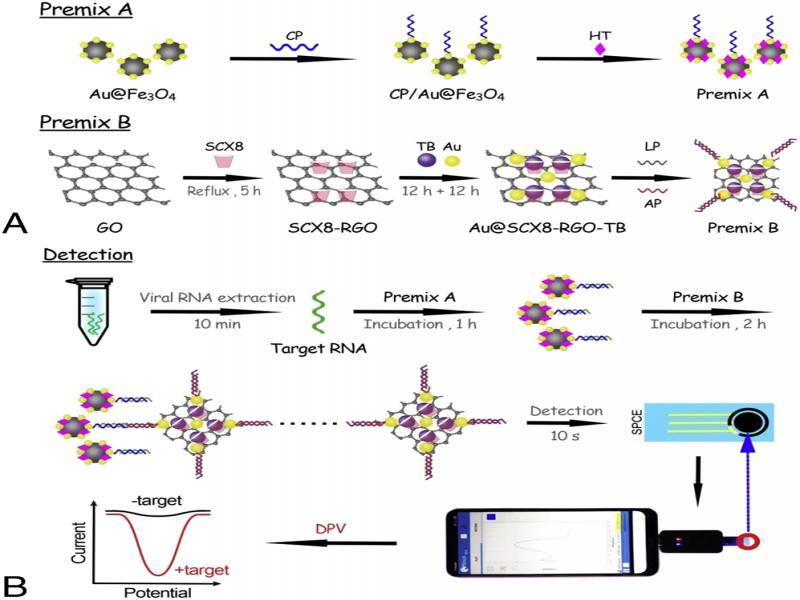
Figure 6:
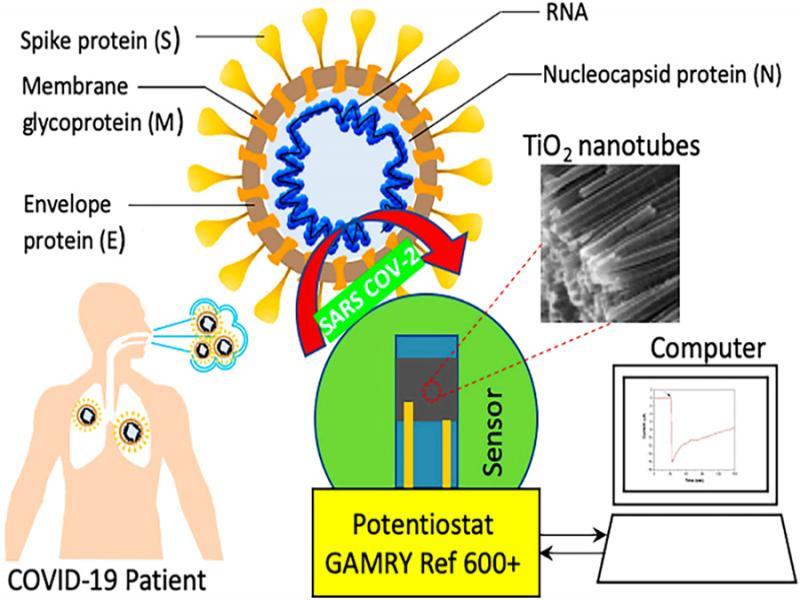
Figure 7:
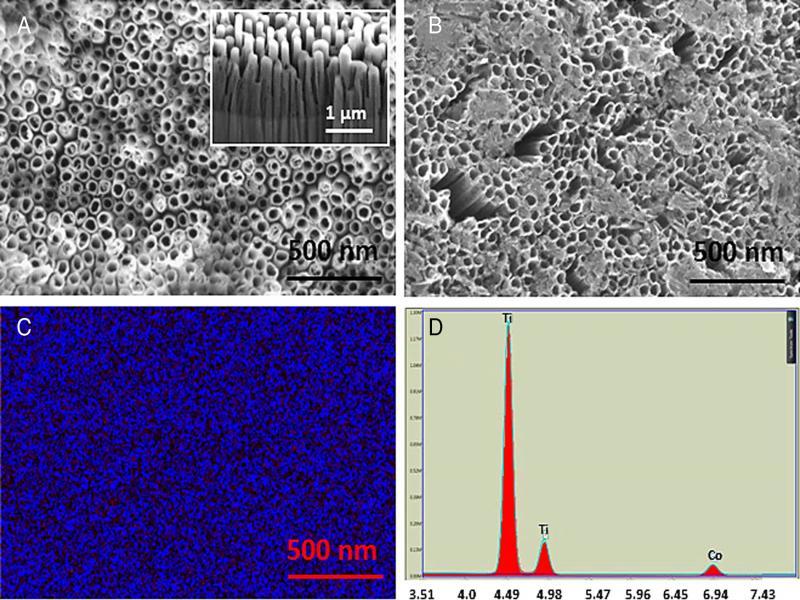
Figure 8:
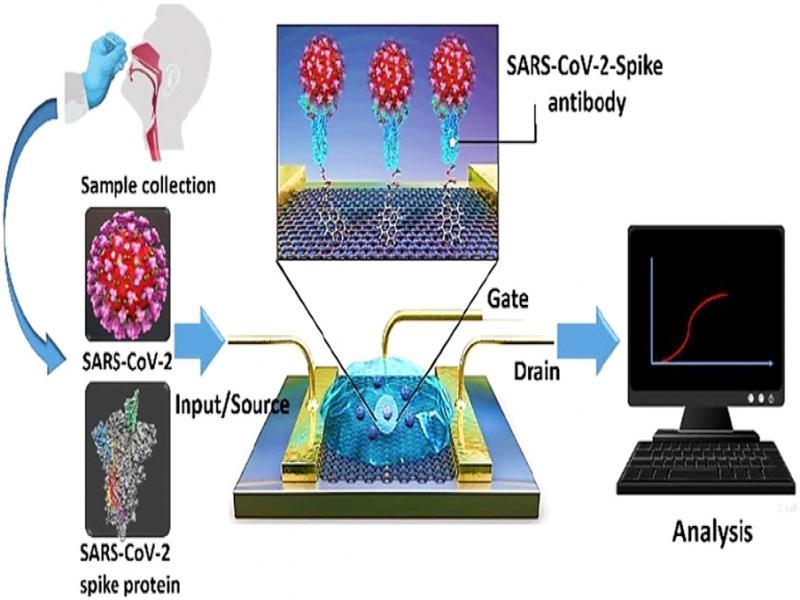
Figure 9:
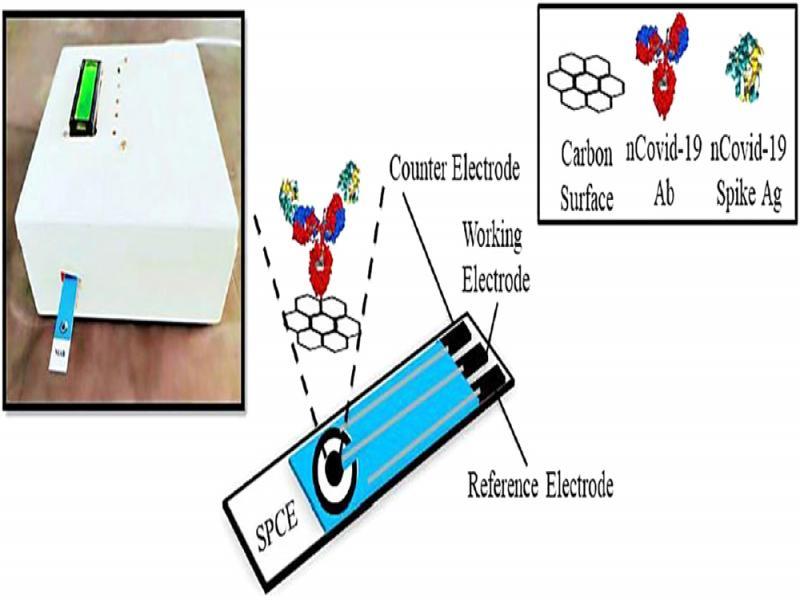
Figure 10:

Figure 11:
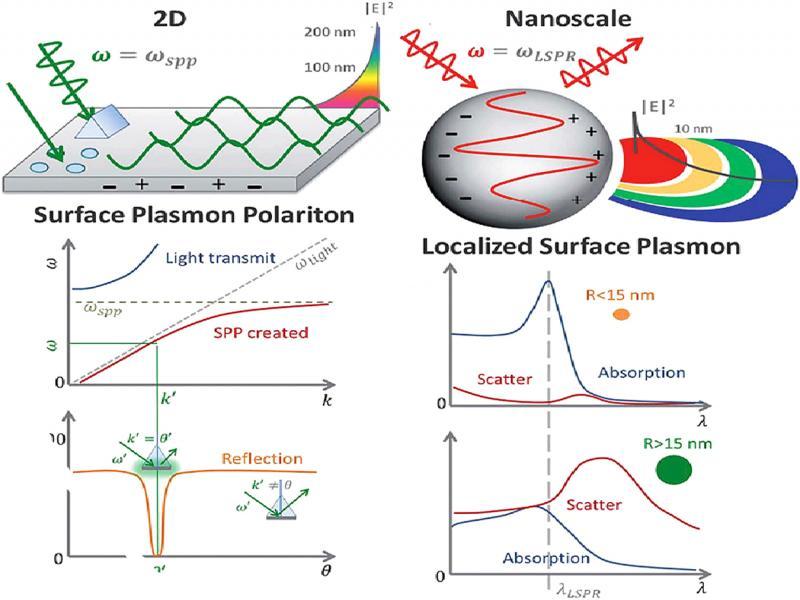
Figure 12:
Figure 13:
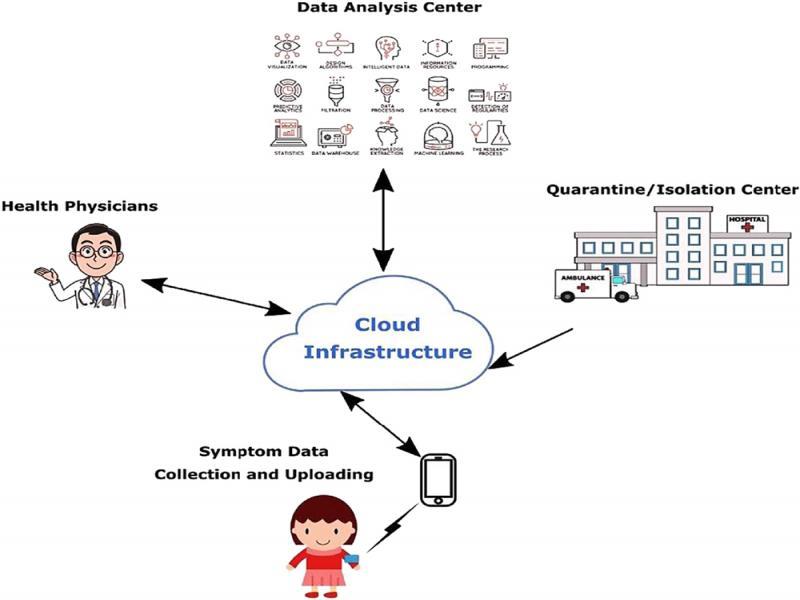
Figure 14:
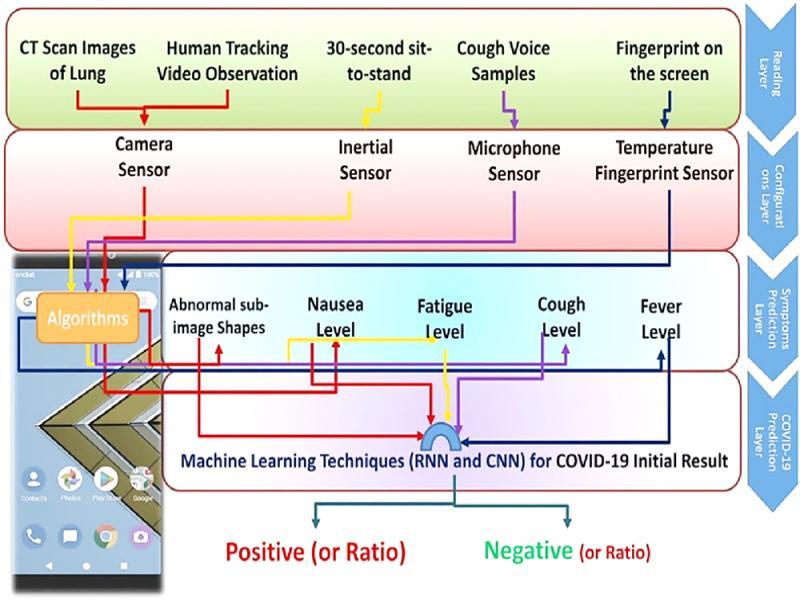
Figure 15:
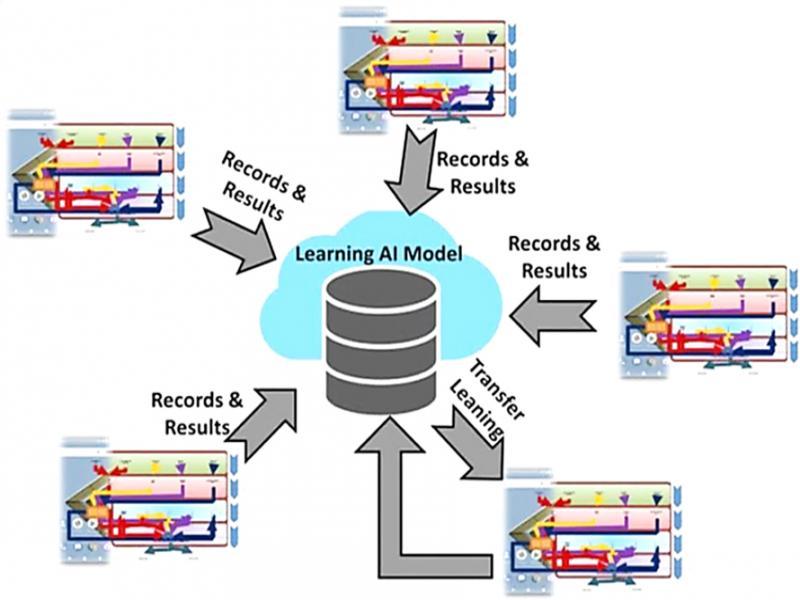
Figure 16:
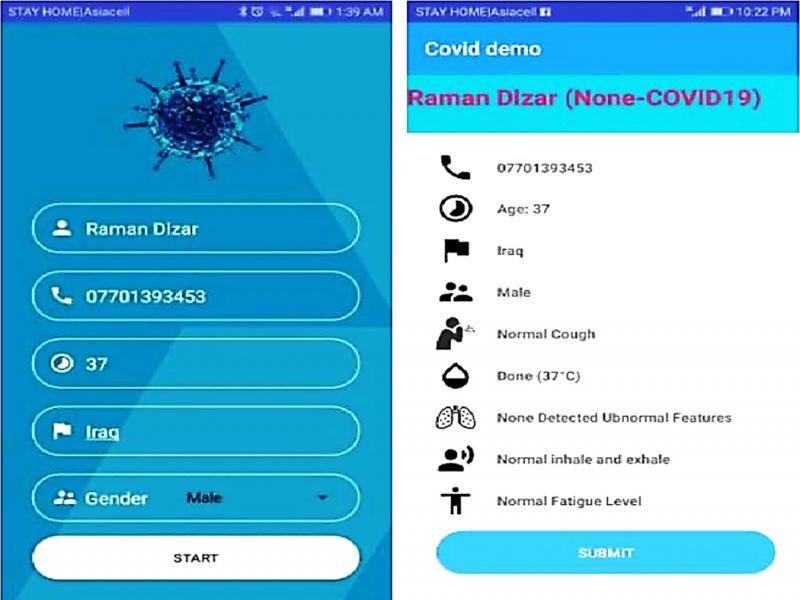
Figure 17:
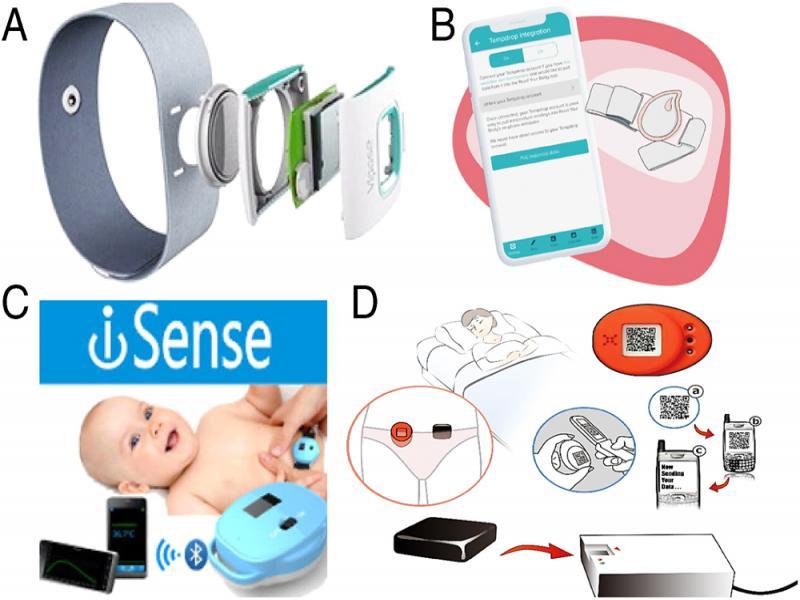
Figure 18:
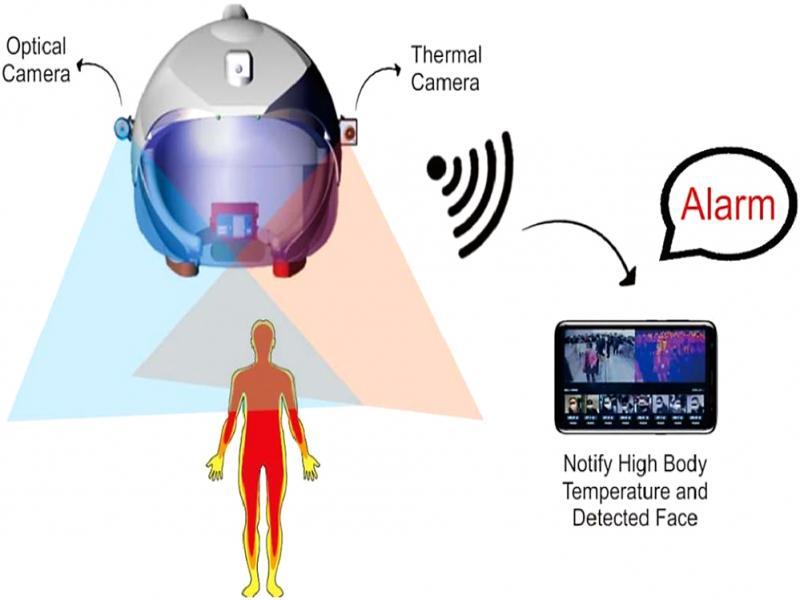
Figure 19:

Figure 20:

Figure 21:

Figure 22:
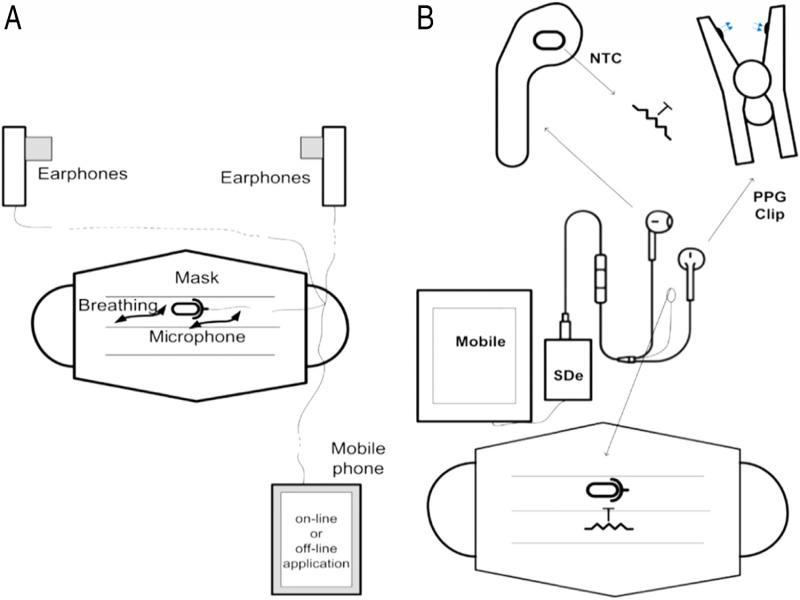
Figure 23:
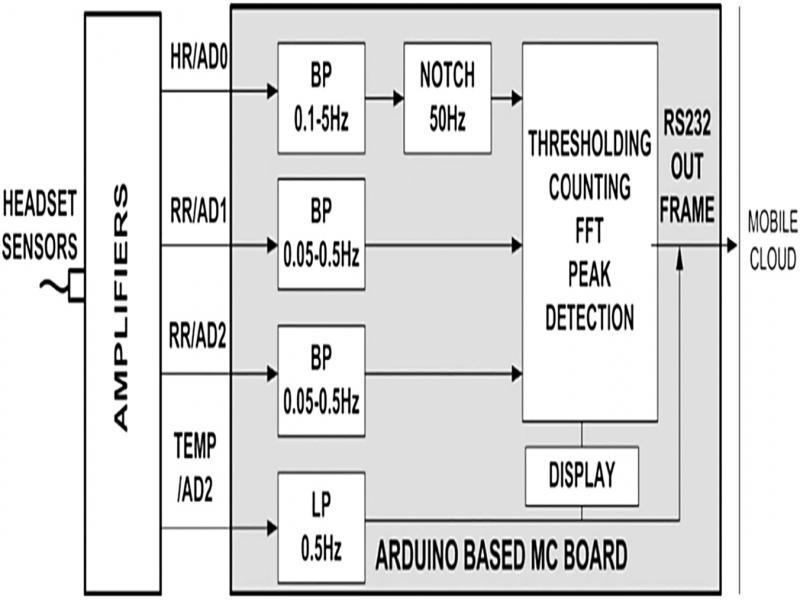
Figure 24:
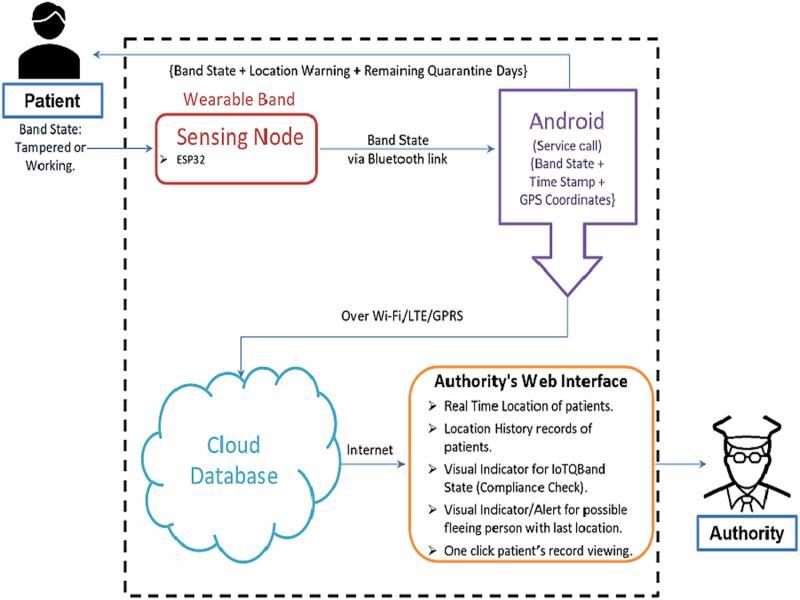
Figure 25:
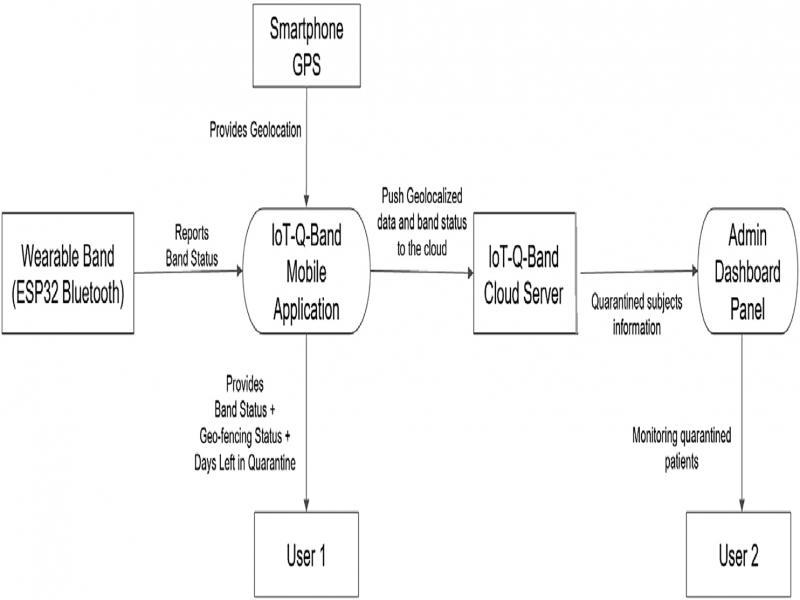
Figure 26:
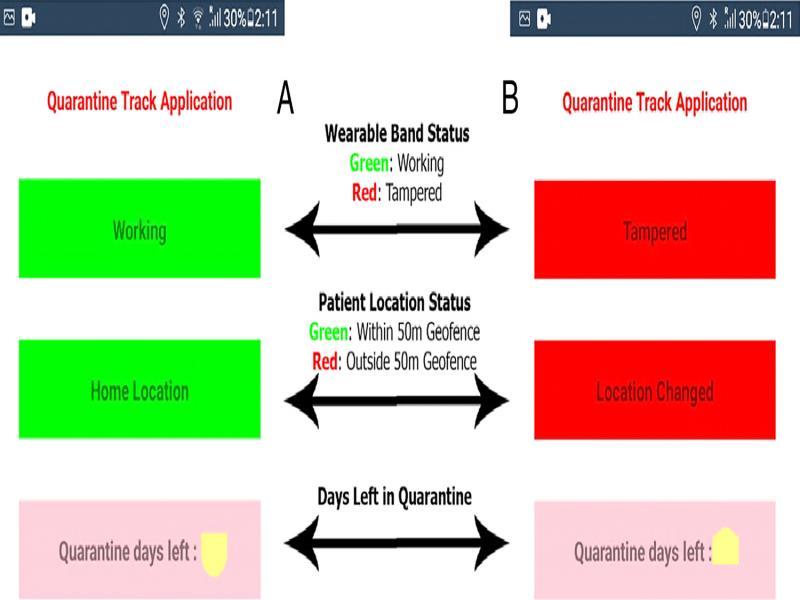
Figure 27:
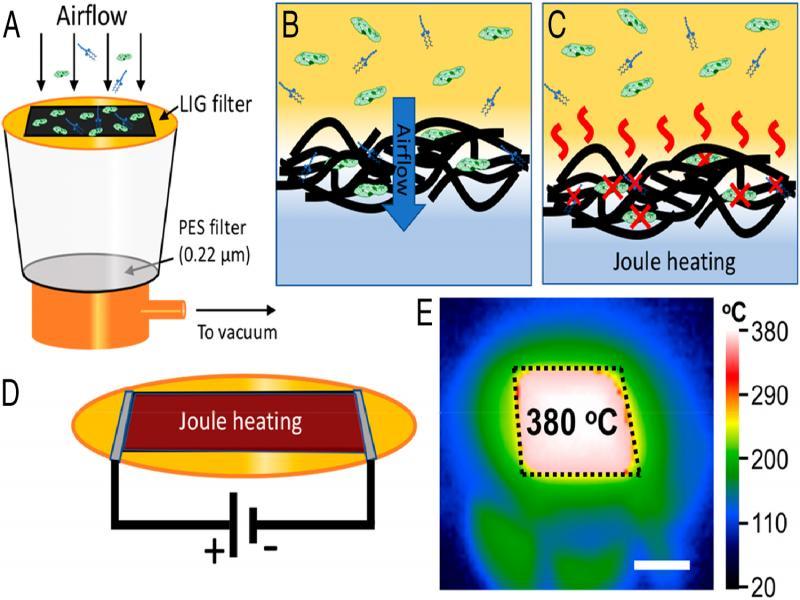
Figure 28:

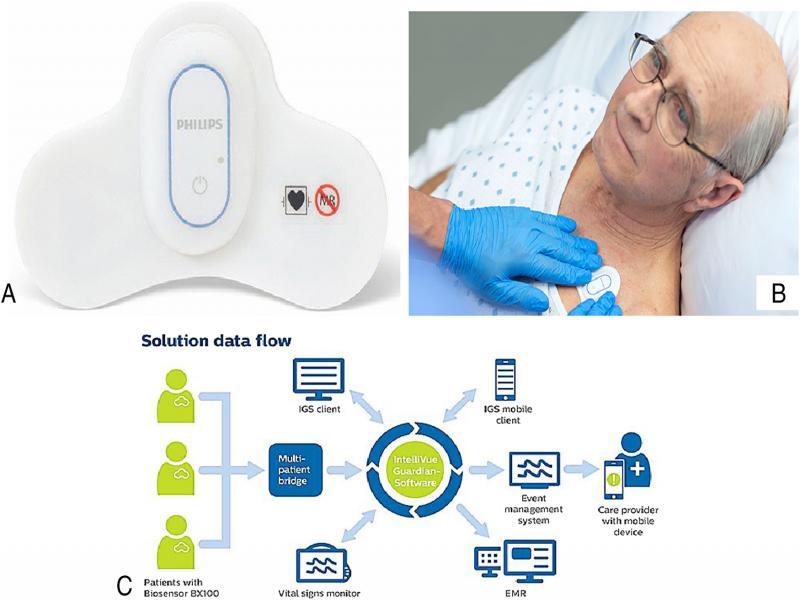
Figure 29:
Advantages and disadvantages of different magnetic nano-sensors technologies (Wu et al_, 2020)_
| Platform | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| GMR | High sensitivity | Multiple washing steps usually required, thus needing well-trained technicians, but can be wash-free, which reduces the sensitivity |
| Availability of a portable device | Time-consuming | |
| Mass production capability | High cost per test; nanofabrication of GMR biosensors required | |
| MTJ | High sensitivity | Multiple washing steps usually required, thus needing well-trained technicians, but can be wash-free, which reduces the sensitivity |
| Mass production capability | High noise; large distance from the MNP to the sensor surface | |
| Hard-to-acquire linear response | ||
| Complicated fabrication process | ||
| Time-consuming | ||
| High cost per test; nanofabrication of MTJ biosensors required | ||
| MPS, surface-based | High sensitivity | Multiple washing steps usually required, thus needing well-trained technicians, but can be wash-free, which reduces the sensitivity |
| Low cost per test | Time-consuming | |
| Availability of a portable device | ||
| MPS, volume-based | One-step wash-free detection allowed | Medium sensitivity |
| Immunoassays that can be hand-held by non-technicians | ||
| Low cost per test | ||
| Availability of a portable device | ||
| NMR | Availability of a portable device | Multiple washing steps usually required, thus needing well-trained technicians, but can be wash-free, which reduces the sensitivity |
| Time-consuming | ||
| Medium sensitivity |
A full list of extracted features (Sun et al_, 2020)_
| Category | Modality | Features | Extraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Smartphone location | Homestay | The time spent within 200m radius of home location (determined using DBSCAN) |
| Maximum traveled distance from home | The maximum distance traveled from home location | ||
| Smartphone Bluetooth | Maximum number of nearby devices | The maximum number of Bluetooth-enabled nearby devices | |
| Fitbit step count | Step count | Daily total of Fitbit step count | |
| Functional measures | Fitbit sleep | Sleep duration | Daily total duration of sleep categories (light, deep, and rem) |
| Bedtime | The first sleep category of the night | ||
| Fitbit heart rate | Average heart rate | The daily average heart rate | |
| Phone usage | Smartphone user interaction | Unlock duration | The total duration of phone in the unlocked state |
| Smartphone usage event | Social app use duration | The total duration spent on social apps (Google Play categories of Social, Communication, and Dating) |
Comparison between the scientific works reported in the second section, in terms of the detection technology, target species, LOD, detection time, application scenario and scalability_
| Scientific work | Detection mechanism | Target species | LOD | Detection time | Application scenario | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. (2020) | GMR | H1N1 virus H3N2 virus | 15 ng/mL 125 TCID50/ml | 10 min | Virus screening | Low |
| Orlov et al. (2016) | MPS | BoNT A, B and E | 0.22, 0.11, 0.32 ng/mL | 25 min | Food quality | Medium |
| Zhang et al. (2013) | MPS | ssDNA | 400 pM | 10 sec | DNA analysis | Medium |
| Lei et al. (2015) | NMR | CuSO4 | 0.2 µM | 1 min | cell isolation, cell culture, DNA amplification | Medium |
| Zhao et al. (2021) | electrochemical | SARS-CoV-2 virus | 200 copies/mL | 10 sec | Virus screening | High |
| Vadlamani et al. (2020) | electrochemical | SARS-CoV-2 virus | 14 nM | 30 sec | Virus screening | High |
| Chin et al. (2017) | electrochemical | JEV virus | 5–20 ng/mL | 20 min | Virus screening | High |
| Seo et al. (2020) | FET-based | SARS-CoV-2 virus | 1.7 fM | 20 sec | Virus screening | High |
| Moitra et al. (2020) | LSPR | SARS-CoV-2 | 0.18 ng/µL | 10 min | Virus screening | Low |