The market is a fundamental category in economics, encompassing all buying and selling transactions between buyers and sellers. While it is often associated with a physical location, the market is more than just a place where transactions occur. It is a dynamic mechanism shaped by supply and demand, as well as a set of institutions and regulations that influence market operations. The enforcement of these rules is the responsibility of the state, which employs specialized agencies to oversee compliance (Antczak-Stępniak, 2019).
The real estate market consists of two main segments: the goods market and the services market. The goods market involves the trading of real estate properties, whereas the services market includes activities such as real estate brokerage and notarial services (Korombel & Krysiak, 2024).
From a legal perspective, real estate refers to a defined area of land and everything permanently attached to it, either naturally (e.g., trees and vegetation) or artificially (e.g., buildings and infrastructure). The Polish real estate market, particularly after the post-communist transformation, plays a crucial role in the country’s economic and financial landscape (Gołąbska, 2019).
In a market economy, real estate serves multiple functions. It is not only a means of meeting housing needs but also an investment asset and a form of security for mortgage liabilities. Although investing in real estate carries a degree of risk, it is generally perceived as a stable and secure investment compared to other asset classes. Additionally, real estate is a reliable hedge against inflation, particularly in the long term (Davis, 2007).
Beyond its financial role, real estate serves various economic purposes, including use, investment, income generation, credit financing, and asset management (Lin & Fei, 2014). Unlike other market commodities, such as currencies or securities, real estate is a unique economic resource essential for production and service activities (Feng, 2021).
Property transactions involve the transfer of rights rather than the physical exchange of land or buildings. These transactions can occur both in market-based contexts (buying and selling) and non-market-based contexts (donations and inheritance). Furthermore, the real estate sector relies on a wide range of professionals, including legal experts, construction companies, and government authorities responsible for zoning and land-use regulations. Their combined efforts ensure the stability, growth, and efficient operation of the market.
This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of key statistics and trends shaping the Polish real estate sector. The analysis focuses on property prices, rental yields, transaction volumes, and regional disparities, offering insights into the factors driving market dynamics (The Polish Real Estate Guide, 2022). Additionally, the study examines the impact of economic conditions, demographic shifts, and government policies on the sector’s evolution. By exploring recent trends such as the growing demand for rental properties, the expansion of the commercial real estate market, and the increasing role of technology in property transactions, the paper seeks to highlight both opportunities and challenges facing investors, policymakers, and homebuyers. Furthermore, the research considers future market developments, including regulatory adjustments, sustainability initiatives, and foreign investment trends, to provide a forward-looking perspective on the industry’s trajectory.
The real estate market in Poland is developing dynamically, reflecting both economic and social changes (Polczyk & Konowalczuk, 2017). Housing prices, demand for properties, and the availability of mortgage loans are key factors shaping the current market situation. In recent years, we have observed significant price fluctuations, growing interest in rentals, and the expansion of new development projects.
The real estate market in Poland has experienced dynamic changes in recent years, driven by both economic and social factors. The demand for housing, alongside shifting economic conditions, has influenced trends in property prices, availability, and the overall housing market landscape. Understanding these trends is crucial for evaluating the market’s future trajectory. One of the important indicators of housing conditions is the average usable floor space per person, which reflects both the living standards and the evolving housing needs of the population. Figure 1 presents data on the average usable floor space per person in Poland from 2018 to 2024, offering insights into the country’s housing development over this period.
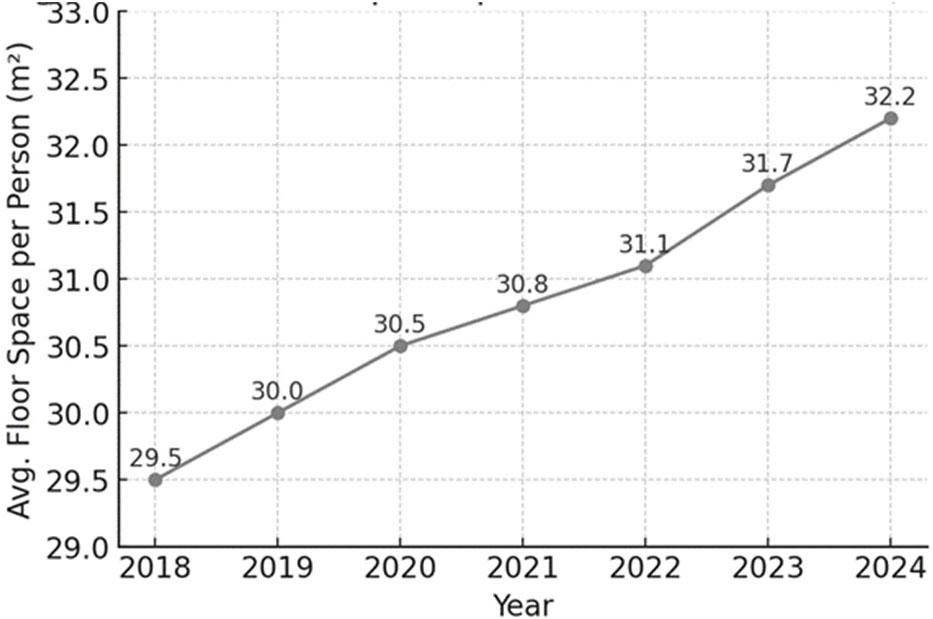
The average usable floor space per person in Poland from 2018 to 2024 (own research based on GUS, 2024)
Figure 1 illustrates the changes in the average usable floor space per person in Poland over the period from 2018 to 2024. Throughout these years, a consistent upward trend is evident, indicating a gradual improvement in housing conditions across the country. The average floor space available to each resident has increased annually, suggesting enhanced living standards and a positive trajectory in housing development.
Several factors contribute to this growth. Economic improvements, including rising household incomes and stable employment rates, have enabled more individuals and families to afford larger homes or undertake renovations that increase usable living space. The observed trend also reflects broader social and economic policies aimed at supporting housing development, such as government incentives for residential construction and urban revitalization projects. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on quality of life and well-being has influenced housing preferences, with more people seeking environments that offer sufficient space for work, leisure, and family life, a need that became especially pronounced during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. This upward trend could also be associated with the growing demand for more spacious homes, especially in urban areas, as well as the effects of economic factors like rising wages and low unemployment.
Overall, the data presented in the chart highlights the ongoing evolution of housing standards in Poland and underscores the importance of continued monitoring and policy support to sustain this positive development in the years ahead.
Market conditions are also influenced by demographic changes, rising construction material costs, and central bank policies regarding interest rates. The commercial real estate sector and increasing interest from foreign investors are also playing an increasingly important role. In this article, we will examine the basic statistics regarding the Polish real estate market, analysing current trends and forecasts for the near future. The situation on the real estate market in recent years has been influenced by the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, which were further exacerbated by the economic consequences of Russia’s aggression in Ukraine in early 2022. The lockdown initially caused a significant decline in housing demand. However, after substantial fiscal support for the economy and a reduction in interest rates, demand – supported by credit – saw a notable increase. The Russian-Ukrainian war and its economic repercussions, including rising inflation, led to shocks on the real estate market, affecting both demand and supply. With inflation, the cost of financing property purchases rose significantly, which sharply dampened demand for loans, property sales, and new development projects, as seen in the first half of 2023. Gradual inflation slowdown in 2023, along with the introduction of the “Safe Credit 2 %” housing loan in the second half of the year, contributed to a significant rise in housing demand. Record-low unemployment and rising wages supported high housing demand. The increase, coupled with low supply, alongside sustained high energy prices, land costs, and labour expenses, led to rising property prices. Developers gradually began increasing the number of investments. Simultaneously, strong demand for rental properties grew, which contributed to rising rents, particularly in Warsaw (Gołąbska, 2024).
Key observations regarding the real estate market in Poland in 2023 (Rynek nieruchomości – raport …, 2023) include: The estimated value of residential real estate in Poland at the end of 2023 was approximately PLN 7.1 trillion, compared to PLN 6.5 trillion at the end of 2022. The estimated value of commercial properties stood at around PLN 400 billion, up from PLN 380 billion in 2022. The value of residential properties at the end of the period accounted for about 209 % of GDP, while commercial properties made up approximately 12 % of GDP.
The housing situation in the country improved: the number of housing units per 1,000 people increased (approximately 420 compared to 412 in 2022), and the average usable floor space per person rose (about 31.7 m2 compared to 31.1 m2 in 2022). At the same time, the average number of people per household decreased (2.38 compared to 2.42 in 2022) (Raport o sytuacji na rynku nieruchomości mieszkaniowych i komercyjnych w Polsce w 2023 r., 2024).
A real estate agent is an intermediary whose main task is to facilitate a transaction between two parties, such as a seller and a buyer. However, in their professional work, the agent deals not only with formal matters, such as preparing contracts and documents, but also with other issues more closely related to communication with clients. The key responsibilities of a real estate agent include:
Preparing real estate listings for sale or rent;
Presenting listings, for example, on the internet or in agency advertising newspapers;
Communicating with property owners or landlords, as well as with potential clients;
Conducting property viewings, taking photos, and making videos;
Showing properties to interested clients, i.e., presenting apartments, houses, or commercial spaces;
Acquiring new listings through conversations with clients;
Handling the formalities of transactions, such as drafting sale contracts, rental agreements, and preparing all necessary documents;
Advising clients (Rymarzak, 2009).
Therefore, a real estate agent has many tasks in their daily work and must make use of both hard and soft skills. On one hand, the person in this position has certain formal responsibilities related to knowledge of the real estate market and the creation of contracts, while on the other hand, there are communication and negotiation tasks. A good real estate agent is able to encourage clients to purchase or rent a particular property (Kucharska-Stasiak, 2005; 2007).
In addition to these responsibilities, a real estate agent also plays an essential role in managing client expectations and providing valuable insights into the local market. They must stay up to date with market trends, pricing fluctuations, and legal changes that could affect property transactions. By understanding both the needs of buyers and the goals of sellers, an agent can tailor their approach to ensure the best possible outcome for all parties involved.
Moreover, building strong relationships with clients is crucial for a real estate agent’s success. Word of mouth and referrals are often key sources of new business, so maintaining professionalism and trust is vital. The ability to adapt to various client personalities and negotiate effectively, while being transparent and ethical in all dealings, sets apart the most successful agents in the competitive real estate industry. Real estate agents in Poland play a key role in property transactions, both in the secondary and primary markets. Real estate agents assist clients in finding suitable offers, negotiating transaction terms, and also provide advice on legal and financial matters related to the real estate market (Cyran, 2006).
In Poland, real estate agents must hold a professional license, which is obtained after completing a relevant course and passing a state exam. This license is required to conduct real estate brokerage activities. Additionally, real estate agents in Poland must adhere to specific ethical and professional standards regulated by industry organizations such as the Polish Federation of Real Estate Market (PFRN).
Real estate agents in Poland specialize in different market segments, including residential properties, commercial real estate, land, and both long-term and short-term rentals. Due to their knowledge of local markets and legal regulations, agents can effectively advise clients and help them find optimal solutions.
In recent years, the real estate market in Poland has been developing dynamically, and the role of real estate agents is becoming increasingly important, especially in cities with high demand for residential and commercial properties. In addition to their core responsibilities, real estate agents in Poland often assist clients in navigating the complexities of property financing, and helping them secure loans or mortgages through various financial institutions. They also provide valuable insights into market trends and property values, which can be crucial for making informed decisions, especially for first-time buyers or investors.
Moreover, many real estate agents collaborate with other professionals in the industry, such as lawyers, notaries, architects, and construction specialists, to ensure that all aspects of a transaction are handled smoothly and legally. This cooperation helps clients avoid potential pitfalls and ensures efficient completion of transactions.
Figure 2 illustrates the number of real estate agents in Poland from 2018 to 2024.
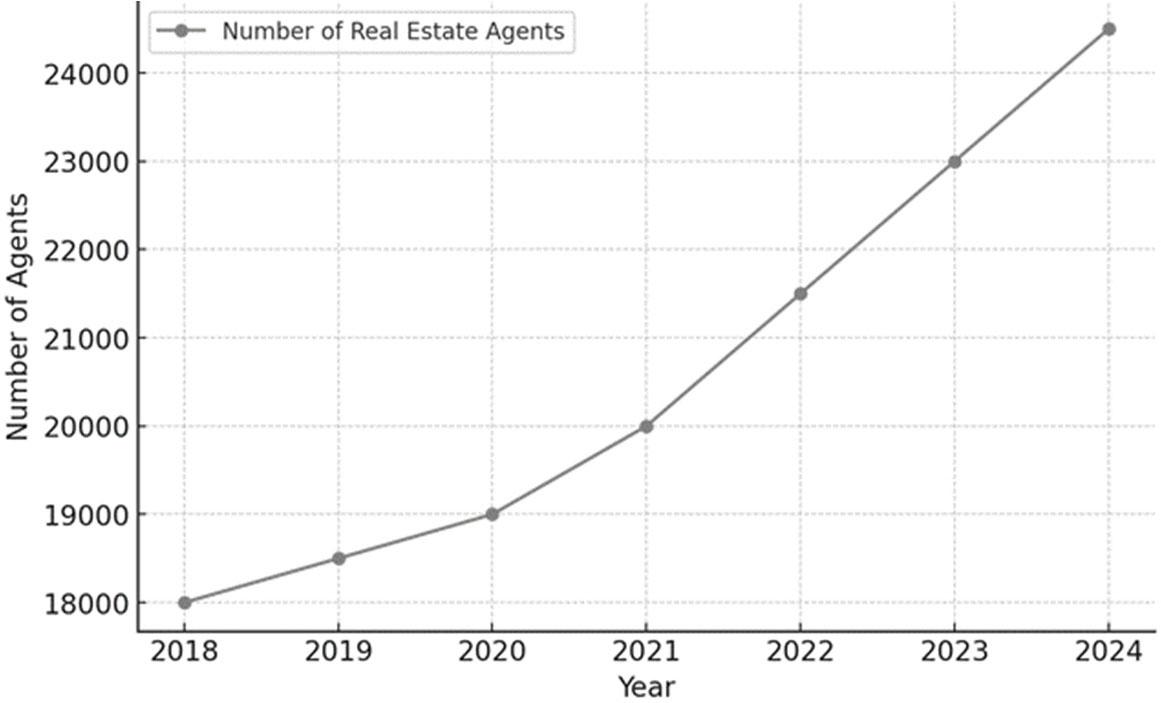
Real Estate Agents in Poland in 2018–2024 (own research based on GUS, 2024)
This upward trend may be linked to the growing activity in the real estate market, driven by factors such as urbanization, increasing housing demand, and favourable economic conditions, including low unemployment and rising incomes. The expansion of digital tools, online property platforms, and virtual property viewings has also contributed to the evolution and professionalization of the sector, attracting more individuals to the profession.
Between 2018 and 2024, the number of real estate agents in Poland grew steadily from approximately 18,000 to over 24,000, reflecting the rising demand for professional real estate services. This increase is influenced by the expanding real estate market, the growing complexity of transactions, and greater reliance on professional agents for legal and financial guidance.
Real estate agents often collaborate with other industry professionals, such as lawyers, notaries, architects, and construction specialists, ensuring transactions are handled smoothly and legally. This cooperation helps clients avoid potential pitfalls and complete processes efficiently.
Shifting customer expectations have also played a significant role, with clients increasingly seeking comprehensive advisory services throughout the buying or renting process. At the same time, regulatory changes and the complexity of property transactions have heightened the need for professional assistance for both buyers and sellers. As the real estate market in Poland continues to evolve, the role of agents is expected to expand beyond traditional brokerage to include consulting in legal, financial, and investment matters. Heightened competition among agents has fostered more specialized services, higher quality standards, and improved customer service.
Moreover, the growing popularity of digital real estate platforms and technology-driven tools has encouraged professionals to adapt to modern trends, leveraging technology to enhance property information access and streamline transactions. The ongoing digitalization of the industry, combined with rising demand for rental properties and investment opportunities, will likely shape the future of real estate services in Poland. Despite these changes, real estate agents remain vital intermediaries, connecting buyers, sellers, and tenants in an increasingly dynamic environment. Real estate agencies play a key role in the Polish residential and commercial property market, assisting both buyers and sellers in transactions. They act as intermediaries between parties, offering professional advice, access to a wide range of listings, and legal and administrative support.
There are many real estate agencies in Poland, ranging from large nationwide networks to smaller, local firms. Popular brands include Metrohouse, RE/MAX, and Freedom Nieruchomości, but the market also features many independent offices specializing in specific segments, such as luxury properties, rental apartments, or commercial buildings.
Currently, real estate agents in Poland do not need a license to work in the industry, but many professionals obtain certifications and participate in training programs to enhance their qualifications. Skilled agents assist clients with negotiations, market analysis, and the legal formalities involved in buying, selling, or renting properties (Ławińska & Korombel, 2021).
In recent years, Polish real estate agencies have increasingly adopted modern technologies such as virtual tours, advanced CRM systems, and digital marketing to reach clients more effectively. The dynamic growth of the market ensures that intermediary services remain an essential part of the property buying, selling, and rental process.
Additionally, growing competition in the industry is driving agencies to improve service standards and implement innovative solutions, such as process automation and personalized investment consulting. More offices are also focusing on transparency and professional ethics, which helps build client trust and contributes to the further development of Poland’s real estate brokerage market. The Polish real estate market continues to evolve, influenced by economic and social changes, with housing prices, property demand, and mortgage loan availability shaping the current landscape. In recent years, significant price fluctuations, increasing interest in rentals, and the expansion of new development projects have been observed.
The Polish real estate market is a dynamic sector influenced by economic, demographic, and policy factors. While urban centers continue to experience rising property prices and strong demand, smaller towns and rural areas remain more affordable. Key market drivers include interest rate fluctuations, housing supply dynamics, and broader macroeconomic trends. Investors, policymakers, and individuals must closely analyse these factors to navigate the evolving landscape.
Recent trends highlight an increasing demand for rental properties, the expansion of the commercial real estate sector, and the growing role of real estate agencies in facilitating transactions. As competition intensifies, companies are adopting innovative solutions, modern technologies, and improved customer service standards. Despite challenges such as rising construction costs and fluctuating interest rates, the Polish real estate market remains attractive to both investors and homebuyers.
In 2024, the market is shaped by inflationary pressures, evolving government policies, and the growing emphasis on sustainability. Energy-efficient buildings are gaining traction among investors and regulators, while hybrid work models continue to reshape demand for office spaces. The expansion of institutional rental housing is also expected to play a more significant role in addressing housing needs. Additionally, the rising popularity of smart home technologies and digital real estate platforms is streamlining property transactions, making them more accessible and efficient for buyers and sellers alike.
Looking ahead, the Polish real estate market will continue to evolve under the influence of economic, technological, and demographic changes. Key developments will include regulatory adjustments, digital transformation in transaction processes, and shifts in housing affordability. The construction sector is expected to face further challenges related to labour shortages and supply chain disruptions, potentially affecting new housing projects and overall market dynamics. At the same time, foreign investment in Polish real estate is projected to increase, particularly in the commercial and logistics sectors, driven by Poland’s strategic location in Europe.
While challenges persist, the sector remains a crucial pillar of the national economy. To ensure long-term stability and growth, proactive policy measures, sustainable development strategies, and continuous market analysis will be essential. Strengthening public-private partnerships and encouraging green building initiatives could further enhance the market’s resilience and attractiveness in the coming years.
In Poland, the real estate agency industry is highly competitive, with many agencies striving to differentiate themselves through specialization, customer service, and innovative marketing strategies. The demand for well-trained, professional agents is rising as buyers and investors seek reliable guidance in navigating the complexities of the market. Real estate agents are also increasingly involved in property management services, assisting with long-term rental agreements, maintenance, and tenant relations.
Looking to the future, real estate agents in Poland will continue to adapt to changing market conditions, such as shifts in housing demand and the increasing integration of technology into real estate transactions. Their expertise will remain crucial in helping clients navigate the complexities of property investment, legal processes, and market trends. As the industry evolves, it will be essential for agents to stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and client needs to maintain their competitiveness in the market.