Table 1
Baseline characteristics of 6,228 Dong, 4,986 Miao, and 5,404 Bouyei ethnic groups by cardiovascular diseases status.
| VARIABLES | DONG ETHNIC GROUP | MIAO ETHNIC GROUP | BOUYEI ETHNIC GROUP | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NON-CVDS | CVDS | P | NON-CVDS | CVDS | P | NON-CVDS | CVDS | P | |||
| No. of participants | 5,978 (96.00) | 250 (4.00) | 4,790 (96.07) | 196 (3.93) | 5,199 (96.21) | 205 (3.79) | |||||
| Age (years) | 51.96 (44.99–60.13) | 61.11 (54.12–67.00) | <0.001 | 50.45 (42.51–59.18) | 62.08 (53.68–68.63) | <0.001 | 50.87 (43.89–58.05) | 60.16 (53.11–66.77) | <0.001 | ||
| Men | 2,052 (34.33) | 112 (44.80) | 0.001 | 1,740 (36.33) | 79 (40.31) | 0.257 | 1,540 (29.62) | 85 (41.46) | <0.001 | ||
| Rural | 4,636 (77.84) | 188 (75.20) | 0.326 | 3,421 (71.57) | 119 (60.71) | 0.001 | 4,554 (87.59) | 169 (82.44) | 0.029 | ||
| Tobacco smoking status | 0.118 | 0.571 | 0.736 | ||||||||
| Never | 4,761 (79.66) | 180 (72.00) | 3,748 (78.25) | 154 (78.57) | 4,301 (82.73) | 164 (80.00) | |||||
| Former | 210 (3.51) | 28 (11.20) | 171 (3.57) | 12 (6.12) | 161 (3.10) | 21 (10.24) | |||||
| Current | 1,006 (16.83) | 42 (16.80) | 871 (18.18) | 30 (15.31) | 737 (14.18) | 20 (9.76) | |||||
| Alcohol drinking weekly | 188 (3.14) | 1 (14.00) | 0.032 | 204 (4.26) | 9 (4.59) | 0.821 | 155 (2.98) | 8 (3.90) | 0.450 | ||
| Total physical activity (METs h/d) | 24.96 (14.00–37.16) | 17.55 (8.30–30.65) | <0.001 | 25.18 (13.40–38.80) | 12.12 (5.60–27.03) | <0.001 | 23.95 (13.37–37.10) | 14.80 (7.01–28.00) | <0.001 | ||
| Total energy intake (kcal/week) | 10.22 (8.20–12.97) | 9.24 (7.35–12.08) | <0.001 | 10.61 (8.16–13.67) | 9.71 (7.84–12.23) | 0.001 | 10.65 (8.15–13.81) | 9.94 (7.44–12.83) | 0.005 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.74 (21.46–26.15) | 24.38 (21.81–26.15) | 0.224 | 24.79 (22.51–27.10) | 25.50 (22.97–27.80) | 0.038 | 23.84 (21.59–26.20) | 24.94 (22.20–27.06) | <0.001 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | 121.60 (110.33–135.67) | 129.50 (115.00–144.00) | <0.001 | 122.30 (111.00–136.67) | 134.30 (118.33–147.67) | <0.001 | 121.30 (110.33–135.67) | 135.30 (120.67–151.33) | <0.001 | ||
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.00 (72.67–87.00) | 81.00 (74.67–90.67) | 0.003 | 80.33 (73.33–88.33) | 83.33 (75.67–92.00) | 0.001 | 80.33 (74.00–88.33) | 86.00 (78.33–94.67) | <0.001 | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.29 (4.96–5.68) | 5.30 (4.94–5.75) | 0.643 | 5.20 (4.90–5.60) | 5.45 (5.06–5.92) | <0.001 | 5.14 (4.86–5.51) | 5.28 (5.02–5.73) | <0.001 | ||
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.87 (4.29–5.51) | 4.84 (4.10–5.52) | 0.267 | 4.96 (4.35–5.60) | 5.04 (4.41–5.98) | 0.162 | 4.87 (4.31–5.52) | 4.97 (4.41–5.67) | 0.081 | ||
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.51 (1.08–2.22) | 1.58 (1.18–2.39) | 0.116 | 1.43 (1.02–2.12) | 1.61 (1.22–2.30) | 0.002 | 1.38 (0.99–2.02) | 1.57 (1.16–2.14) | 0.002 | ||
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.46 (1.22–1.73) | 1.37 (1.15–1.62) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.02–2.12) | 1.43 (1.25–1.60) | 0.206 | 1.49 (1.32–1.69) | 1.49 (1.33–1.67) | 0.772 | ||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.94 (2.38–3.50) | 2.96 (2.26–3.60) | 0.824 | 2.81 (2.30–3.40) | 2.90 (2.35–3.61) | 0.042 | 2.45 (2.03–2.93) | 2.54 (2.15–3.13) | 0.022 | ||
| SUA (mg/dL) | 5.36 (4.45–6.52) | 5.85 (4.87–7.24) | <0.001 | 5.39 (4.49–6.45) | 5.69 (4.86–7.08) | <0.001 | 5.02 (4.18–6.08) | 5.78 (4.60–6.72) | <0.001 | ||
| Scr (µmol/L) | 65.00 (56.00–77.00) | 71.00 (59.00–85.00) | <0.001 | 62.00 (54.00–74.00) | 68.00 (59.00–79.50) | <0.001 | 60.00 (53.00–70.00) | 67.00 (57.00–79.00) | <0.001 | ||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 81.00 (75.00–87.00) | 76.00 (70.00–82.00) | <0.001 | 84.00 (77.00–90.00) | 76.00 (71.00–82.00) | <0.001 | 84.00 (78.00–90.00) | 78.00 (72.00–84.00) | <0.001 | ||
| HUA | 1,545 (25.84) | 92 (36.80) | <0.001 | 1,189 (24.82) | 66 (33.67) | 0.005 | 969 (18.64) | 66 (32.20) | <0.001 | ||
[i] Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HUA, hyperuricemia; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; METs h/d, metabolic equivalent tasks hours/day; SBP, systolic blood pressure; Scr, serum creatinine; SUA, serum uric acid; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides.
Data are number (percentage) or median (interquartile range).
P comparing non-CVDs and CVDs.
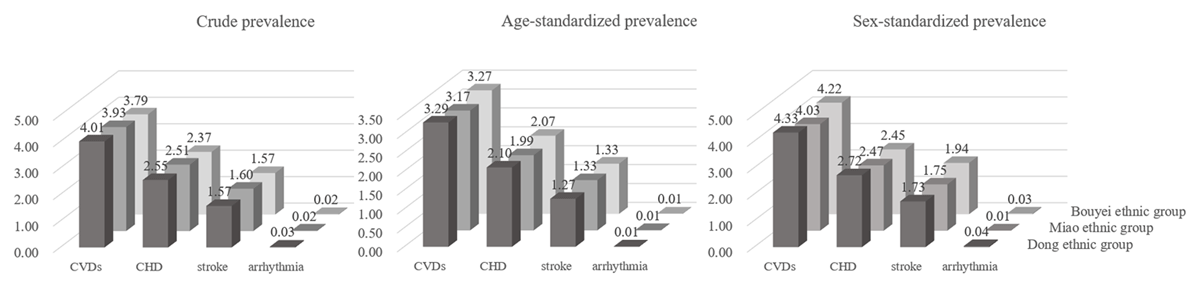
Figure 1
The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. CHD, coronary heart disease; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases.
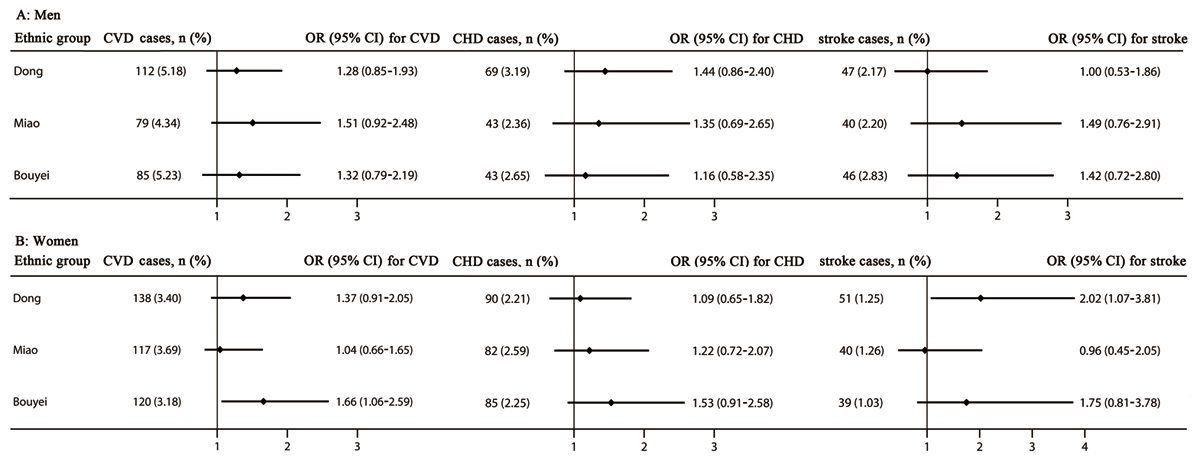
Figure 2
The risk of cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, and stroke stratified by sex. Adjusted for age, residence, tobacco smoking status, alcohol drinking status, total physical activity, total energy intake, family history of cardiovascular diseases, body mass index, and systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, and triglycerides levels. CHD, coronary heart disease; CI, confidence interval; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; OR, odd ratio.
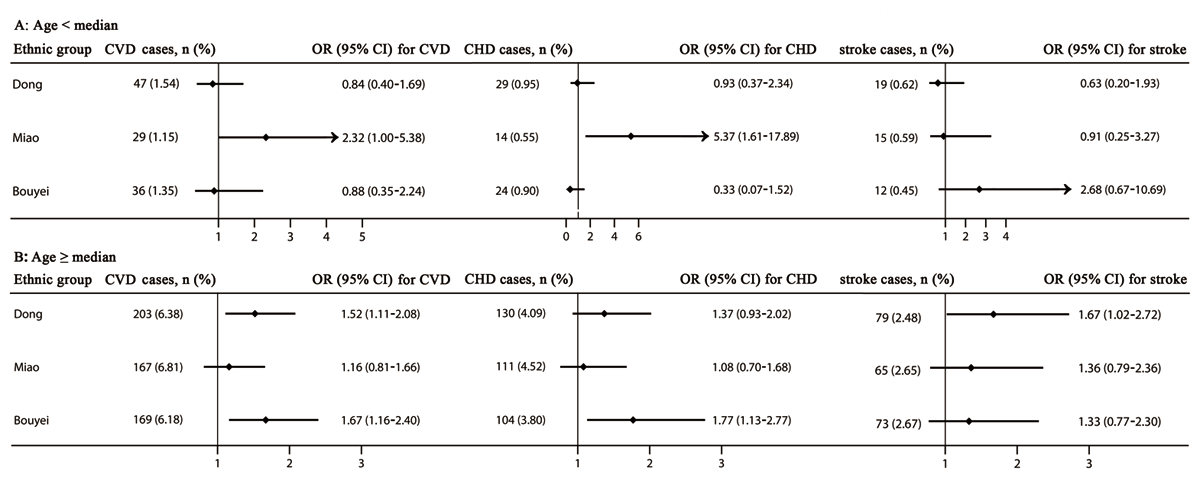
Figure 3
The risk of cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, and stroke stratified by the median of age. Adjusted for sex, residence, tobacco smoking status, alcohol drinking status, total physical activity, total energy intake, family history of cardiovascular diseases, body mass index, and systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, and triglycerides levels. CHD, coronary heart disease; CI, confidence interval; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; OR, odd ratio. The median of age were 52, 51, and 51 years in the Dong, Miao, and Bouyei ethnic groups, respectively.
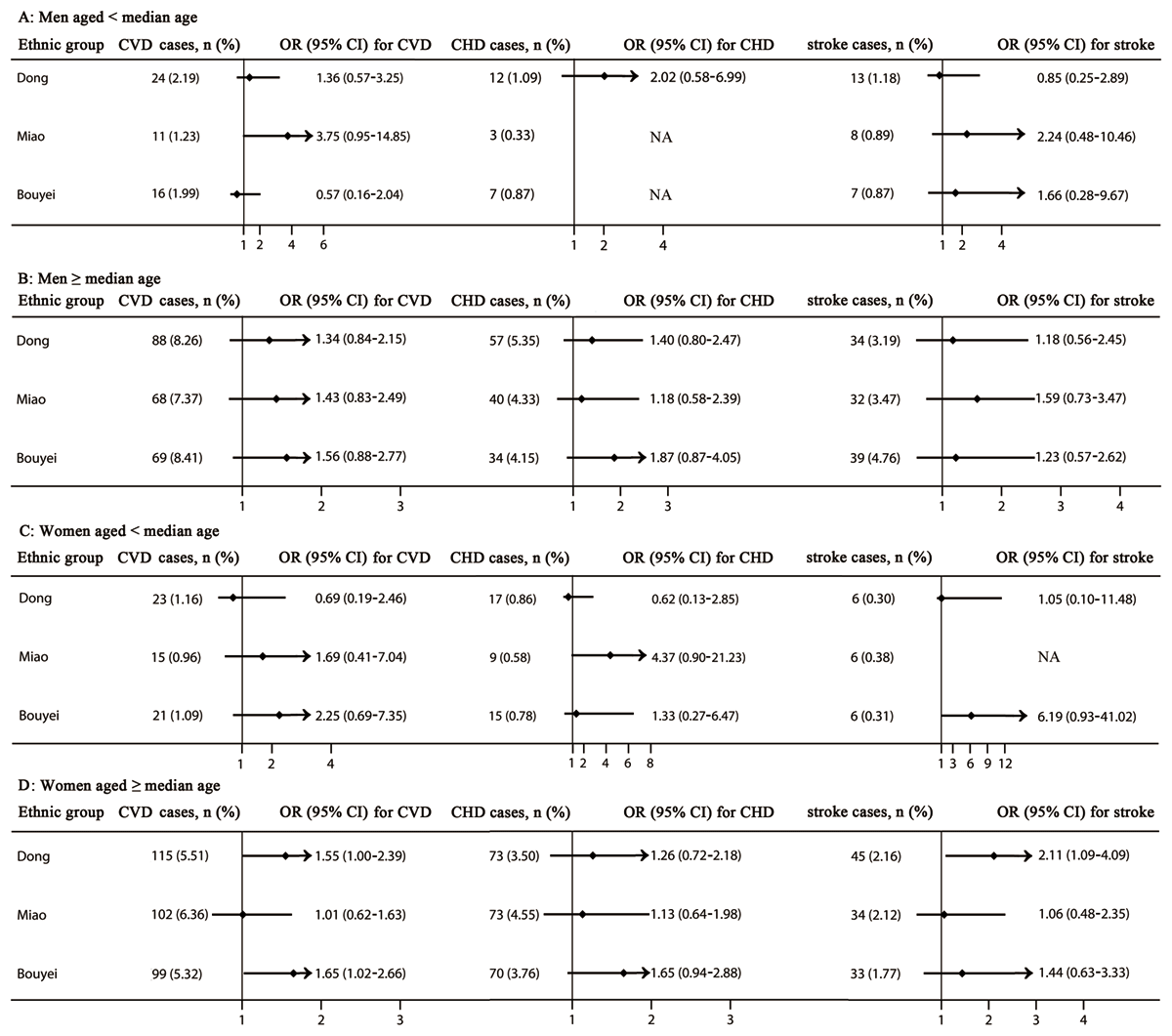
Figure 4
The risk of cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, and stroke stratified by sex and the median of age. Adjusted for residence, tobacco smoking status, alcohol drinking status, total physical activity, total energy intake, family history of cardiovascular diseases, body mass index, and systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, and triglycerides levels. CHD, coronary heart disease; CI, confidence interval; CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; NA, not applicable; OR, odd ratio. The median of age were 54, 52, and 52 years in men, 51, 50, and 51 years in women, in the Dong, Miao, and Bouyei ethnic groups, respectively.
