Figure 1
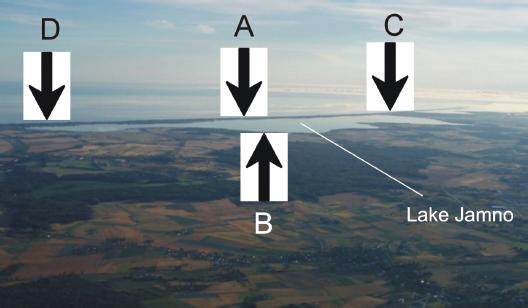
Figure 2
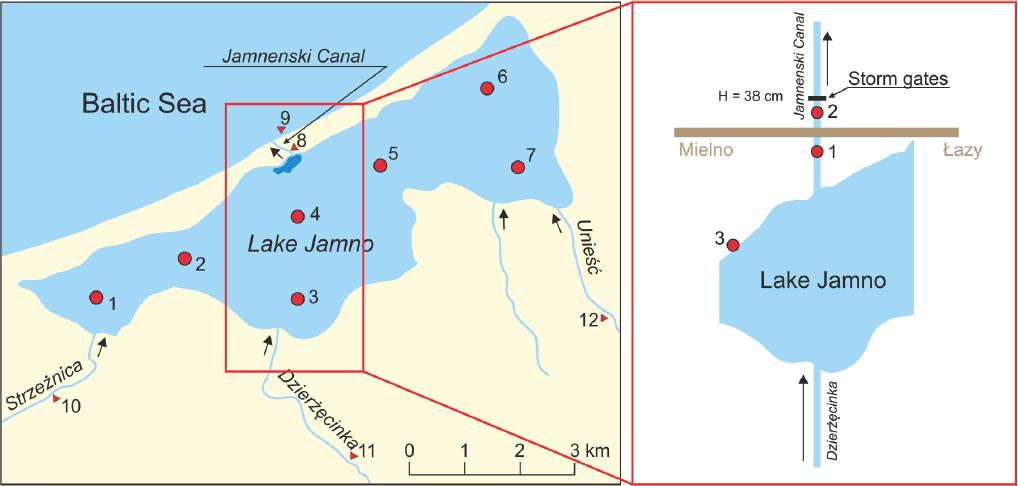
Figure 3
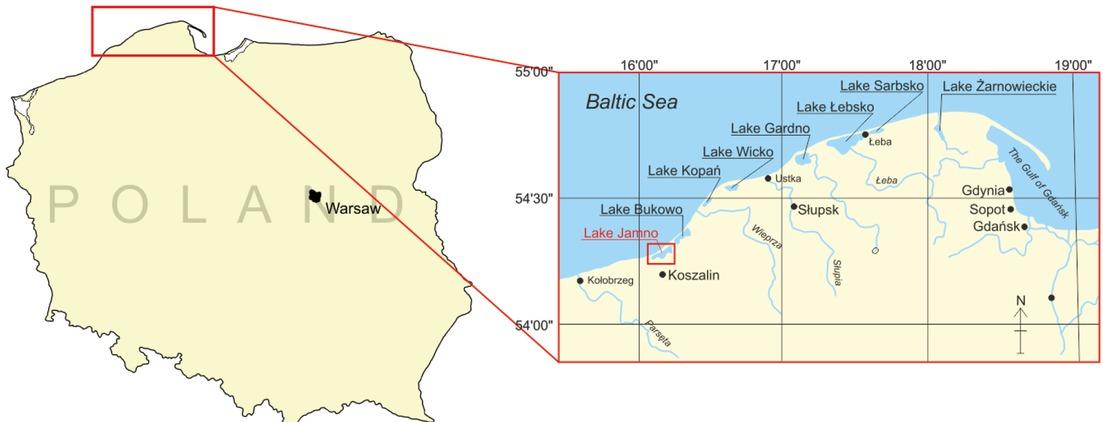
Figure 4
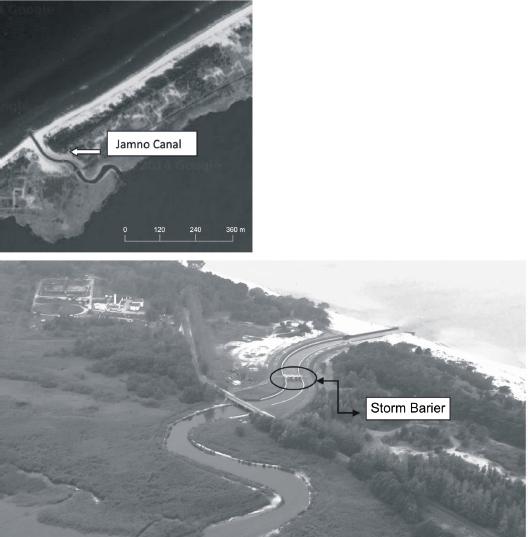

Figure 5
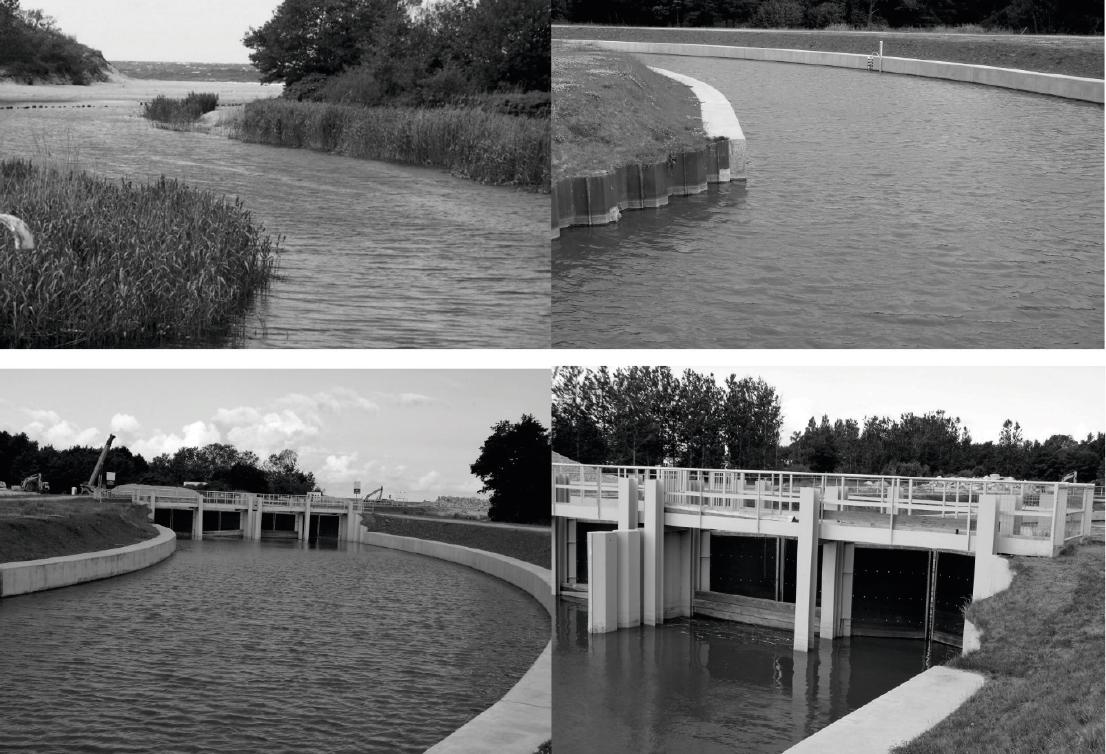

Figure 6

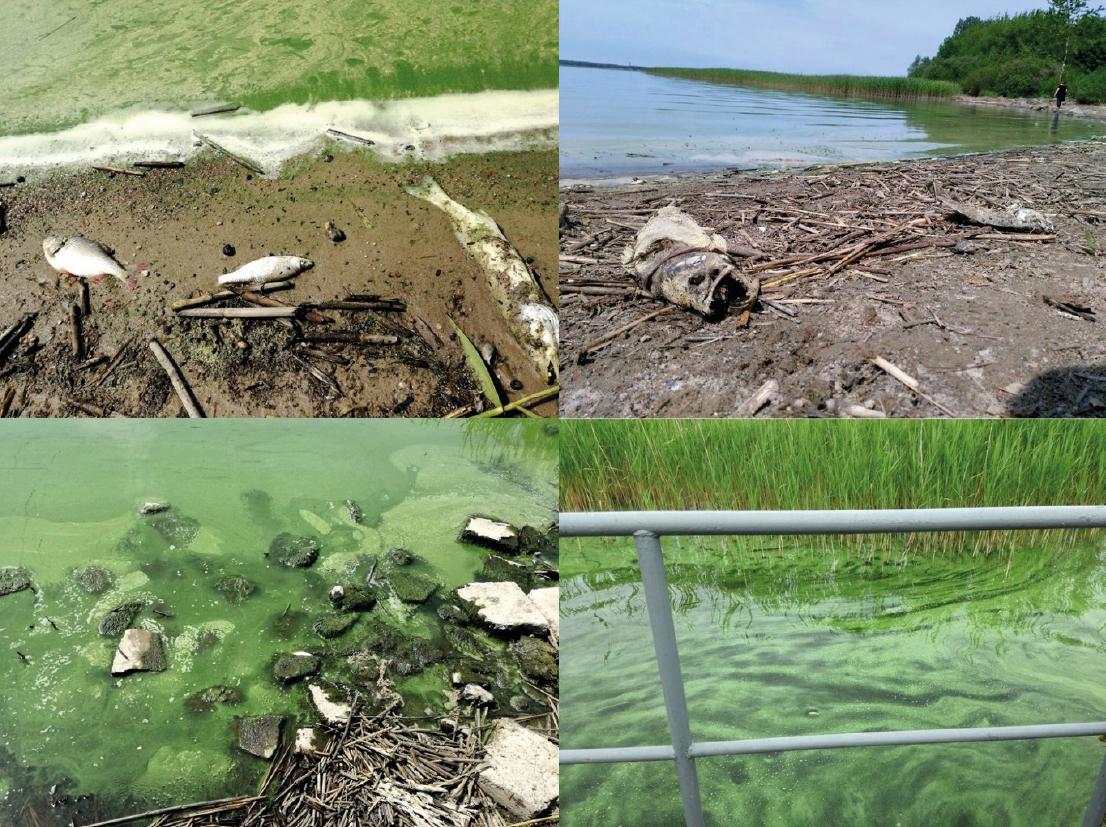
Figure 7

Figure 8
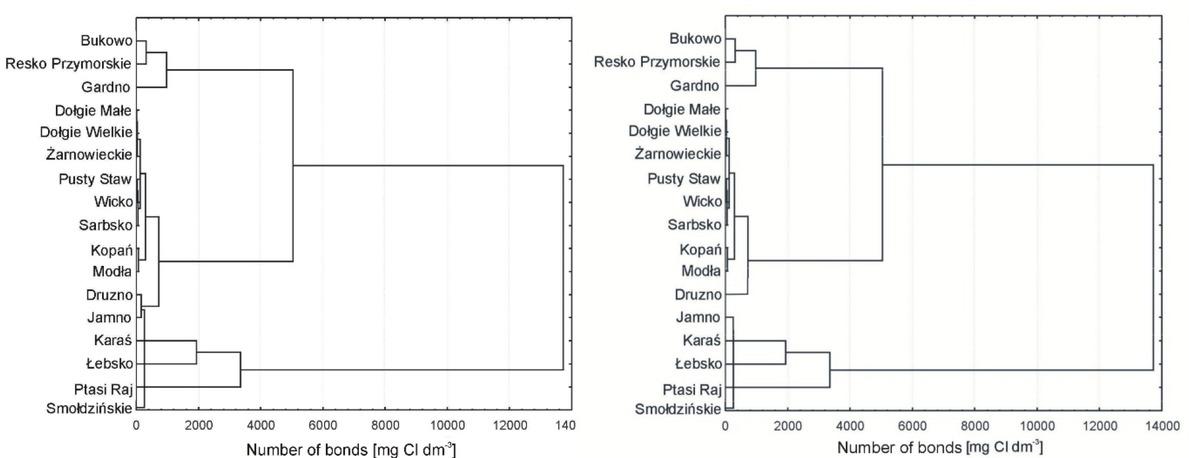
Figure 9

Figure 10
Figure 11

Figure 12

Descriptive statistics for the chloride ion (mg l−1) and electric conductivity (μS cm−1) in water of Lake Jamno
| Indicator | Arithmetic average | Standard deviation | Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| Chloride | 297.8 | 173.2 | 162.8 | 99.1 | 698.0 | 477.0 | 133.0 | 70.0 | 54.7 | 57.2 |
| Conductivity | 1184.8 | 925.1 | 540.6 | 367.2 | 2870.0 | 2150.0 | 693.0 | 591.0 | 45.6 | 39.7 |
Average values of selected physical and chemical data obtained in the field in 2013–2015
| Site no. | Chloride (mg l−1) | Conductivity (μS cm−1) | Location of the measuring point |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44.0 | 404 | Jamno Canal (400 m from the shoreline of the lake) |
| 2 | 78.0 | 508 | Jamno Canal (600 m from the shoreline of the lake) |
| 3 | 38.0 | 394 | Lake Jamno (north–western part) |
Descriptive statistics for the chloride ion (mg l−1) and electric conductivity (μS cm−1) in water of the Jamneński Canal
| Indicator | Arithmetic average | Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloride | 457.0 | 925.0 | 44.0 | 77.8 |
| Conductivity | 1899.0 | 6995.0 | 855.0 | 60.0 |