Figure 1.

Figure 2.
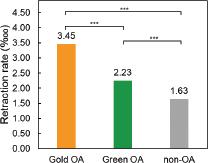
Figure 3.
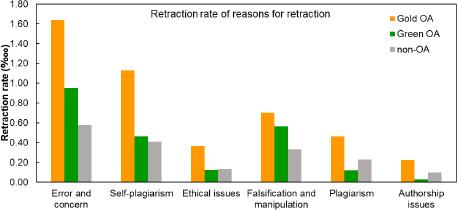
Figure 4.

Figure 5.

Figure A1.
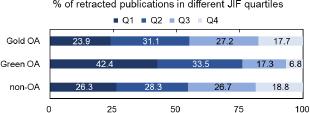
Figure A2.

Category of reasons for retraction_
| Major reason | Original reasons identified by Retraction Watch database |
|---|---|
| Error and concern | Error in image/data/text/results and/or conclusions/methods/materials (general)/ cell lines/tissues/analyses; Concerns/issues about image/data/results/referencing/ attributions; Contamination of reagents/materials (general)/cell lines/tissues; Unreliable data/image/results; Results not reproducible |
| Plagiarism | Plagiarism of text/image/data/article; Euphemisms for plagiarism |
| Self-plagiarism | Self-plagiarism of text/image/data/article; Euphemisms for self-plagiarism; Salami slicing |
| Falsification and manipulation | Falsification/fabrication of results/image/data; Manipulation of results/images; Hoax publication; Paper mill; Fake peer review; Sabotage of materials/methods |
| Authorship issues | Forged authorship; Concerns/Issues about authorship |
| Ethical issues | Legal reasons/legal threats; Civil/criminal proceedings; Ethical violations; Lack of ethical approval; informed/patient consent-none/retracted; Infringement of patient privacy; Lack of balance/bias issues; Conflict of interest; Copyright claims |
| Others | Other reasons for retraction |
| Not available/ lack of information | |
The proportion and retraction time lag of different reasons for retraction_
| Reasons for retraction | % of reasons of retraction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold OA | Green OA | non-OA | Total | Retraction time lag (year) | |
| Self-plagiarism | 25% | 21% | 23% | 23% | 3.75 |
| Falsification and manipulation | 16% | 25% | 19% | 18% | 3.67 |
| Ethical issues | 8% | 6% | 8% | 8% | 2.92 |
| Error and concern | 36% | 42% | 32% | 34% | 2.90 |
| Authorship issues | 5% | 1% | 6% | 5% | 2.44 |
| Plagiarism | 10% | 5% | 13% | 12% | 2.40 |