Fig. 1.
![The structure of SARS-CoV-2. ssRNA genome (26–32 kb) in the center, four structural proteins: spike glycoprotein (S), envelope protein (E), matrix protein (M), and nucleocapsid protein (N). Apart from these, many accessory proteins are also present but not shown in the Figure [22].](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/647092a171e4585e08aa0366/j_PM-2021.60.1.02_fig_001.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251205%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251205T005725Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=f46a175e579be1c88189d7f694e896aace90a40d1ef166412ba15bef2dc05575&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
Fig. 2.
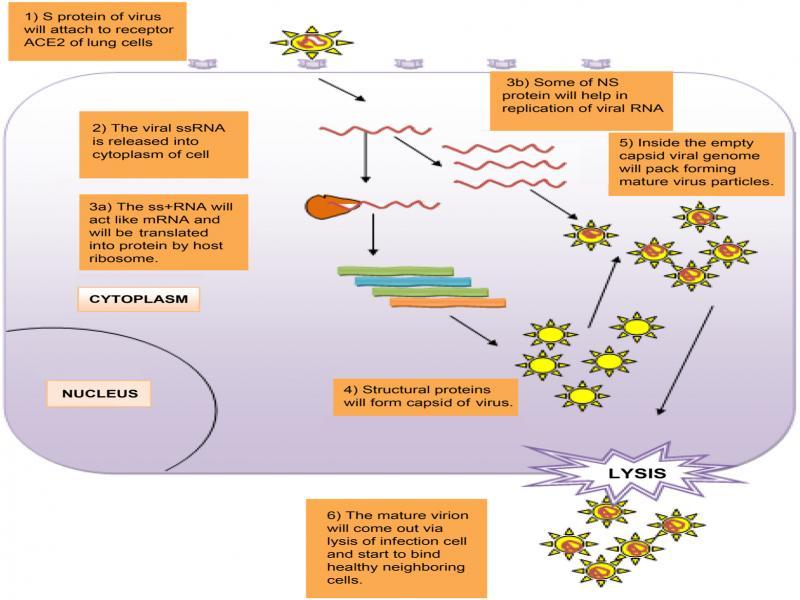
Fig. 3.
![ORF’s of the genome of HB01 strain of SARS-CoV-2 (previously called 2019-nCoV) are shown. Structural proteins are encoded at the 3’ terminus and non-structural at the 5’ terminus (Modified from [40]).](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/647092a171e4585e08aa0366/j_PM-2021.60.1.02_fig_003.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251205%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251205T005725Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=14b43a09b0955f2cf2fef438d0df04f2563c4729e27580e80978e2a3aeaa4e2b&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
Te functions of non-structural proteins in the replication of coronaviruses are shown (Modified from [8])
| Nsps | Functions |
|---|---|
| Nsp1 | Degrade Cellular mRNA and constrain signaling of IFN |
| Nsp3 | Blocking of host innate immune response and cut polypeptides |
| Nsp4 | Development of double membrane vesicles |
| Nsp5 | Constrain IFN signaling and cleave polypeptides |
| Nsp6 | Restrict expansion of auto phagosomes |
| Nsp7 | Nsp8 and Nsp12 co-factor |
| Nsp8 | Nsp7 and Nsp12 co-factor |
| Nsp9 | Interact with RNA binding and dimerization |
| Nsp10 | Nsp14 and Nsp16 support protein |
| Nsp12 | Primer, which function depends upon Rd-Rp |
| Nsp13 | 5 prime triphosphatase and RNA helicase |
| Nsp14 | Exo ribonuclease activity |
| Nsp15 | Exo ribonuclease activity |
| Nsp16 | Regulate immune responses negatively and 2’-O-MTase |
In process-Vaccines with its Candidates & Phase Trials
| Manufacturer | Vaccine candidate | Phase trials [31] | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moderna | DNA-based vaccines which code or a stabilized form of of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | Phase 3 starts in the 1st week of July. It will include the study of 30,000 patients | [4] |
| Curevac | Lab-made RNA to spur the production of corona proteins | Begins the human trials | https://www.curevac.com/en/covid-19/ |
| Inovio | DNA-based vaccines | Human trials to start in later June | https://www.inovio.com/our-focus-serving-patients/covid-19/ |
| Takis Biotech | DNA-based vaccines | Results of dose-response trials to be published in June | [27] |
| Zydus Cadila | DNA-based vaccines | Project is in pre-clinical trials | https://zyduscadila.com/ |
| Stemirna Therapeutics | mRNA-based vaccines | Clinical trials expected to start in Mid-April | http://www.stemirna.com/en/index.aspx |
| Imperial College London | DNA-based vaccines | Human trial started | https://www.imperial.ac.uk/covid-19-vaccine-trial/ |
| Novavax | Recombinant-protein nanoparticles derived from | Phase I/II started in May 2020 | https://www.novavax.com/covid-19-coronavirus-vaccine-candidate-updates |
| Vaxart | Oral vaccine half of 2020 | Phase I begins in the second | https://vaxart.com/ |
| GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) | A protein-based vaccine with the use of adjuvant | Animal trials | https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/ gsk-and-curevac-to-develop-next-generation- mrna-covid-19-vaccines/ |
| University of Saskatchewan | A protein-based candidate | Animal trials | https://www.vido.org/covid19/covid-19-news/ |
| Sanofi | Recombinant DNA platform swapping the part of corona-virus with genetic material | Phase 1 to be started in the last quarter of 2020 | https://www.sanofi.com/en/about-us/our-stories/sanofi-s-response-in-the-fight-against-covid-19 |
| Geovax Labs/ Bravovax | Develop a live horsepox virus which will be modified to express protein fragments from SARS-CoV-2 | Pre-clinical stage | https://www.geovax.com/news/geovax-progresses-in-coronavirus-covid-19-vaccine-development-program |
| Cansino Biologics | Viral vector-based vaccine | Phase II – All volunteers developed neutralizing antibodies | [42] |
| Grefex | DNA-based vaccines: Adenovirus based vector vaccines that involve a harmless virus that will express foreign genes like SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | Pre-clinical stage | https://www.grefex.com |
| Generex Biotechnology | Te firm uses insect cells from fruit fies to produce viral antigens | Ex-Vivo Human Immune System screening of 33 Ii-Key-SARS-CoV-2 peptides | https://www.generex.com/covid-19 |
Diferent Vaccine Strategies with their Advantages and Disadvantages
| Vaccine strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA vaccines | Easy preparation, | High unstable under physiological conditions | [24] |
| DNA vaccines | Easy preparation | Low immune responses | [24] |
| Viral vector vaccines | Induces high humoral and cellular immune responses | Pre-existing immunity will be a problem | [11] |
| Subunit vaccines | Neutralizing antibodies with high titer, | High cost | [11] |
| Attenuated virus vaccines | Quick development, | Genotypic & phenotypic reversion possible | [25] |
| Inactivated virus vaccines | Easy preparation, | Not applicable for immunosuppressed individuals | [25] |
Te diferences found in proteins of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2
| Protein | SARS-CoV | SARS-CoV-2 |
|---|---|---|
| 8a | Present | Absent |
| 8b | 84 amino acids | 121 amino acids |
| 3b | 154 amino acids | 22 amino acids |