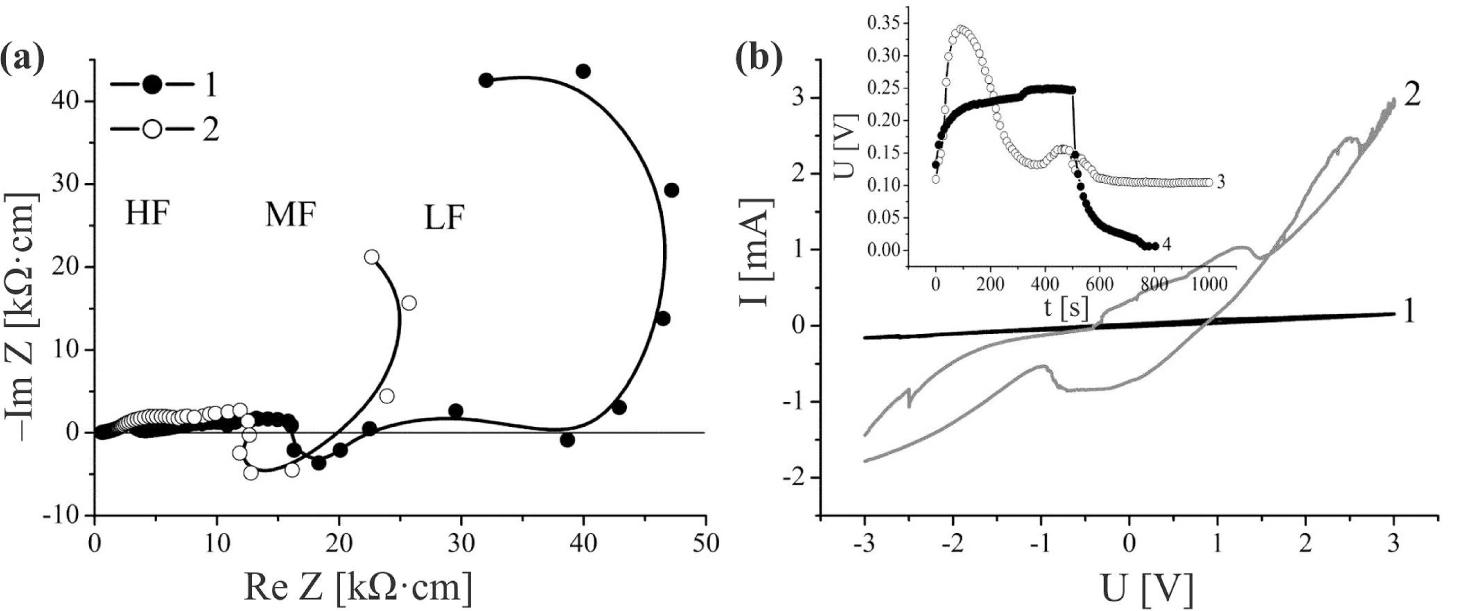
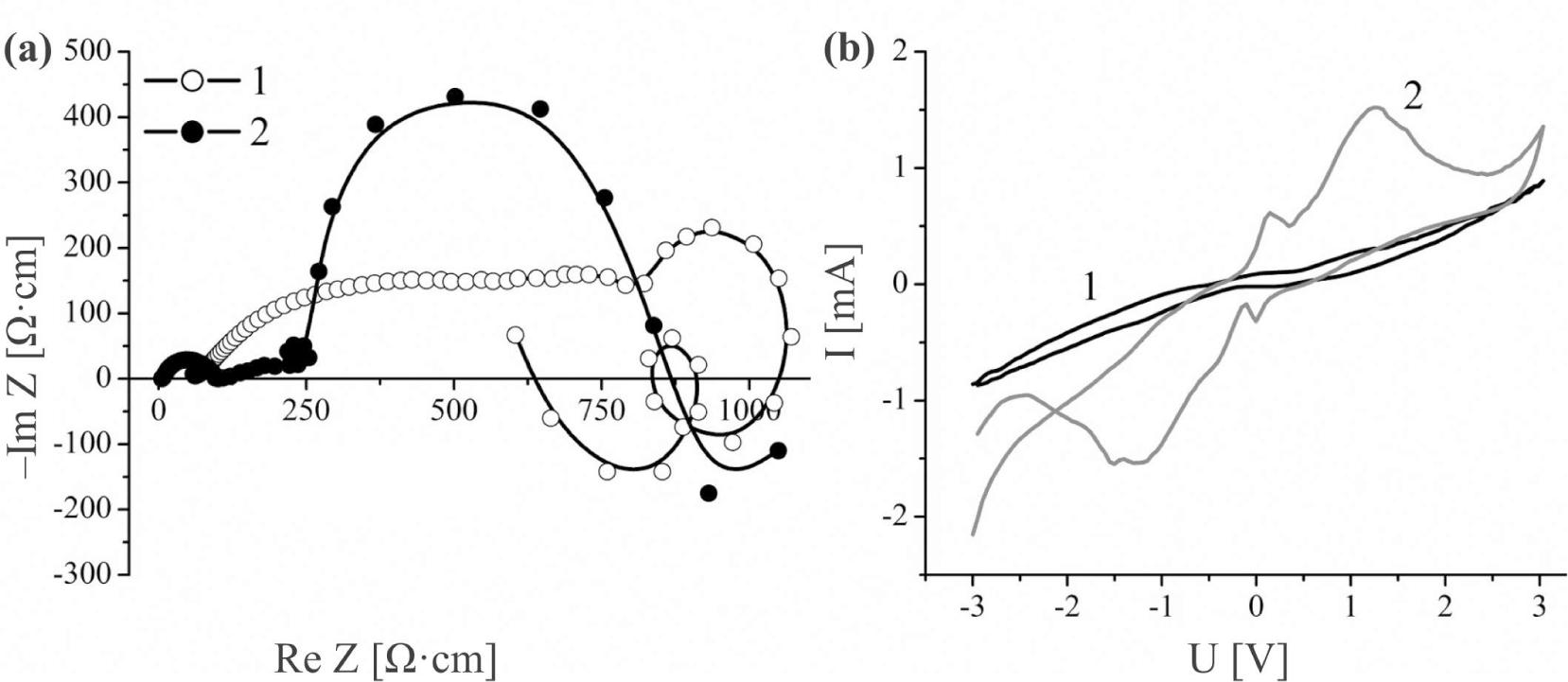
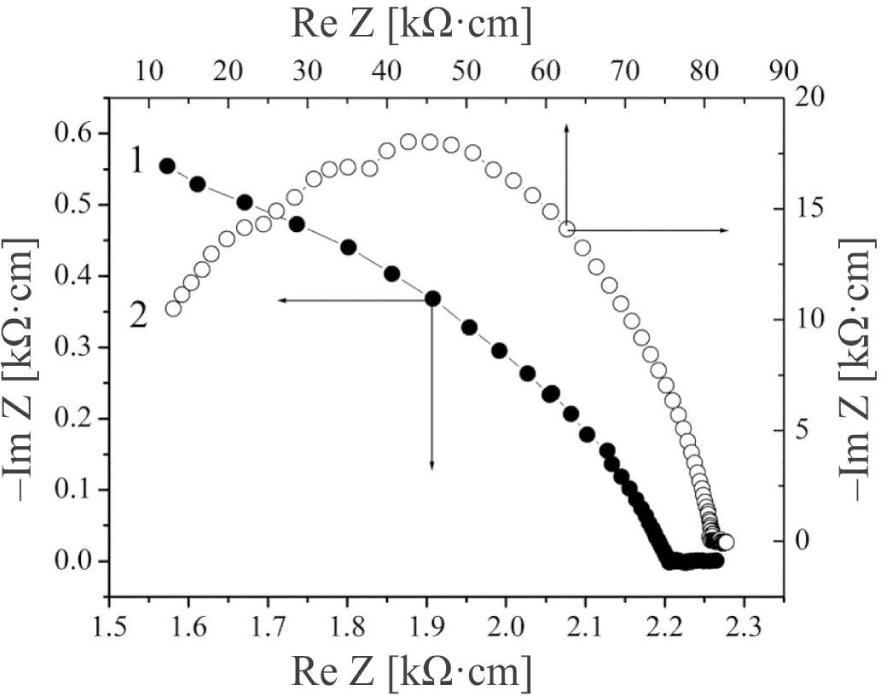
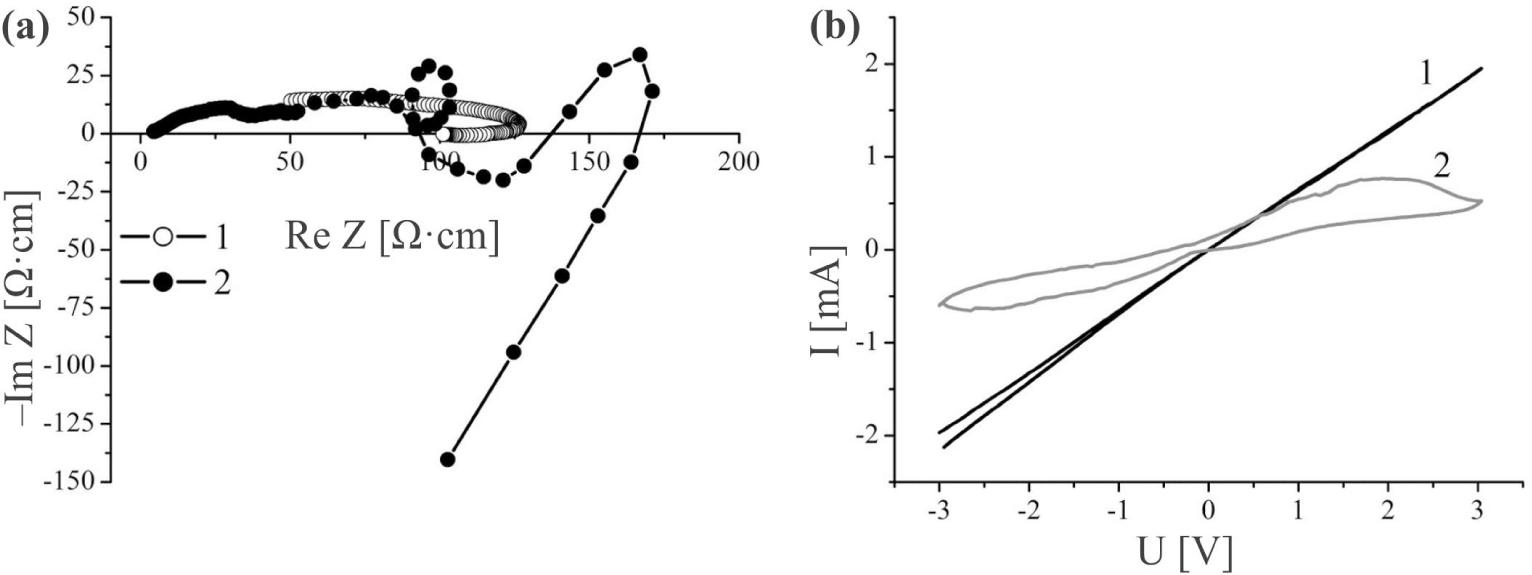
![Nyquist diagrams of the original expanded GaSe matrix (1), and nanostructure of GaSe ‹his›(2) with the respective equivalent circuit diagrams [10]. Equivalent circuit diagrams are shown in the insets (a) and (b) on the righthand side of the figure.](https://sciendo-parsed.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/647250fc215d2f6c89dc3e5d/j_msp-2017-0019_fig_001.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Content-Sha256=UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD&X-Amz-Credential=AKIA6AP2G7AKOUXAVR44%2F20251204%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251204T131704Z&X-Amz-Expires=3600&X-Amz-Signature=9284a28b963546c2b0c21bcd235204bb9ed01671c6d500eb60b81ad300697675&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&x-amz-checksum-mode=ENABLED&x-id=GetObject)
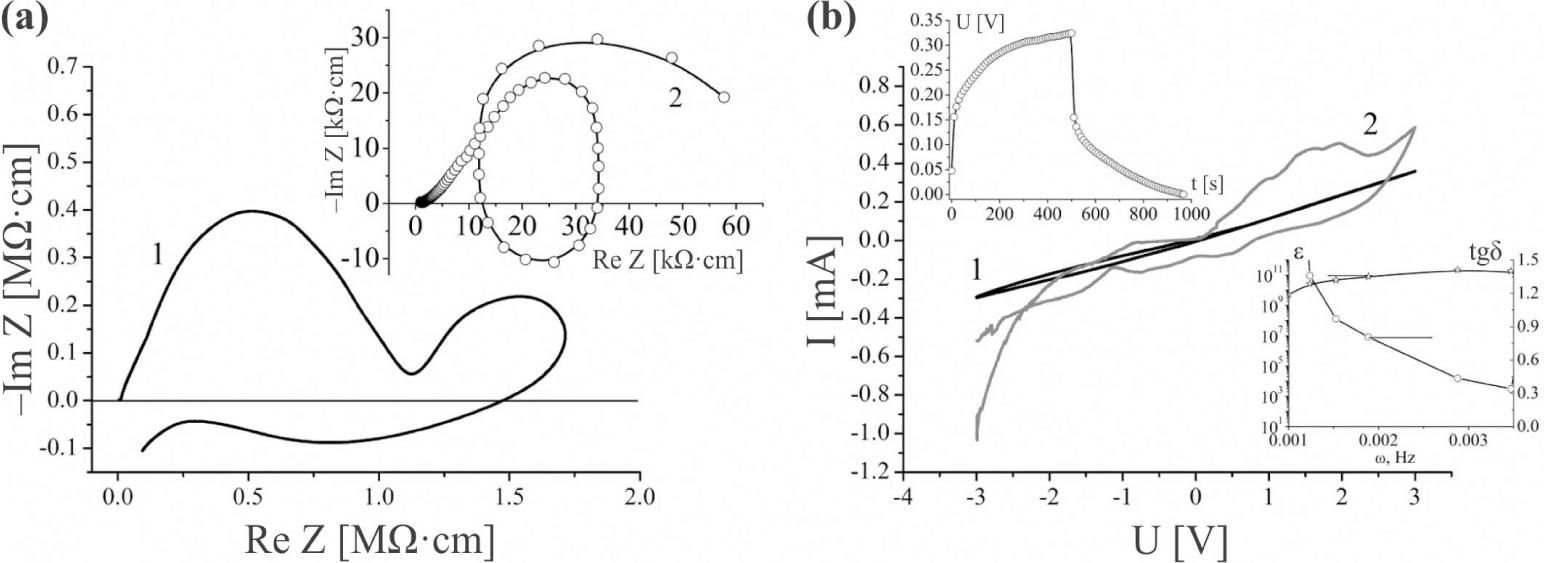
Parameters of the model (b)_
| Element | R1 | CPE1 | R2 | CPE2 | R3 | CPE3 | L | R4 | CPE4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| of the model | [Ω] | [F] | [Ω] | [F] | [Ω] | [F] | [H] | [Ω] | [F] |
| Value | 6.57E7 | 2.93E-14 | 2.96E8 | 4.79E-12 | 8.77E8 | 1.73E-8 | 4.63E3 | 3.04E9 | 1.17E-10 |
Parameters of the model (a)_
| Element | BCPE1 | BCPE2 | R | CPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| of the model | [Ω] | [Ω] | [Ω] | [F] |
| Value | 2.15E8 | 1.01E8 | 1.73E8 | 4.47E-12 |